ALDOL
- CAS NO.:107-89-1
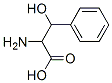
- Empirical Formula: C4H8O2
- Molecular Weight: 88.11
- MDL number: MFCD00024164
- EINECS: 203-530-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-13 11:27:13
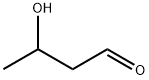
What is ALDOL?
Chemical properties
Aldol is a flammable, colorless to pale yellow, syrupy liquid. Pungent odor
The Uses of ALDOL
Acetaldol is manufactured by condensing of acetaldehyde in aqueous NaOH and is used to produce rubber vulcanizers, accelerators and age retardants, perfumes, and in ore flotation. It is a hypnotic and sedative.
The Uses of ALDOL
manufacture of rubber vulcanizers, accelerators and age resisters; in perfumes; ore flotation.
General Description
A clear white to yellow syrupy liquid. Denser than water. Flash point 150°F. Contact may irritate skin and eyes. Moderately toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
An aldehyde and alcohol. Aldehydes are frequently involved in self-condensation or polymerization reactions. These reactions are exothermic; they are often catalyzed by acid. Aldehydes are readily oxidized to give carboxylic acids. Flammable and/or toxic gases are generated by the combination of aldehydes with azo, diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, nitrides, and strong reducing agents. Aldehydes can react with air to give first peroxo acids, and ultimately carboxylic acids. These autoxidation reactions are activated by light, catalyzed by salts of transition metals, and are autocatalytic (catalyzed by the products of the reaction). The addition of stabilizers (antioxidants) to shipments of aldehydes retards autoxidation. Flammable and/or toxic gases are generated by the combination of alcohols with alkali metals, nitrides, and strong reducing agents. They react with oxoacids and carboxylic acids to form esters plus water. Oxidizing agents convert them to aldehydes or ketones. Alcohols exhibit both weak acid and weak base behavior. They may initiate the polymerization of isocyanates and epoxides.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Safety Profile
Poison via skin contact. Moderately toxic by ingestion. A skin and eye irritant. A flammable liquid and fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame; emits crotonaldehyde and water when heated. See CROTONALDEHYDE. Can react with oxidtzing materials.
Potential Exposure
Aldol is used as a solvent and to manufacture rubber accelerators, perfumes; in fungicides; and in engraving, cadmium plating
Shipping
UN2839 Aldol, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1Poison Inhalation Hazard
Purification Methods
An ethereal solution of aldol is washed with a saturated aqueous solution of NaHCO3, then with water. The non-aqueous layer is dried with anhydrous CaCl2 and distilled immediately before use. The fraction, b 80-81o/20mm, is collected as a thick liquid which decomposes at 85o/atm. It is a sedative and a hypnotic but is used in perfumery. [Mason et al. J Am Chem Soc 76 2255 1954]. [Beilstein 1 H 824, 1 I 419, 1 II 868, 1 III 3195, 1 IV 3984.]
Incompatibilities
Danger! May be subject to spontaneous polymerization. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires orexplosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Heat above 83 C causes the formation of crotonaldehyde vapor (which may cause explosion) and water.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Properties of ALDOL
| Melting point: | <25 °C |
| Boiling point: | bp20 83° |
| Density | d16 1.109 |
| vapor density | 3.04 |
| refractive index | 1.4238 |
| Flash point: | 150°F (OC) |
| pka | 14.50±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | Clear, white-to-yellow syrupy liquid |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Acetaldol (107-89-1) |
Safety information for ALDOL
Computed Descriptors for ALDOL
New Products
DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate N,O-Dimethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE Levothyroxine Impurity-F Montelukast EP Impurity-D/Montelukast USP Related Compound C Atorvastatin FXA Impurity/Atorvastatin Cyclic 6-Hydroxy Impurity Sodium Salt Isosulfan blue Keto N-Oxide Impurity Ivermectin Impurity F N-Nitroso des Methyl Tramadol/N-Nitroso-N-Desmethyl-Tramadol (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 1,4-bis(methylsulfonyl)butane 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene CSA (DL-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid) 2-Hydroxy-4-methylnicotinic acid 3-iodo-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine (2S)-1-((2S,3S)-3-(2-methylbutyl)-4-oxooxetan-2-yl)pentadecan-2-yl formylleucinate 1-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethane-1-sulfonyl chloride S-(1-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) ethanethioateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 674783-97-2 98+View Details
674783-97-2 98+View Details
674783-97-2 -
 H-D-TRP(FOR)-OH HCL 98+View Details
H-D-TRP(FOR)-OH HCL 98+View Details
367453-01-8 -
 DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine 117391-50-1 98+View Details
DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine 117391-50-1 98+View Details
117391-50-1 -
 1923-70-2 Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate 98+View Details
1923-70-2 Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate 98+View Details
1923-70-2 -
 49830-37-7 98+View Details
49830-37-7 98+View Details
49830-37-7 -
 3-Amino-3-(4-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
3-Amino-3-(4-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
325-89-3 -
 1428243-26-8 98+View Details
1428243-26-8 98+View Details
1428243-26-8 -
 1-aminocyclopentane carbonitrile, HCl 98+View Details
1-aminocyclopentane carbonitrile, HCl 98+View Details
16195-83-8
