Xanthan gum
Synonym(s):Gum xanthan;Xanthan gum from Xanthomonas campestris
- CAS NO.:11138-66-2
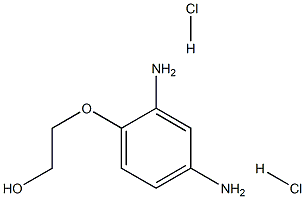
- Empirical Formula: C8H14Cl2N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 241.11496
- MDL number: MFCD00131256
- EINECS: 234-394-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-13 11:18:36
What is Xanthan gum ?
Chemical properties
Xanthan gum occurs as a cream- or white-colored, odorless, freeflowing, fine powder. Its viscosity of 1% solution is 1,200-1,600 mPas.
The Uses of Xanthan gum
Xanthan Gum is a gum obtained by microbial fermentation from the xanthomonas campestris organism. it is very stable to viscosity change over varying temperatures, ph, and salt concentrations. it is also very pseudoplastic which results in a decrease in viscosity with increasing shear. it reacts synergistically with guar gum and tara gum to provide an increase in viscosity and with carob gum to provide an increase in viscosity or gel formation. it is used in salad dressings, sauces, desserts, baked goods, and beverages at 0.05–0.50%.
Background
Xanthan gum is a polysaccharide gum derived from* Xanthomonas campestris* by a pure-culture fermentation process and purified by recovery with isopropyl alcohol. The major constituents include D-glucose, D-mannose, and D-glucuronic acid. Xanthan gum is a direct food additive permitted for direct addition to food for human consumption by the FDA. It is used as a thickening agent and stabilizer in emulsions.
Production Methods
Xanthan gum is a polysaccharide produced by a pure-culture aerobic fermentation of a carbohydrate with Xanthomonas campestris. The polysaccharide is then purified by recovery with propan-2-ol, dried, and milled.
brand name
Rhodigel (Vanderbilt).
General Description
As xanthan is a polysaccharide used in many applications such as a food additive, enzyme substrate or rheology modifier, it is useful to have a xanthan standard with a clearly defined narrow molecular weight distribution. Xanthan is produced by fermentation from Xanthomonas campestris.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Xanthan gum is widely used in oral and topical pharmaceutical formulations, cosmetics, and foods as a suspending and stabilizing agent. It is also used as a thickening and emulsifying agent. It is nontoxic, compatible with most other pharmaceutical ingredients, and has good stability and viscosity properties over a wide pH and temperature range. Xanthan gum is also used as a hydrocolloid in the food industry, and in cosmetics it has been used as a thickening agent in shampoo.
Safety Profile
When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Safety
Xanthan gum is widely used in oral and topical pharmaceutical
formulations, cosmetics, and food products, and is generally
regarded as nontoxic and nonirritant at the levels employed as a
pharmaceutical excipient.
The estimated acceptable daily intake for xanthan gum has been
set by the WHO at up to 10 mg/kg body-weight.
No eye or skin irritation has been observed in rabbits and no skin
allergy has been observed in guinea pigs following skin exposure.
No adverse effects were observed in long term feeding studies with
rats (up to 1000 mg/kg/day) and dogs (up to 1000 mg/kg/day). No
adverse effects were observed in a three-generation reproduction
study with rats (up to 500 mg/kg/day).
LD50 (dog, oral): >20 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): >45 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): >1 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IP): >50 mg/kg
LD50 (mouse, IV): 100–250 mg/kg
Preparation
Xanthan gum is made from a bacteria found on the leaf surfaces of green vegetables, including broccoli, brussels sprouts, cauliflower, cabbage, kale, rutabaga, and turnip. The bacteria is fermented (much like cheese or wine), then dried and ground into powder.
Xanthan gum Application
Xanthan gum (cornstarch gum) is a texturizer, carrier agent, and gelling agent in foods and cosmetic preparations. It also stabilizes and thickens formulations. This gum is produced through a fermentation of carbohydrate and Xanthomonas campestris. It is a chemical for chemical delivery systems and control in signal pathway experiments. It is sometimes used to make medicine. Xanthan gum is used for diabetes, constipation, dry eye, and many other conditions, but no good scientific evidence supports most of these uses.
Side Effects
Xanthan gum is safe when up to 15 grams per day are taken. It can cause side effects, such as intestinal gas (flatulence) and bloating. People exposed to xanthan gum powder might experience flu-like symptoms, nose and throat irritation, and lung problems.
Storage
Xanthan gum is a stable material. Aqueous solutions are stable over
a wide pH range (pH 3–12), although they demonstrate maximum
stability at pH 4–10 and temperatures of 10–60°C. Xanthan gum
solutions of less than 1% w/v concentration may be adversely
affected by higher than ambient temperatures: for example,
viscosity is reduced. Xanthan gum provides the same thickening,
stabilizing, and suspending properties during long-term storage at
elevated temperatures as it does at ambient conditions. In addition,
it ensures excellent freeze–thaw stability. Solutions are also stable in
the presence of enzymes, salts, acids, and bases. Vanzan NF-ST is
especially designed for use in systems containing high salt
concentrations as it dissolves directly in salt solutions, and its viscosity is relatively unaffected by high salt levels as compared with
general purpose grades.
The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container in a
cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
Xanthan gum is an anionic material and is not usually compatible with cationic surfactants, polymers, or preservatives, as precipitation occurs. Anionic and amphoteric surfactants at concentrations above 15% w/v cause precipitation of xanthan gum from a solution. It is compatible with most synthetic and natural viscosity-increasing agents, many strong mineral acids, and up to 30% inorganic salts. If it is to be combined with cellulose derivatives, then xanthan gum free of cellulase should be used to prevent depolymerization of the cellulose derivative. Xanthan gum solutions are stable in the presence of up to 60% water-miscible organic solvents such as acetone, methanol, ethanol, or propan-2- ol. However, above this concentration precipitation or gelation occurs.
Xanthan gum is incompatible with oxidizing agents, some tablet film-coatings, carboxymethylcellulose sodium, dried aluminum hydroxide gel, and some active ingredients such as amitriptyline, tamoxifen, and verapamil.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral solutions, suspensions, and tablets; rectal and topical preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Xanthan gum
| Melting point: | 64.43 °C |
| storage temp. | Hygroscopic, -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Soluble in water giving a highly viscous solution, practically insoluble in organic solvents. |
| form | Solid |
| color | Off-White to Pale Yellow |
| Odor | sl. organic odor, tasteless |
| Merck | 14,10057 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C8H12N2O2.2ClH/c9-6-1-2-8(7(10)5-6)12-4-3-11;;/h1-2,5,11H,3-4,9-10H2;2*1H |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 11138-66-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Xanthan gum (11138-66-2) |
Safety information for Xanthan gum
Computed Descriptors for Xanthan gum
| InChIKey | VXYWXJXCQSDNHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C(O)COC1=CC=C(N)C=C1N.[H]Cl.[H]Cl |
Xanthan gum manufacturer
Hexon Laboratories Private Limited
New Products
N,O-Dimethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Bupropian related compound F Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile 4-Fluorothiophenol (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile 4-Bromo BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Xanthan Gum 99%View Details
Xanthan Gum 99%View Details -
 Xanthan Gum 99%View Details
Xanthan Gum 99%View Details -
 Xanthan Gum CASView Details
Xanthan Gum CASView Details -
 Xanthan Gum CASView Details
Xanthan Gum CASView Details -
 Xanthan Gum PowderView Details
Xanthan Gum PowderView Details
11138-66-2 -
 Xanthan Gum Powder, Packaging Type: HDPE BagView Details
Xanthan Gum Powder, Packaging Type: HDPE BagView Details
11138-66-2 -
 Xanthan Gum, Packaging Size: 25 KgView Details
Xanthan Gum, Packaging Size: 25 KgView Details
11138-66-2 -
 Xanthan Gum TransparentView Details
Xanthan Gum TransparentView Details
11138-66-2
