Potassium hydroxide
Synonym(s):Potassium hydroxide;Caustic potash;Potassium hydroxide solution;Potassium hydroxide hydrate;caustic potash monohydrate
- CAS NO.:1310-58-3
- Empirical Formula: KOH
- Molecular Weight: 56.11
- MDL number: MFCD00003553
- EINECS: 215-181-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-13 11:17:26
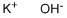
What is Potassium hydroxide ?
Absorption
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) in aqueous solutions completely dissociates into K+ and OH- ions. Because of the neutralization of OH- by gastric HCl and the rapid blood pH regulation action (buffer capacity of extracellular body fluids, respiratory and renal compensation mechanisms), an alkalosis due to the OH- ions after KOH oral dosage in non-irritating conditions is thus prevented .
The uptake of potassium, in potassium hydroxide form, is much less than the oral uptake with therapeutic doses of KCl for treating potassium deficiency, of up to 10 g/day. Furthermore, the oral uptake of potassium from food/natural sources or from food additives is likely to be also much higher.
Toxicity
The Ld50 of potassium hydroxide in rats ranges from 0.273 - 1.230 g KOH/kg body weight/day.
Adverse effects include vomiting, diarrhea, skin blistering, gastrointestinal disturbance, and burns.
Potassium Hydroxide can irritate the lungs. Repeated exposure may cause bronchitis to develop with coughing, phlegm, and/or shortness of breath.
Description
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) is a strong base commonly used in organic chemistry. It is typically bought in pellet form as 85% KOH, 15% water. The pKa of the conjugate acid of potassium hydroxide is 15.7. The hydroxide ion is not only a base, it is also an effective nucleophile. It is capable of nucleophilic reactions such as the diplacement of alkyl halides to form alcohols, and the hydrolysis of esters and nitriles to carboxylic acids.
Chemical properties
Potassium hydroxide occurs as a white or nearly white fused mass. It is available in small pellets, flakes, sticks and other shapes or forms. It is hard and brittle and shows a crystalline fracture. Potassium hydroxide is hygroscopic and deliquescent; on exposure to air, it rapidly absorbs carbon dioxide and water with the formation of potassium carbonate. Soluble in water, alcohol, glycerol; slightly soluble in ether.
Indications
Medically, the microscopic examination of potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparations is utilized in the diagnosis of fungal hyphae or trichomonads .
Samples from hair, skin, or nail tissue are obtained by scraping with a scalpel, cotton-tipped applicator and are inoculated directly onto the KOH solution .
In addition to the above, potassium hydroxide is used as a softener for nail grooves .
Background
Medically, potassium hydroxide (KOH) is widely used in the wet mount preparation of various clinical specimens for microscopic visualization of fungi and fungal elements in skin, hair, nails, and even vaginal secretions.
Recently, it has been studied for efficacy and tolerability in the treatment of warts. It was determined that topical KOH solution was found to be a safe and effective treatment of plane warts.
Production Methods
Potassium hydroxide is made by the electrolysis of potassium chloride. Commercial grades may contain chlorides as well as other impurities.
Indications
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) is a strong alkali that digests proteins and epidermal debris. In one study, 10% solution was applied b.i.d. to each lesion for 30 days with excellent clearance. The side effects included stinging of the lesion and one case of secondary infection. Also reported were the occurrence of a hypertrophic scar as well as some persistent or transitory hyper- and hypopigmentation. The same authors who used the 5% KOH solution completed further studies and they found it to be as effective-yet with decreased side effects.
Health Hazard
Potassium hydroxide is a strongly alkaline, hydrophilic substance and therefore solid potassium hydroxide is highly corrosive. It reacts with fat and can cause irreversible damage to any site of contact with the body (for example skin or eyes). Solutions of potassium hydroxide in water at concentrations above 0.5% (w/w) are irritating at points of contact and, at higher concentrations, the solutions can be corrosive. Potassium hydroxide does not cause skin allergies.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) is widely used in pharmaceutical formulations
to adjust the pH of solutions. It can also be used to react with weak
acids to form salts.
Therapeutically, potassium hydroxide is used in various
dermatological applications.
Pharmacokinetics
The corrosiveness of potassium hydroxide renders it a very useful agent in the decomposition/removal soft tissue and hair removal. It is incorporated into some nail products, shaving creams, and soaps .
Safety
Potassium hydroxide is widely used in the pharmaceutical and food
industries and is generally regarded as a nontoxic material at low
concentrations. At high concentrations it is a corrosive irritant to
the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.
(rat, oral): 0.273 g/kg
Metabolism
KOH in aqueous solution is entirely dissociated into K+ and OH- ions. Due to the neutralization of OH- by gastric HCl and the quick and efficient blood pH regulation mechanisms (buffer capacity of extra cellular body fluids, respiratory and renal compensation mechanisms), an alkalosis due to the OH- ions after KOH oral dosage in non-irritating conditions is prevented .
The Uses of Potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) is also known as caustic potash. It is a strong alkali or a solid base compound that can be used in a variety of industrial applications. It finds its usage in the production of soaps, cleaners and detergents.
Purification Methods
Its carbonate content can be reduced by rinsing potassium hydroxide sticks rapidly with water prior to dissolving them in boiled out distilled water. Alternatively, a slight excess of saturated BaCl2 or Ba(OH)2 can be added to the solution which, after shaking well, is set aside so that the BaCO3 is allowed to separate out.
Incompatibilities
Potassium hydroxide is a strong base and is incompatible with any compound that readily undergoes hydrolysis or oxidation. Violent reaction with acids, alcohols, water, metals (when wet), halogenated hydrocarbons; maleic anhydride. Heat is generated if KOH comes in contact with water and carbon dioxide from the air. It should not be stored in glass or aluminum containers, Corrosive to zinc, aluminum, tin and lead in the presence of moisture releasing combustible/explosive hydrogen gas. Can absorb water from air and give off sufficient heat to ignite surrounding combustible materials.
Properties of Potassium hydroxide
| Melting point: | 361 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1320°C |
| Density | 1.450 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 719 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 52 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | powder |
| appearance | White solid |
| color | white |
| Specific Gravity | 1.09 |
| PH | 10.98(1 mM solution);11.95(10 mM solution);12.88(100 mM solution); |
| Odor | Odorless |
| explosive limit | 3.5-15.0%(V) (ethanol) |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive & Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,7640 |
| Exposure limits | Ceiling in air 2 mg/m3 (ACGIH). |
| Dielectric constant | 3.3(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable, but very hygroscopic. Dissolves exothermically in water. Incompatible with most metals, strong acids, acid chlorides, organic materials, zinc, aluminium, nitroalkanes, nitrobenzene, chlorine dioxide. Reacts vigorously with a wide variety of other materials. Readily absorbs water and carbon dioxide from the air. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1310-58-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Potassium hydroxide(1310-58-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Potassium hydroxide (1310-58-3) |
Safety information for Potassium hydroxide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H290:Corrosive to Metals H302:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P234:Keep only in original container. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Potassium hydroxide
| InChIKey | KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Potassium hydroxide manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Leo Chemo Plast Pvt. Ltd.
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile valeronitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Potassium hydroxide 98%View Details
Potassium hydroxide 98%View Details -
 Potassium Hydroxide, For ACS analysis; Usually contains 10-15% water CAS 1310-58-3View Details
Potassium Hydroxide, For ACS analysis; Usually contains 10-15% water CAS 1310-58-3View Details
1310-58-3 -
 Potassium hydroxide CAS 1310-58-3View Details
Potassium hydroxide CAS 1310-58-3View Details
1310-58-3 -
 Potassium hydroxide , 85% Pellets 99%View Details
Potassium hydroxide , 85% Pellets 99%View Details -
 Potassium Hydroxide Flake CASView Details
Potassium Hydroxide Flake CASView Details -
 Potassium hydroxide solution in ethanol CASView Details
Potassium hydroxide solution in ethanol CASView Details -
 Potassium hydroxide solution 47% CASView Details
Potassium hydroxide solution 47% CASView Details -
 Potassium hydroxide solution in ethanol CASView Details
Potassium hydroxide solution in ethanol CASView Details
