Thiosulfuric acid
- CAS NO.:13686-28-7
- Empirical Formula: H2O3S2
- Molecular Weight: 114.15
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 17:34:33
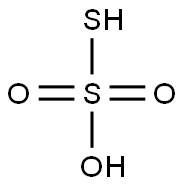
What is Thiosulfuric acid?
Absorption
Sodium thiosulfate taken orally is not systemically absorbed. Most of the thiosulfate is oxidized to sulfate or is incorporated into endogenous sulphur compounds; a small proportion is excreted through the kidneys. In pediatric patients given the recommended intravenous dose of sodium thiosulfate, the Cmax of thiosulfate was 13 ± 1.2 mM, and increased proportionally to dose over the range of 4 g/m2 to 20 g/m2. Thiosulfate accumulation is not expected following the intravenous administration of sodium thiosulfate on 2 consecutive days.
Toxicity
The effects in humans of large doses of sodium thiosulfate have not been thoroughly studied. Sodium thiosulfate administered orally (3 g per day) for 1-2 weeks resulted in reductions in room air arterial oxygen saturation to as low as 75%. One week after discontinuation, subjects returned to baseline oxygen saturations. A single dose of 20 mL of 10% sodium thiosulfate administered intravenously did not have an effect on oxygen saturation.
In rats, the oral LD50 of sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate is 5000 mg/kg.[L43327] The carcinogenic activity of sodium thiosulfate has not been evaluated. An in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay showed that sodium thiosulfate was not mutagenic in the absence nor presence of metabolic activation.
Physical properties
Thiosulfuric acid is a sulfur oxoacid. The free acid
cannot be prepared by acidifying thiosulfate salts
as the acid readily decomposes in water. Anhydrous methods of producing
the acid are:
H2S+ SO3→H2S2O3·nEt2O (in diethyl ether at 78°C)
Na2S2O3+2HCl/2NaCl+H2S2O3·2Et2O
(in diethyl ether at 78°C)
HSO3Cl+H2S→HCl+H2S2O3 (low temperature)
The anhydrous acid also decomposes below 0°C:
H2S2O3→H2S+ SO3
There is another isomeric form, a white crystalline
adduct of hydrogen sulfide and sulfur trioxide, H2S·SO3, which can also be prepared at low temperature.
Indications
Thiosulfuric acid (as sodium thiosulfate) is indicated for sequential intravenous use with sodium nitrite for the treatment of acute cyanide poisoning that is judged to be life-threatening. Sodium thiosulfate is also indicated to reduce the risk of ototoxicity associated with cisplatin in pediatric patients 1 month of age and older with localized, non-metastatic solid tumors in the US. In Europe, it is indicated for the same prevention of ototoxicity for patients 1 month of age to < 18 years old.
Background
Thiosulfuric acid is available in its salt forms sodium thiosulfate and sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate. Sodium thiosulfate is part of the World Health Organization’s list of essential medicines, and it has a variety of industrial uses, including food preservative, water de-chlorinator and paper pulp bleaching agent. Sodium thiosulfate is rapidly degraded in the stomach; therefore, it is normally administered through other routes, such as intravenous or topical. Sodium thiosulfate is approved for the treatment of acute cyanide poisoning and it is frequently used in conjunction with sodium nitrite (a salt form of nitrous acid). Sodium thiosulfate is also used to reduce the risk of ototoxicity associated with cisplatin. When administered 6 hours after cisplatin chemotherapy, Sodium thiosulfate leads to a lower incidence of cisplatin-induced hearing loss among children without affecting its effectiveness.
Definition
ChEBI: Sulfurothioic S-acid is a thiosulfuric acid. It has a role as a mouse metabolite. It is a conjugate acid of a hydroxidodioxidosulfidosulfate(1-). It is a tautomer of a sulfurothioic O-acid.
Pharmacokinetics
Sodium thiosulfate doses of 20, 15 and 10 g/m2 deliver sodium loads of 162, 121 and 81 mmol/m2. One hour after infusion, the administration of sodium thiosulfate causes a transient increase in sodium of approximately 6 mmol/L; however, levels return to baseline 18 to 24 hours after infusion. The pharmacodynamics of sodium thiosulfate as an antidote for the treatment of acute cyanide poisoning were evaluated by measuring the rate of conversion of cyanide to thiocyanate. Pretreatment with sodium thiosulfate to achieve a steady state level of 2 μmol/mL increased the rate of conversion of cyanide to thiocyanate over 30-fold in dogs. The use of sodium thiosulfate may cause hypersensitivity reactions and lead to hypernatremia and hypokalemia. It may also lead to nausea and vomiting.
Metabolism
Thiosulfate sulfur transferase and thiosulfate reductase metabolize thiosulfate to form sulfite, which is oxidized to sulfate.
Properties of Thiosulfuric acid
| Density | 1.867±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | -4.23±0.18(Predicted) |
Safety information for Thiosulfuric acid
Computed Descriptors for Thiosulfuric acid
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
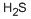

You may like
-
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
1310-58-3 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
