Sodium benzoate
Synonym(s):Benzoic acid sodium salt;BENZOTRON
- CAS NO.:532-32-1
- Empirical Formula: C7H5NaO2
- Molecular Weight: 144.10317
- MDL number: MFCD00012463
- EINECS: 208-534-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-24 17:36:03
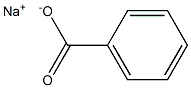
What is Sodium benzoate?
Description
Sodium benzoate is a controversial, common food preservative approved by the FDA with the E number E211, which allows for a dietary limit of 0-5 mg/kg body weight. While some studies suggest it may be useful for treating conditions such as depression, pain, schizophrenia, autism spectrum disorder, and neurodegenerative diseases, other studies suggest it can cause mutagenic effects, produce oxidative stress, disrupt hormones, and reduce fertility.
Chemical properties
Sodium benzoate occurs as a white granular or crystalline, slightly hygroscopic powder. It is odorless, or with faint odor of benzoin and has an unpleasant sweet and saline taste.
Occurrence
Benzoic acid occurs naturally in many plants and in animals. The salt is not found to occur naturally.
The Uses of Sodium benzoate
Sodium benzoate is used as a food preservative. It exhibits bacteriostatic and fungistatic activity under acidic conditions, with an optimal pH between 2.5 and 4.0; use above pH 4.5 is not recommended. It is active against yeasts and bacteria. It is most widely used in acidic foods such as salad dressings (vinegar), carbonated beverages (carbonic acid), jams and juices (citric acid), pickles (vinegar), and condiments. Its usage ranges from 0.03% to 0.10%. It is also used as a preservative in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. It is also used as whistle mix fuel in fireworks; this powder, when compressed into a tube and ignited, produces a whistling sound. This fuel is also one of the fastest-burning rocket fuels, producing significant thrust and smoke, but is highly explosive.
What are the applications of Application
Sodium benzoate is a benzene compound used as a synthetic reagent
Definition
ChEBI: An organic sodium salt resulting from the replacement of the proton from the carboxy group of benzoic acid by a sodium ion.
Definition
sodium benzoate: An either colourlesscrystalline or white amorphouspowder, C6H5COONa, soluble inwater and slightly soluble in ethanol.It is made by the reaction of sodiumhydroxide with benzoic acid and isused in the dyestuffs industry and asa food preservative. It was formerlyused as an antiseptic.
Production Methods
Sodium benzoate is prepared by adding benzoic acid to a hot concentrated solution of sodium carbonate until effervescence ceases. The solution is then evaporated, cooled and allowed to crystallize or evaporate to dryness, and then granulated.
General Description
Sodium benzoate is a sodium salt of benzoic acid, that is freely soluble in water compared to benzoic acid. It is generally used as an antimicrobial preservative in cosmetics, food, and pharmaceuticals.
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control, provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmaceutical Applications
Sodium benzoate is used primarily as an antimicrobial preservative
in cosmetics, foods, and pharmaceuticals. It is used in concentrations
of 0.02–0.5% in oral medicines, 0.5% in parenteral products,
and 0.1–0.5% in cosmetics. The usefulness of sodium benzoate as a
preservative is limited by its effectiveness over a narrow pH range.
Sodium benzoate is used in preference to benzoic acid in some
circumstances, owing to its greater solubility. However, in some
applications it may impart an unpleasant flavor to a product.
Sodium benzoate has also been used as a tablet lubricant at 2–5%
w/w concentrations. Solutions of sodium benzoate have also been administered, orally or intravenously, in order to determine liver
function.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Sodium benzoate also has pharmaceutical applications and is component of syrup and transparent tablet. High levels of sodium benzoate may trigger histamine release and also induce cell damage. It is recommended for the treatment of urea cycle disorders. However, high levels of sodium benzoate may contribute to glycine deficiency and may impose neuromodulatory effects.
Safety Profile
Poison by subcutaneous and intravenous routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion, intramuscular, and intraperitoneal routes. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. Larger doses of 8-10 g by mouth may cause nausea and vomiting. Small doses have little or no effect. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Na2O. See also BENZOIC ACID.
Safety
Ingested sodium benzoate is conjugated with glycine in the liver to
yield hippuric acid, which is excreted in the urine. Symptoms of systemic benzoate toxicity resemble those of salicylates. Whereas
oral administration of the free-acid form may cause severe gastric
irritation, benzoate salts are well tolerated in large quantities: e.g. 6
g of sodium benzoate in 200mL of water is administered orally as a
liver function test.
Clinical data have indicated that sodium benzoate can produce
nonimmunological contact urtcaria and nonimmunological
immediate contact reactions. However, it is also recognized that
these reactions are strictly cutaneous, and sodium benzoate can
therefore be used safely at concentrations up to 5%. However, this
nonimmunological phenomenon should be considered when
designing formulations for infants and children.
Other adverse effects include anaphylaxis and urticarial
reactions, although a controlled study has shown that the incidence
of urticaria in patients given benzoic acid is no greater than that
with a lactose placebo.
It has been recommended that caffeine and sodium benzoate
injection should not be used in neonates; however, sodium
benzoate has been used by others in the treatment of some neonatal
metabolic disorders. It has been suggested that there is a general
adverse effect of benzoate preservatives on the behavior of 3-yearold
children, which is detectable by parents, but not by a simple
clinical assessment.
The WHO acceptable daily intake of total benzoates, calculated
as benzoic acid, has been estimated at up to 5 mg/kg of bodyweight.
LD50 (mouse, IM): 2.3 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IV): 1.4 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 1.6 g/kg
LD50 (rabbit, oral): 2.0 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IV): 1.7 mg/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 4.1 g/kg
Hazard
In combination with ascorbic acid (vitamin C, E300), sodium benzoate and potassium benzoate form benzene, a known carcinogen. However, in most beverages that contain both, the benzene levels are below those considered dangerous for consumption. Heat, light and shelf life can affect the rate at which benzene is formed.
Potential Exposure
Sodium benzoate is used as a food and feed additive, flavor, packaging material; pharmaceutical; preservative for food products and tobacco; anti-fungal agent; antiseptic, rust, and mildew inhibitor; intermediate in the manufacture of dyes. Used as a human hygiene biocidal product.
Daily Uses
Sodium benzoate serves as a preservative to inhibit mold growth in food products. Widely utilized across various food items such as mayonnaise, margarine, carbonated beverages, jams, jellies, sauces, and tomato paste, it extends the shelf life of these products for up to two years from the purchase date. Typically employed at concentrations below 0.5% by volume, sodium benzoate is also incorporated into other household commodities such as mouthwash, lotion, and certain medications for its preservative properties.
Storage
Aqueous solutions may be sterilized by autoclaving or filtration. The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container, in a cool, dry place.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Safety
Sodium benzoate is considered safe, but scientists have shown that negative side effects happen when it's mixed with ascorbic acid (vitamin C). Their studies show that it turns into benzene, a chemical that may cause cancer.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from EtOH (12mL/g). [Beilstein 9 IV 27.]
Properties and Applications
|
TEST ITEMS |
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE |
WHITE POWDER |
|
CONTENT OF SODIUM BENZOATE |
99.0% min |
DRY LOSS |
0.10% max |
pH VALUE |
8 |
TOTAL CHLORIDE |
300 ppm max |
TRANSPARENCE |
PASS |
TOTAL HEAVY METAL |
0.001% max |
As CONTENT |
0.0002% max |
Mechanism of food preservation
The mechanism starts with the absorption of benzoic acid into the cell. If the intracellular pH changes to 5 or lower, the anaerobic fermentation of glucose through phosphofructokinase is decreased by 95 %, thereby inhibiting the growth and survival of micro-organisms that cause food spoilage.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with quaternary compounds, gelatin, ferric salts, calcium salts, and salts of heavy metals, including silver, lead, and mercury. Preservative activity may be reduced by interactions with kaolin or nonionic surfactants.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (dental preparations; IM and IV injections; oral capsules, solutions and tablets; rectal; and topical preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Sodium benzoate
| Melting point: | >300 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1,44 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| FEMA | 3025 | SODIUM BENZOATE |
| Flash point: | >100°C |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Crystals, Granules, Flakes or Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 4.03[at 20 ℃] |
| color | White |
| PH | 7.0-8.5 (25℃, 1M in H2O) |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Merck | 14,8582 |
| BRN | 3572467 |
| Stability: | Stable, but may be moisture senstive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, alkalis, mineral acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 532-32-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Sodium benzoate(532-32-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium benzoate (532-32-1) |
Safety information for Sodium benzoate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium benzoate
| InChIKey | WXMKPNITSTVMEF-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Sodium benzoate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
J J Chemicals
Paras Trademart Private Limited
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

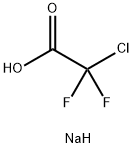
You may like
-
 Sodium Benzoate I.P. 99%View Details
Sodium Benzoate I.P. 99%View Details -
 Sodium Benzoate 99%View Details
Sodium Benzoate 99%View Details -
 SODIUM BENZOATE 99%View Details
SODIUM BENZOATE 99%View Details -
 Sodium Benzoate 99%View Details
Sodium Benzoate 99%View Details -
 Sodium benzoate 99%View Details
Sodium benzoate 99%View Details -
 Sodium benzoate 98%View Details
Sodium benzoate 98%View Details -
 Sodium benzoate 98%View Details
Sodium benzoate 98%View Details -
 Sodium Benzoate CASView Details
Sodium Benzoate CASView Details
