Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose
Synonym(s):Carboxymethylcellulose, Sodium Salt, High Viscosity - CAS 9004-32-4 - Calbiochem;Carboxymethylcellulose, Sodium Salt, Low Viscosity - CAS 9004-32-4 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:9004-32-4
- Empirical Formula: C6H7O2(OH)2CH2COONa
- Molecular Weight: 0
- MDL number: MFCD00081472
- EINECS: 618-378-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-03-06 19:22:19
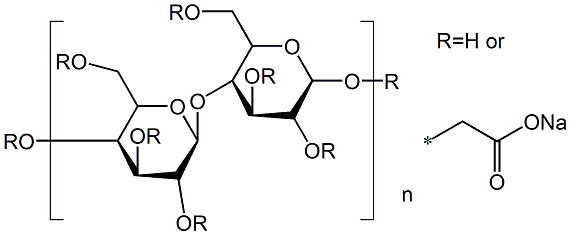
What is Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose?
Chemical properties
Carboxymethylcellulose sodium occurs as a white to almost white, odorless, tasteless, granular powder. It is hygroscopic after drying.
The Uses of Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) is a food-grade, water-soluble gum used as a thickener, adhesive, emulsifier, flocculant, chelating agent, water-retention agent, sizing agent, and film-forming agent. CMC is also used in drilling muds, dirt suspension agents in detergents, resin latex paints, adhesives, printing inks, textile sizing agents, and as a general protective colloid. It is also used as a stabilizer in foods; in pharmaceuticals as a suspending agent and tablet excipient; as a viscosity modifier to stabilize emulsions; as a lubricant in artificial tears; and for characterizing endoglucanase activity.
Production Methods
Alkali cellulose is prepared by steeping cellulose obtained from wood pulp or cotton fibers in sodium hydroxide solution. The alkaline cellulose is then reacted with sodium monochloroacetate to produce carboxymethylcellulose sodium. Sodium chloride and sodium glycolate are obtained as by-products of this etherification.
brand name
Celluvisc (Allergan); Refresh Plus, Cellufresh Formula (Allergan).
Pharmaceutical Applications
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) is an anionic derivative widely used in oral and topical pharmaceutical formulations. Its aqueous solutions can be used to suspend powders for topical, oral, and parenteral administration. It is also used as a tablet binder and disintegrant, as well as to stabilize emulsions. CMC is also used in self-adhesive ostomy, wound care, and skin patches as a mucoadhesive, absorbing wound exudate or transepidermally absorbing water and sweat. It has also been reported to act as a cytoprotective agent.
Safety
Carboxymethylcellulose sodium is used in oral, topical, and some
parenteral formulations. It is also widely used in cosmetics,
toiletries, and food products, and is generally regarded as a
nontoxic and nonirritant material. However, oral consumption of
large amounts of carboxymethylcellulose sodium can have a
laxative effect; therapeutically, 4–10 g in daily divided doses of the
medium- and high-viscosity grades of carboxymethylcellulose
sodium have been used as bulk laxatives.
The WHO has not specified an acceptable daily intake for
carboxymethylcellulose sodium as a food additive since the levels
necessary to achieve a desired effect were not considered to be a
hazard to health. However, in animal studies, subcutaneous
administration of carboxymethylcellulose sodium has been found to
cause inflammation, and in some cases of repeated injection
fibrosarcomas have been found at the site of injection.
Hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions have occurred in
cattle and horses, which have been attributed to carboxymethylcellulose
sodium in parenteral formulations such as vaccines and
penicillins.
LD50 (guinea pig, oral): 16 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 27 g/kg
Description
CMC can be used as a binder in the preparation of graphene nano-platelet based inks for the fabrication of dye sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). It can also be used as a viscosity enhancer in the development of tyrosinase based inks for the formation of electrodes for biosensor applications. CMC is used as a support material for a variety of cathodes and anodes for microbial fuel cells.
Storage
Carboxymethylcellulose sodium is a stable, though hygroscopic
material. Under high-humidity conditions, carboxymethylcellulose
sodium can absorb a large quantity (>50%) of water. In tablets, this
has been associated with a decrease in tablet hardness and an
increase in disintegration time.
Aqueous solutions are stable at pH 2–10; precipitation can occur
below pH 2, and solution viscosity decreases rapidly above pH 10.
Generally, solutions exhibit maximum viscosity and stability at pH
7–9.
Carboxymethylcellulose sodium may be sterilized in the dry state
by maintaining it at a temperature of 1608℃ for 1 hour. However,
this process results in a significant decrease in viscosity and some
deterioration in the properties of solutions prepared from the
sterilized material.
Aqueous solutions may similarly be sterilized by heating,
although this also results in some reduction in viscosity. After
autoclaving, viscosity is reduced by about 25%, but this reduction is
less marked than for solutions prepared from material sterilized in
the dry state. The extent of the reduction is dependent on the
molecular weight and degree of substitution; higher molecular
weight grades generally undergo a greater percentage reduction in
viscosity. Sterilization of solutions by gamma irradiation also
results in a reduction in viscosity.
Aqueous solutions stored for prolonged periods should contain
an antimicrobial preservative.
The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container in a
cool, dry place.
Purification Methods
Dialyse it for 48hours against distilled water and freeze-dry if a solid is required.
Properties and Applications
|
TEST ITEMS |
SPECIFICATION |
|
|
CMC-LV |
CMC-HV |
|
|
Appearance |
Cream colored and free flowing powder |
Cream colored and free flowing powder |
|
Degree of Substitution |
0.6-0.9 |
0.6-0.9 |
|
pH |
6-9 |
6-9 |
|
Moisture % |
10% max |
10% max |
|
Sodium CMC content on dry basis |
70% min |
70% min |
|
Viscosity at 600RPM |
90 max in deionized water 10 max 4% salt water mud,API water loss |
30 max in deionized water 30 min in 4% salt water 30 min in 4% saturated salt water 10 max 4% salt water mud,API water loss |
Incompatibilities
Carboxymethylcellulose sodium is incompatible with strongly
acidic solutions and with the soluble salts of iron and some other
metals, such as aluminum, mercury, and zinc. It is also incompatible
with xanthan gum. Precipitation may occur at pH < 2, and also
when it is mixed with ethanol (95%).
Carboxymethylcellulose sodium forms complex coacervates
with gelatin and pectin. It also forms a complex with collagen
and is capable of precipitating certain positively charged proteins.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (dental preparations; intraarticular, intrabursal, intradermal, intralesional, and intrasynovial injections; oral drops, solutions, suspensions, syrups and tablets; topical preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Nonmedicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose
| Melting point: | 274 °C (dec.) |
| Density | 1,6 g/cm3 |
| FEMA | 2239 | CARBOXYMETHYLCELLULOSE |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | H2O: 20 mg/mL, soluble |
| form | low viscosity |
| pka | 4.30(at 25℃) |
| color | White to light yellow |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | pH (10g/l, 25℃) 6.0~8.0 |
| PH Range | 6.5 - 8.5 |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Merck | 14,1829 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (9004-32-4) |
Safety information for Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose
Computed Descriptors for Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose manufacturer
Attar Global
Remedy Labs
Chemoil Pharma
Techno Pharmchem
Pharma Links
Chemie Trade
H. K. Group
New Products
Cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxylic acid Cyclopentane-1,2-dione 2-Bromo-5-iodopyridine 4-isothiocyanato-2-(trifluoroMethyl)benzonitrile Amino-4-methoxyben-zeneacetic acid 3-Aminophenylacetic acid 1-AMino-cyclobutaneMethanol HCl (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid Cefuroxime EP Impurity-A N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity 3-Hydroxypropionitrile valeronitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 5-azidovalericacid 4-bromo-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid Isopropyl amine Hydrochloride tert-butyl 4-(6-(8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-7-oxo-6-vinyl-7,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-2-ylamino)pyridin-3-yl)piperazine-1-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Carboxymethyl Cellulose sodium 99%View Details
Carboxymethyl Cellulose sodium 99%View Details
9004-32-4 -
 Carboxy Methyl Cellulose Sodium Salt (SQ) CAS 9004-32-4View Details
Carboxy Methyl Cellulose Sodium Salt (SQ) CAS 9004-32-4View Details
9004-32-4 -
 Carboxymethyl Cellulose Sodium Salt (CMC Sodium) CAS 9004-32-4View Details
Carboxymethyl Cellulose Sodium Salt (CMC Sodium) CAS 9004-32-4View Details
9004-32-4 -
 Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose average Mw ~90,000 CAS 9004-32-4View Details
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose average Mw ~90,000 CAS 9004-32-4View Details
9004-32-4 -
 Carboxymethyl cellulose CAS 9004-32-4View Details
Carboxymethyl cellulose CAS 9004-32-4View Details
9004-32-4 -
 Carboxymethyl Cellulose Sodium Salt (CMC Sodium) CAS 9004-32-4View Details
Carboxymethyl Cellulose Sodium Salt (CMC Sodium) CAS 9004-32-4View Details
9004-32-4 -
 Carboxymethylcellulose sodium salt CAS 9004-32-4View Details
Carboxymethylcellulose sodium salt CAS 9004-32-4View Details
9004-32-4 -
 Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose CmcView Details
Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose CmcView Details
9004-32-4
