Sodium bicarbonate
Synonym(s):Sodium bicarbonate;Sodium hydrogen carbonate;Sodium bicarbonate solution;aqueous sodium bicarbonate;soda bicarbonate
- CAS NO.:144-55-8
- Empirical Formula: CHNaO3
- Molecular Weight: 84.01
- MDL number: MFCD00003528
- EINECS: 205-633-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-21 16:49:52
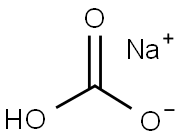
What is Sodium bicarbonate?
Description
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) is commonly referred to as baking soda by people outside of chemistry. It is amphoteric, meaning it can neutralize both acids and bases. The most common use of NaHCO3 is as a saturated aqueous solution for performing a basic wash during an aqueous workup.
Chemical properties
Sodium bicarbonate occurs as an odorless, white, crystalline powder with a saline, slightly alkaline taste. The crystal structure is monoclinic prisms. Grades with different particle sizes, from a fine powder to free-flowing uniform granules, are commercially available.
Physical properties
White crystalline powder or granules; monoclinic crystals; density 2.20 g/cm3; decomposes around 50°C, begins to lose carbon dioxide; converts to sodium carbonate at 100°C; soluble in water, 10g/100 mL at 20°C; slowly decomposes to CO2 and Na2CO3 in aqueous solution at ambient temperature; decomposes to Na2CO3 in boiling water; aqueous solution slightly alkaline; pH of 0.1M solution at 25°C is about 8.3; insoluble in alcohol; decomposes in acids.
The Uses of Sodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate, used in the formof baking soda and baking powder, is the most common leavening agent. When baking soda,which is an alkaline substance, is added to a mix, it reacts with an acid ingredient to producecarbon dioxide. The reaction can be represented as: NaHCO3(s) + H+ → Na+(aq) + H2O(l) +CO2(g), where H+ is supplied by the acid. Baking soda is also used as a source of carbon dioxide for carbonatedbeverages and as a buffer.In addition to baking, baking soda has numerous household uses. It is used as a generalcleanser, a deodorizer, an antacid, a fire suppressant, and in personal products such as toothpaste.
The second largest use of sodium bicarbonate, accounting for approximately 25% of totalproduction, is as an agricultural feed supplement. In cattle it helps maintain rumen pH andaids fiber digestibility; for poultry it helps maintain electrolyte balance by providing sodiumin the diet, helps fowl tolerate heat, and improves eggshell quality.
Sodium bicarbonate is used in the chemical industry as a buff ering agent, a blowingagent, a catalyst, and a chemical feedstock.
Indications
Sodium bicarbonate is used for the treatment of metabolic acidosis which may occur in severe renal disease, uncontrolled diabetes, circulatory insufficiency due to shock or severe dehydration, extracorporeal circulation of blood, cardiac arrest and severe primary lactic acidosis. Also is indicated in severe diarrhea which is often accompanied by a significant loss of bicarbonate.
Further indicated in the treatment of certain drug intoxications, including barbiturates (where dissociation of the barbiturateprotein complex is desired), in poisoning by salicylates or methyl alcohol and in hemolytic reactions requiring alkalinization of the urine to diminish nephrotoxicity of blood pigments.
Production Methods
Sodium bicarbonate is manufactured either by passing carbon dioxide into a cold saturated solution of sodium carbonate, or by the ammonia–soda (Solvay) process, in which first ammonia and then carbon dioxide is passed into a sodium chloride solution to precipitate sodium bicarbonate while the more soluble ammonium chloride remains in solution.
Definition
Baking soda: A white solid formed either by passing an excess of carbon dioxide through sodium carbonate or hydroxide solution, or by precipitation when cold concentrated solutions of sodium chloride and ammonium hydrogencarbonate are mixed. Sodium hydrogencarbonate decomposes on heating to give sodium carbonate, carbon dioxide, and water. With dilute acids, it yields carbon dioxide. It is used as a constituent of baking powder, in effervescent beverages, and in fire extinguishers. Its aqueous solutions are alkaline as a result of salt hydrolysis. Sodium hydrogencarbonate forms monoclinic crystals.
Production Methods
Most sodium bicarbonate in the United States is made synthetically by the reaction of sodium carbonate solution (Na2CO3) with carbon dioxide: Na2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) → 2NaHCO3(aq). It can also be produced using the Solvay process, which uses ammonia, carbon dioxide, and salt to produce sodium bicarbonate according to the following series of reactions: 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) → (NH4)2CO3(aq)
(NH4)2CO3(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) → 2NH3HCO3(aq)
NH4HCO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) → NaHCO3(s) + NH4Cl(aq).
brand name
Neut (Abbott); Soda Mint (Lilly).
Air & Water Reactions
Stable in dry air, but slowly decomposes in moist air. Moderately water soluble. Decomposes slowly in water (accelerated by agitation) .
Reactivity Profile
Sodium bicarbonate reacts exothermically with acids to generate non-toxic carbon dioxide gas. Decomposes when heated. Incompatible with acids, acidic salts (dopamine hydrochloride, pentazocine lactate, many alkaloidal salts) aspirin and bismuth salicylate.
Fire Hazard
Literature sources indicate that Sodium bicarbonate is noncombustible.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Sodium bicarbonate is generally used in pharmaceutical formulations as a source of carbon dioxide in effervescent tablets and granules. It is also widely used to produce or maintain an alkaline pH in a preparation.
Additionally, sodium bicarbonate is used in solutions as a buffering agent for erythromycin, lidocaine, local anesthetic solutions, and total parenteral nutrition (TPN) solutions. In some parenteral formulations, e.g. niacin, sodium bicarbonate is used to produce a sodium salt of the active ingredient that has enhanced solubility. Sodium bicarbonate has also been used as a freeze-drying stabilizer and in toothpastes.
Therapeutically, sodium bicarbonate may be used as an antacid, and as a source of the bicarbonate anion in the treatment of metabolic acidosis. Sodium bicarbonate may also be used as a component of oral rehydration salts and as a source of bicarbonate in dialysis fluids; it has also been suggested as a means of preventing radiocontrast-induced nephrotoxicity.
Biological Activity
Commonly used laboratory reagent
Biochem/physiol Actions
Sodium bicarbonate can be used to treat salicylate poisoning.
Pharmacokinetics
Intravenous sodium bicarbonate therapy increases plasma bicarbonate, buffers excess hydrogen ion concentration, raises blood pH and reverses the clinical manifestations of acidosis.
Clinical Use
Metabolic acidosis
Alkalinisation of urine
Renoprotection against contrast media
Safety Profile
Low toxicity by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. A nuisance dust. Human systemic effects: changes in potassium levels, increased urine volume, metabolic acidosis, nausea or vomiting, respiratory changes, sodium level changes. Mutation data reported.
Safety
Sodium bicarbonate is used in a number of pharmaceutical
formulations including injections and ophthalmic, otic, topical,
and oral preparations.
Sodium bicarbonate is metabolized to the sodium cation, which
is eliminated from the body by renal excretion, and the bicarbonate
anion, which becomes part of the body’s bicarbonate store. Any
carbon dioxide formed is eliminated via the lungs. Administration
of excessive amounts of sodium bicarbonate may thus disturb the
body’s electrolyte balance, leading to metabolic alkalosis or possibly
sodium overload with potentially serious consequences. The
amount of sodium present in antacids and effervescent formulations
has been sufficient to exacerbate chronic heart failure, especially in
elderly patients.
Orally ingested sodium bicarbonate neutralizes gastric acid with
the evolution of carbon dioxide and may cause stomach cramps and
flatulence.
When used as an excipient, sodium bicarbonate is generally
regarded as an essentially nontoxic and nonirritant material.
LD50 (mouse, oral): 3.36 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 4.22 g/kg
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Sodium bicarbonate is indicated to treat metabolic acidosis and alkalinize the urine. It is also used as adjunctive therapy in treating hypercalcemic or hyperkalemia crises.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Increases lithium excretion.
Metabolism
Oral bicarbonate, such as sodium bicarbonate, neutralises gastric acid with the production of carbon dioxide. Bicarbonate not involved in that reaction is absorbed and in the absence of a deficit of bicarbonate in the plasma, bicarbonate ions are excreted in the urine, which is rendered alkaline, and there is an accompanying diuresis.
Storage
Sodium bicarbonate is stable in dry air but slowly decomposes in moist air and should therefore be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry place.
Safety
Sodium bicarbonate is likely safe when used appropriately, short-term. Over-the-counter antacid products containing sodium bicarbonate are considered safe and effective by the US FDA. Taking sodium bicarbonate in very high doses is possibly unsafe. It is also possibly unsafe to take sodium bicarbonate that it is not fully dissolved into a solution. Stomach rupture and serious changes in electrolyte levels have occurred.
Purification Methods
Crystallise sodium bicarbonate from hot water (6mL/g). The solid should not be heated above 40℃ due to the formation of carbonate.
Incompatibilities
Sodium bicarbonate reacts with acids, acidic salts, and many
alkaloidal salts, with the evolution of carbon dioxide. Sodium
bicarbonate can also intensify the darkening of salicylates.
In powder mixtures, atmospheric moisture or water of crystallization
from another ingredient is sufficient for sodium bicarbonate
to react with compounds such as boric acid or alum. In liquid
mixtures containing bismuth subnitrate, sodium bicarbonate reacts
with the acid formed by hydrolysis of the bismuth salt.
In solution, sodium bicarbonate has been reported to be
incompatible with many drug substances such as ciprofloxacin, amiodarone, nicardipine, and levofloxacin.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (injections; ophthalmic preparations; oral capsules, solutions, and tablets). Included in parenteral (intravenous infusions and injections) and nonparenteral medicines (chewing gums; ear drops; eye lotions; oral capsules, chewable tablets, effervescent powders, effervescent tablets, granules, soluble tablets, orodispersible tablets, and tablets; suppositories and suspensions) licensed in the UK.
Properties of Sodium bicarbonate
| Melting point: | >300 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 851°C |
| Density | 2.16 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | 1.500 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | solution (7.5%) |
| appearance | White crystalline solid |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 2.159 |
| PH | 8.27(1 mM solution);8.22(10 mM solution);8.02(100 mM solution); |
| pka | (1) 6.37, (2) 10.25 (carbonic (at 25℃) |
| PH Range | 7.8 - 8.2 |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | 9 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Decomposition | 50 °C |
| Merck | 14,8583 |
| BRN | 4153970 |
| Stability: | Stable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 144-55-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium bicarbonate (144-55-8) |
Safety information for Sodium bicarbonate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H303:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
CEFA CILINAS BIOTICS PVT LTD
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile valeronitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Sodium Bi Carbonate 99%View Details
Sodium Bi Carbonate 99%View Details -
 Sodium Bi Carbonate 99%View Details
Sodium Bi Carbonate 99%View Details -
 SODIUM BICARBONATE 98%View Details
SODIUM BICARBONATE 98%View Details -
 Sodium bicarbonate 99%View Details
Sodium bicarbonate 99%View Details -
 Sodium bicarbonate 98%View Details
Sodium bicarbonate 98%View Details -
 Sodium hydrogen carbonate CAS 144-55-8View Details
Sodium hydrogen carbonate CAS 144-55-8View Details
144-55-8 -
 Sodium hydrogen carbonate, 98% 99%View Details
Sodium hydrogen carbonate, 98% 99%View Details -
 sodium bicarbonate CASView Details
sodium bicarbonate CASView Details
