Poly(ethylene glycol-ran-propylene glycol) monobutyl ether
Synonym(s):Poly(ethylene glycol-ran-propylene glycol) monobutyl ether
- CAS NO.:9038-95-3
- Empirical Formula: C9H20O3
- Molecular Weight: 176.26
- MDL number: MFCD00198079
- EINECS: 231-545-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:49
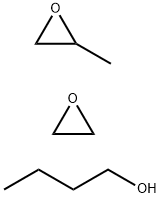
What is Poly(ethylene glycol-ran-propylene glycol) monobutyl ether?
Description
Poly(ethylene glycol-ran-propylene glycol) monobutyl ether is a block copolymer that consists of a hydrophilic poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) segment and a hydrophobic poly(propylene glycol) (PPO) segment. One of the significant features of PEG-PPO monobutyl ether is its amphiphilic nature. This means that it has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions within its structure. This property allows PEG-PPO monobutyl ether to form micelles in aqueous solutions, where the hydrophobic PPO segments aggregate in the core while the hydrophilic PEG segments form the outer shell. The formation of micelles gives PEG-PPO monobutyl ether its surfactant properties. In pharmaceuticals, it is utilized as an excipient in drug formulations to improve solubility, stability, and controlled release of drugs. It can also be employed as a carrier for drug delivery systems, enhancing the bioavailability and targeting of therapeutic agents. Furthermore, PEG-PPO monobutyl ether finds applications in cosmetics as an emulsifier and solubilizer for various formulations. The mechanism of action of PEG-PPO monobutyl ether relies on its ability to self-assemble into micelles in aqueous solutions. When added to a system, the hydrophobic PPO segments aggregate together, forming a core, while the hydrophilic PEG segments create a protective shell around the core. This self-assembly process enables PEG-PPO monobutyl ether to solubilize hydrophobic substances and stabilize emulsions. It can also enhance the penetration and absorption of drugs through biological membranes.
Chemical properties
liquid
The Uses of Poly(ethylene glycol-ran-propylene glycol) monobutyl ether
Hydraulic fluids, metal working fluids and lubricants, heat transfer fluids, solder assist fluids, quenchants, lubricants, solvents, plasticizers and foam control agents.
The Uses of Poly(ethylene glycol-ran-propylene glycol) monobutyl ether
Ucon? HTF 14 is a thermoseparating polymer (TSP) that can be used in aqueous two-phase extraction (ATPE) due to its decreasing solubility in its aqueous solution as the temperature rises. It is also used in a polymer coating on solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fibers using the sol-gel technique to impart thermal resistance and stability.
What are the applications of Application
Poly(ethylene glycol-ran-propylene glycol) monobutyl ether is a polymer lubricant for proteomics research
Properties of Poly(ethylene glycol-ran-propylene glycol) monobutyl ether
| Boiling point: | >200 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.056 g/mL at 25 °C |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| solubility | H2O: at <40 °Csoluble |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C4H10O.C3H6O.C2H4O/c1-2-3-4-5;1-3-2-4-3;1-2-3-1/h5H,2-4H2,1H3;3H,2H2,1H3;1-2H2 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Propylene oxide ethylene oxide polymer monobutyl ether (9038-95-3) |
Safety information for Poly(ethylene glycol-ran-propylene glycol) monobutyl ether
Computed Descriptors for Poly(ethylene glycol-ran-propylene glycol) monobutyl ether
| InChIKey | YTJMOZGBQLKJKS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C(CO)CC.C1OC1.CC1OC1 |
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Poly(ethylene glycol-ran-propylene glycol) monobutyl ether CAS 9038-95-3View Details
Poly(ethylene glycol-ran-propylene glycol) monobutyl ether CAS 9038-95-3View Details
9038-95-3 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
