Acetic acid
Synonym(s):Glacial acetic acid;Acetic acid;aa;Ethanoic acid;Acetic acid solution
- CAS NO.:64-19-7
- Empirical Formula: C2H4O2
- Molecular Weight: 60.05
- MDL number: MFCD00011354
- EINECS: 200-580-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-15 13:03:24
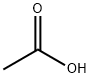
What is Acetic acid?
Description
Acetic acid is a colourless liquid or crystal with a sour, vinegar-like odour and is one of the simplest carboxylic acids and is an extensively used chemical reagent. It is the principal component of vinegars and pyroligneous acid. As one of the earliest flavoring agents, Vinegars are used extensively in preparing salad dressing and mayonnaise, sour and sweet pickles and numerous sauces and catsups.
Chemical properties
Acetic acid, also known as ethanoic acid, is a colorless liquid with a pungent, vinegar-like odor and the chemical formula CH3COOH. It is the main component of vinegar and is used as a food additive, in household cleaners, and for the production of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and other chemicals. 
History
Vinegar is a dilute aqueous solution of acetic acid. The use of vinegar is well documented in ancient history, dating back at least 10,000 years. Egyptians used vinegar as an antibiotic and made apple vinegar. Babylonians produced vinegar from wine for use in medicines and as a preservative as early as 5000 b.c.e. Hippocrates (ca. 460–377 b.c.e.), known as the “father of medicine,” used vinegar as an antiseptic and in remedies for numerous conditions including fever, constipation, ulcers, and pleurisy.
The Uses of Acetic acid
Acetic acid is an important industrial chemical. It is used in the manufacture ofcellulose acetate, acetate rayon, and variousacetate and acetyl compounds; as a solventfor gums, oils, and resins; as a food preservative in printing and dyeing; and in organicsynthesis. Acetic acid is used as table vinegar, as preservative and as an intermediate in the chemical industry, e.g. acetate fibers, acetates, acetonitrile, pharmaceuticals, fragrances, softening agents, dyes (indigo) etc.
Indications
Used to treat infections in the ear canal.
Background
Acetic acid is a product of the oxidation of ethanol and of the destructive distillation of wood. It is used locally, occasionally internally, as a counterirritant and also as a reagent. (Stedman, 26th ed) Acetic acid otic (for the ear) is an antibiotic that treats infections caused by bacteria or fungus.
Definition
ChEBI: Acetic acid is a simple monocarboxylic acid containing two carbons. It has a role as a protic solvent, a food acidity regulator, an antimicrobial food preservative and a Daphnia magna metabolite. It is a conjugate acid of an acetate.
Production Methods
Acetic acid is used in numerous industrial chemical preparations and the large-scale productionof acetic acid takes place through several processes. The main method of preparation ismethanol carbonylation. In this process, methanol reacts with carbon monoxide to give aceticacid:
CH3OH(l) + CO(g) → CH3COOH(aq).
Because the reaction requires high pressures (200atmospheres), this method was not used until the 1960s, when the development of specialcatalysts allowed the reaction to proceed at lower pressures. A methanol carbonylation proceduredeveloped by Monsanto bears the company’s name. The second most common methodto synthesize acetic acid is by the catalytic oxidation of acetaldehyde:
2 CH3CHO(l) + O2(g) →2 CH3COOH(aq).
Butane may also be oxidized to acetic acid according to the reaction:
2 C4H10(l) +5O2(g) → 4 CH3COOH(aq) + 2H2O(l).
This reaction was a major source of acetic acid beforethe Monsanto process. It is carried out at a temperature of approximately 150°C and 50 atmospheres pressure.
brand name
Vosol (Carter-Wallace).
Aroma threshold values
Aroma characteristics at 1.0%: sour pungent, cider vinegar, slightly malty with a brown nuance.
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 15 ppm: sour, acidic tangy.
Reactivity Profile
Acetic acid reacts exothermically with chemical bases. Subject to oxidation (with heating) by strong oxidizing agents. Dissolution in water moderates the chemical reactivity of acetic acid, A 5% solution of acetic acid is ordinary vinegar. Acetic acid forms explosive mixtures with p-xylene and air.
Health Hazard
Glacial acetic acid is a highly corrosive liquid. Contact with the eyes can produce mild to moderate irritation in humans. Contact with the skin may produce burns. Ingestion of this acid may cause corrosion of the mouth and gastrointestinal tract. The acute toxic effects are vomiting, diarrhea, ulceration, or bleeding from intestines and circulatory collapse. Death may occur from a high dose (20–30 mL), and toxic effects in humans may be felt from ingestion of 0.1–0.2 mL. An oral LD50 value in rats is 3530 mg/kg (Smyth 1956).
Glacial acetic acid is toxic to humans andanimals by inhalation and skin contact. Inhumans, exposure to 1000 ppm for a fewminutes may cause eye and respiratory tractirritation. Rabbits died from 4-hour exposureto a concentration of 16,000 ppm in air.
Flammability and Explosibility
Acetic acid is a combustible substance (NFPA rating = 2). Heating can release vapors that can be ignited. Vapors or gases may travel considerable distances to ignition source and "flash back." Acetic acid vapor forms explosive mixtures with air at concentrations of 4 to 16% (by volume). Carbon dioxide or dry chemical extinguishers should be used for acetic acid fires.
Toxicity
Dilute acetic acid solutions containing up to 10% w/w of acetic
acid have been used topically following jellyfish stings.Dilute
acetic acid solutions containing up to 5% w/w of acetic acid have
also been applied topically to treat wounds and burns infected with
Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
The lowest lethal oral dose of glacial acetic acid in humans is
reported to be 1470 mg/kg.The lowest lethal concentration on
inhalation in humans is reported to be 816 ppm.Humans, are,
however, estimated to consume approximately 1 g/day of acetic acid
from the diet.
LD50 (mouse, IV): 0.525 g/kg
LD50 (rabbit, skin): 1.06 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 3.31 g/kg
Storage
Acetic acid should be used only in areas free of ignition sources, and quantities greater than 1 liter should be stored in tightly sealed metal containers in areas separate from oxidizers.
Incompatibilities
Acetic acid reacts with alkaline substances.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed
Properties of Acetic acid
| Melting point: | 16.2 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 117-118 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.049 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.07 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 11.4 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 2006 | ACETIC ACID |
| Flash point: | 104 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | alcohol: miscible(lit.) |
| form | Solution |
| appearance | Colorless liquid |
| pka | 4.74(at 25℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.0492 (20℃) |
| color | colorless |
| Odor | Strong, pungent, vinegar-like odor detectable at 0.2 to 1.0 ppm |
| PH | 3.91(1 mM solution);3.39(10 mM solution);2.88(100 mM solution); |
| PH Range | 2.4 (1.0M solution) |
| Odor Threshold | 0.006ppm |
| explosive limit | 4-19.9%(V) |
| Water Solubility | miscible |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.05 λ: 270 nm Amax: 0.02 λ: 300 nm Amax: 0.01 λ: 500 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| JECFA Number | 81 |
| Merck | 14,55 |
| BRN | 506007 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 133, 122, 6.88, and 1.27 at pH values of 2.13, 3.52, 5.68, and 7.14, respectively (25 °C, Hakuta et
al., 1977) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 10 ppm ~25 mg/m3) (ACGIH,
OSHA, and MSHA); TLV-STEL 15 ppm
(37.5 mg/m3) (ACGIH). |
| Dielectric constant | 4.1(2℃) |
| Stability: | Volatile |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 64-19-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetic acid(64-19-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Acetic acid (64-19-7) |
Safety information for Acetic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Acetic acid
Acetic acid manufacturer
Central & Western (India) Chemicals
Mumbai Healthcare Industries
New Products
Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Rifaximin EP Impurity-G N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile 4-Fluorothiophenol (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 4-Bromo BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Acetic Acid 98%View Details
Acetic Acid 98%View Details -
 Acetic Acid 99%View Details
Acetic Acid 99%View Details -
 Acetic Acid Glacial 99%View Details
Acetic Acid Glacial 99%View Details -
 Acetic acid 98%View Details
Acetic acid 98%View Details -
 Acetic acid, 99% 99%View Details
Acetic acid, 99% 99%View Details -
 Acetic Acid Glacial CASView Details
Acetic Acid Glacial CASView Details -
 Acetic Acid CASView Details
Acetic Acid CASView Details -
 Acetic Acid CASView Details
Acetic Acid CASView Details
