Acetone
Synonym(s):Dimethyl Ketone, 2-Propanone;Dimethyl ketone, Propanone, 2-Propanone
- CAS NO.:67-64-1
- Empirical Formula: C3H6O
- Molecular Weight: 58.08
- MDL number: MFCD00211536
- EINECS: 200-662-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-13 11:17:25
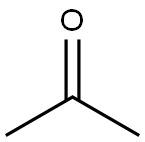
What is Acetone?
Description
Acetone, the simplest ketone, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. Laboratory denizens commonly use it as a solvent and to clean glassware; it is also a component of nail polish removers. Manufacturers use it as a solvent for fats, oils, and polymers and as a feedstock for making other chemicals. Most acetone is a coproduct of the cumene process, whose main purpose is phenol production. Acetone is mildly toxic, but epilepsy patients can benefit from diets that increase acetone levels in the body.
Chemical properties
Acetone, CH3COCH3, also known as 2-propanone and dimethylketone, is a colorless, volatile,flammable liquid that boils at 56°C (133 OF). It is misciblewith water and is oftenused as a solventin the manufacture of lacquers and paints.
Physical properties
Clear, colorless, liquid with a sweet, fragrant odor. Sweetish taste. Odor threshold concentrations ranged from 42 ppmv (Nagata and Takeuchi, 1990) to 100 ppmv (Leonardos et al., 1969). Experimentally determined detection and recognition odor threshold concentrations were 48 mg/m3 (20 ppmv) and 78 mg/m3 (33 ppmv), respectively (Hellman and Small, 1974).
Occurrence
Reported found in apple, pear, grape, pineapple, strawberry, raspberry, tomato, black currant, citrus, onion and potato; also reported found in cocoa leaves, in Mexican goosefoot and in the oils of coriander and lavender. In trace amounts it has been reportedly identified in the oil of bitter orange, in distilled wine and in coffee aroma
History
The traditional method of producing acetone in the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century was to distill acetates, particularly calcium acetate, Ca(C2H3O2)2.
Weizmann discovered a process to produce butyl alcohol and acetone from the bacterium Clostridium acetobutylicum in 1914. With England’s urgent demand for acetone, Winston Churchill (1874–1965) enlisted Weizmann to develop the Weizmann process for acetone production on an industrial scale. Fermentation and distillation techniques for acetone production were replaced starting in the 1950s with the cumene oxidation process . In this process, cumene is oxidized to cumene hydroperoxide, which is then decomposed using acid to acetone and phenol. This is the primary method used to produce phenol, and acetone is produced as a co-product in the process, with a yield of about 0.6:1 of acetone to phenol.
The Uses of Acetone

To an orange, homogeneous solution of CrO3 (12.4 g, 0.123 mol) in H2O (88.4 mL) at 0 C was added H2SO4 (10.8 mL) dropwise via addition funnel over 30 min, with stirring. The addition funnel was rinsed with H2O (1 mL) to give a 1.23 M solution of Jones Reagent. To a solution of the SM (5.24 g, 21.6 mmol) in acetone (75 mL) at RT (immersed in H2O bath) was added Jones Reagent (43.8 mL, 53.9 mmol) via addition funnel over 90 min. The dark reaction mixture was stirred at RT overnight. By HPLC, the reaction was 93% complete. Additional Jones Reagent (18 mL, 1.0 equiv) was added. After stirring another 6.5 h, HPLC indicated 97% completion. Isopropanol (6 mL) was added, and the mixture stirred for 90 min, resulting in a dark green precipitate. The mixture was diluted with ether (600 mL) and washed with 2% aq NaHSO3 (5 x 100 mL). The layers were separated and the aq layer was back-extracted with ether (2 x 100 mL). The combined organics were washed with H2O (100 mL), brine (100 mL), and dried (Na2SO4). The aq layer was back-extacted with ether (100 mL), and the resulting org layer was combined with previous organics. The organics were concentrated to provide the pdt as an off-white solid. The pdt was dissolved in DCM (200 mL), washed with 2% aq NaHSO3, brine, dried (Na2SO4), and concentrated to provide the pdt (96% purity) as a pale yellow solid [3.84 g, 69.3%]. Additional pdt remained in the NaHSO3 aq layer. The aq layer was saturated with NaCl, the pH adjusted to ~3.5, and extracted with ether (3 x 100 mL). The organics were dried (Na2SO4) and concentrated to provide the product (99% purity) as a white solid [1.12 g, 20.2%]. Total yield: [4.96 g, 89.5%]
The Uses of Acetone
Acetone is used in the chemical industry in numerous applications. The primary use of acetone is to produce acetone cyanohydrin, which is then used in the production of methyl methacrylate (MMA). Another use of acetone in the chemical industry is for bisphenol A (BPA). BPA results form the condensation reaction of acetone and phenol in the presence of an appropriate catalyst. BPA is used in polycarbonate plastics, polyurethanes, and epoxy resins. Polycarbonate plastics are tough and durable and are often used as a glass substitute.
In addition to its use as a chemical feedstock and intermediate, acetone is used extensively as an organic solvent in lacquers, varnishes, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. Nail polish remover is one of the most common products containing acetone. Acetone is used to stabilize acetylene for transport .
Definition
ChEBI: Acetone is a methyl ketone that consists of propane bearing an oxo group at C2. It has a role as a polar aprotic solvent, a human metabolite and an EC 3.5.1.4 (amidase) inhibitor. It is a methyl ketone, a ketone body, a volatile organic compound and a member of propanones.
Production Methods
Acetone can be obtained by fermentation (a by-product of n-butanol production), or by catalytic dehydrogenation from isopropanol; it can also be obtained from cumene, a by-product of phenol production; or from propane, a by-product of oxidative cracking.
Reactions
Acetone reacts with many chemicals in a marked manner: (1) with phosphorus pentachloride, yields acetone chloride (CH3)2CCl2, (2) with hydrogen chloride dry, yields both mesityl oxide CH3COCH:C(CH3)2, liquid, bp 132 °C, and phorone (CH3)2C:CHCOCH : C(CH3)2, yellow solid, mp 28 °C, (3) with concentrated H2SO4, yields mesitylene C6H3(CH3)3 (1,3,5), (4) with NH3, yields acetone amines, e.g., diacetoneamine C6H12ONH, (5) with HCN, yields acetone cyanohydrin (CH3)2CHOH·CN, readily converted into alpha-hydroxy acid (CH3)2CHOH·COOH, (6) with sodium hydrogen sulfite, forms acetonesodiumbisulfite (CH3)2 COH·SO3Na white solid, from which acetone is readily recoverable by treatment with sodium carbonate solution, with hydroxylamine hydrochloride, forms acetoxime (CH3)2C:NOH, solid, mp 60 °C, with phenylhydrazine, yields acetonephenyl-hydrazone (CH3)2C:NNHC6H5·H2O, solid,mp 16 °C, anhydrous compound,mp42 °C, (9)with semicarbazide, forms acetonesemicarbazone (CH3)C:NNHCONH2, solid, mp 189 °C, with magnesium methyl iodide in anhydrous ether (“Grignard’s solution”), yields, after reaction with H2O, trimethylcarbinol (CH3)3COH, a tertiary alcohol, with ethyl thioalcohol and hydrogen chloride dry, yields mercaptol (CH3)2C(SC2H5)2, with hypochlorite, hypobromite, or hypoiodite solution, yields chloroform CHCl3, bromoform CHBr3 or iodoformCHI3, respectively, (13)with mostreducing agents, forms isopropyl alcohol (CH3)2CHOH, a secondary alcohol, but with sodium amalgam forms pinacone (CH3)2COH·COH(CH3)2 with sodium dichromate and H2SO4, forms acetic acid CH3COOH plus CO2. When acetone vapor is passed through a tube at a dull red heat, ketene CH2:CO and methane CH4 are formed.
What are the applications of Application
Acetone is used in the following ways:
(1) To make a variety of compounds, such as acetic acid, chloroform, mesityl oxide, and methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK); also used in the manufacture of rayon, film, and explosives.
(2) As a general solvent for fats, oils, waxes, resins, rubber, plastics, paints, varnishes, and rubber cements.
(3) Used in paint and varnish removers; and for purifying paraffin; and for hardening and dehydrating tissues.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 40 to 476 ppm
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a sweetish odor. Flash point 0°F. Less dense than water. Vapors are heavier than air. Used as a solvent in paint and nail polish removers.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Acetone was reported that a mixture of Acetone and chloroform, in a residue bottle, exploded. Since addition of Acetone to chloroform in the presence of base will result in a highly exothermic reaction, Acetone is thought that a base was in the bottle [MCA Case History 1661. 1970]. Also, Nitrosyl chloride, sealed in a tube with a residue of Acetone in the presence of platinum catalyst, gave an explosive reaction [Chem. Eng. News 35(43):60. 1967]. The reaction of nitrosyl perchlorate and Acetone ignites and explodes. Explosions occur with mixtures of nitrosyl perchlorate and primary amine [Ann. Chem. 42:2031. 1909]. Reacts violently with nitric acid. Also causes exothermic reaction when in contact with aldehydes.
Health Hazard
The acute toxicity of acetone is low. Acetone is primarily a central nervous system depressant at high concentrations (greater than 12,000 ppm). Unacclimated volunteers exposed to 500 ppm acetone experienced eye and nasal irritation, but it has been reported that 1000 ppm for an 8-hour day produced no effects other than slight transient irritation to eyes, nose, and throat. Therefore there are good warning properties for those unaccustomed to working with acetone; however, frequent use of acetone seems to cause accommodation to its slight irritating properties. Acetone is practically nontoxic by ingestion. A case of a man swallowing 200 mL of acetone resulted in his becoming stuporous after 1 hour and then comatose; he regained consciousness 12 hour later. Acetone is slightly irritating to the skin, and prolonged contact may cause dermatitis. Liquid acetone produces moderate transient eye irritation. Acetone has not been found to be carcinogenic in animal tests or to have effects on reproduction or fertility.
Fire Hazard
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Flammability and Explosibility
Acetone is extremely flammable (NFPA rating = 3), and its vapor can travel a considerable distance to an ignition source and "flash back." Acetone vapor forms explosive mixtures with air at concentrations of 2 to 13% (by volume). Carbon dioxide or dry chemical extinguishers should be used for acetone fires.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Acetone is used as a solvent or cosolvent in topical preparations, and as an aid in wet granulation.It has also been used when formulating tablets with water-sensitive active ingredients, or to solvate poorly water-soluble binders in a wet granulation process. Acetone has also been used in the formulation of microspheres to enhance drug release.Owing to its low boiling point, acetone has been used to extract thermolabile substances from crude drugs.
Industrial uses
Acetone is a commonly used organic solvent in industry. It is an important solvent component in acrylic/nitrocellulose automotive paints and a preferred reagent in thin-film coating operations using vinylidene chloride-acrylonitrile copolymer formulations. Acetone is also used as a resin diluent for polyester resins and as a cleaning solvent for resin reactors. It is also used to extract fats, oils, waxes, and resins from natural products, dewax lubricating oils, and extract certain essential oils. Acetone is also an important chemical intermediate in the preparation of various oxygenated solvents, including ketones, diacetone alcohol, mesityl oxide, methyl isobutyl ketone, and isophorone.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by various routes. A skin and severe eye irritant. Human systemic effects by inhalation: changes in EEG, changes in carbohydrate metabolism, nasal effects, conjunctiva irritation, respiratory system effects, nausea and vomiting, and muscle weakness. Human systemic effects by ingestion: coma, kidney damage, and metabolic changes. Narcotic in high concentration. In industry, no injurious effects have been reported other than skin irritation resulting from its defatting action, or headache from prolonged inhalation. Experimental reproductive effects. A common air contaminant. Highly flammable liquid. Dangerous disaster hazard due to fire and explosion hazard; can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. Potentially explosive reaction with nitric acid + sulfuric acid, bromine trifluoride, nitrosyl chloride + platinum, nitrosyl perchlorate, chromyl chloride, thiotrithiazyl perchlorate, and (2,4,6-trichloro-l,3,5triazine + water). Reacts to form explosive peroxide products with 2-methyl-1,3butadiene, hydrogen peroxide, and peroxomonosulfuric acid. Ignites on contact with activated carbon, chromium trioxide, dioxygen difluoride + carbon dioxide, and potassium-tert-butoxide. Reacts violently with bromoform, chloroform + alkalies, bromine, and sulfur dichloride. Incompatible with CrO, (nitric + acetic acid), NOCl, nitryl perchlorate, permonosulfuric acid, NaOBr, (sulfuric acid + potassium dichromate), (tho-diglycol + hydrogen peroxide), trichloromelamine, air, HNO3, chloroform, and H2SO4. To fight fire, use Con, dry chemical, alcohol foam. Used in production of drugs of abuse
Safety
Acetone is considered moderately toxic, and is a skin irritant and
severe eye irritant. Skin irritation has been reported due to its
defatting action, and prolonged inhalation may result in headaches.
Inhalation of acetone can produce systemic effects such as
conjunctival irritation, respiratory system effects, nausea, and
vomiting.
LD50 (mouse, oral): 3.0 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IP): 1.297 g/kg
LD50 (rabbit, oral): 5.340 g/kg
LD50 (rabbit, skin): 0.2 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IV): 5.5 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 5.8 g/kg
Potential Exposure
It is used as a solvent in nail polish remover and many other chemicals. Used in the production of lubricating oils and as an intermediate in the manufacture of chloroform and of various pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
Carcinogenicity
Acetone may be weakly genotoxic, but the
majority of assays were negative.7 It was not
tumorigenic in skin painting studies in mice.
The 2003 ACGIH threshold limit valuetime-
weighted average (TLV-TWA) for
acetone is 750ppm (1780mg/m3) with a
short-term excursion level of 1000ppm
(2380mg/m3).
Source
Naturally occurs in blood and urine in small concentrations. Reported in cigarette smoke
(1,100 ppm) and gasoline exhaust (2.3 to 14.0 ppm) (quoted, Verschueren, 1983).
Acetone occurs naturally in many plant species including cuneate Turkish savory (Satureja
cuneifolia), catmint (Nepeta racemosa), Guveyoto (Origanum sipyleum), and Topukcayi shoots
(Micromeria myrtifolia) at concentrations of 20, 2, 2, and 0.1, respectively (Baser et al., 1992,
1993; Ozek et al., 1992; Tumen, 1991). Acetone was also detected in Turkish calamint
(Calamintha nepeta ssp. glandulosa) (Kirimer et al., 1992), pineapples, cauliflower leaves, tea
leaves, West Indian lemongrass, jimsonweed, soybeans, carrots, bay leaves, hop flowers, apples,
tomatoes, water mint leaves, alfalfa, pears, rice plants, white mulberries, clover-pepper, and roses
(Duke, 1992). Acetone also was emitted from many forest plant species (Isidorov et al., 1985).
Acetone was detected in diesel fuel at a concentration of 22,000 μg/g (Schauer et al., 1999).
Identified as an oxidative degradation product in the headspace of a used engine oil (10–30W)
after 4,080 miles (Levermore et al., 2001). Acetone also was detected in automobile exhaust at
concentrations ranging from 0.09 to 4.50 mg/m3 (Grimaldi et al., 1996) and in cigarette smoke at
concentrations ranging from 498 to 869 mg/m3 (Euler et al., 1996).
Gas-phase tailpipe emission rates from California Phase II reformulated gasoline-powered
automobiles with and without catalytic converters were 1.19 and 42 mg/km, respectively (Schauer
et al., 2002).
Vereecken and Peeters (2000) reported that acetone is formed from the reaction of α-pinene and
OH radicals in the atmosphere. This reaction resulted in an acetone yield of 8.5% which is
consistent with available experimental data.
Schauer et al. (2001) measured organic compound emission rates for volatile organic
compounds, gas-phase semi-volatile organic compounds, and particle phase organic compounds
from the residential (fireplace) combustion of pine, oak, and eucalyptus. The gas-phase emission
rates of acetone were 749 mg/kg of pine burned, 462 mg/kg of oak burned, and 79 mg/kg of
eucalyptus burned.
Environmental Fate
Biological. Following a lag time of 20 to 25 h, acetone degraded in activated sludge (30 mg/L)
at a rate constant ranging from 0.016 to 0.020/h (Urano and Kato, 1986). Soil bacteria can mineralize acetone to carbon dioxide (Taylor et al., 1980). Bridié et al. (1979) reported BOD and
COD values of 1.85 and 1.92 g/g using filtered effluent from a biological sanitary waste treatment
plant. These values were determined using a standard dilution method at 20 °C for a period of 5 d.
Similarly, Heukelekian and Rand (1955) reported a 5-d BOD value of 0.85 g/g which is 38.5% of
the ThOD value of 2.52 g/g. Waggy et al. (1994) reported 5, 15, and 28-d BOD values of 14, 74,
and 74%, respectively. Using the BOD technique to measure biodegradation, the mean 5-d BOD
value (mM BOD/mM acetone) and ThOD were 1.52 and 38.0%, respectively (Vaishnav et al.,
1987).
Photolytic. Photolysis of acetone in air yields carbon monoxide and free radicals, but in
isopropanol, pinacol is formed (Calvert and Pitts, 1966). Photolysis of acetone vapor with nitrogen
dioxide via a mercury lamp gave peroxyacetyl nitrate as the major product with smaller quantities
of methyl nitrate (Warneck and Zerbach, 1992).
Chemical/Physical. Hypochlorite ions, formed by the chlorination of water for disinfection
purposes, may react with acetone to form chloroform. This reaction is expected to be significant
within the pH range of 6 to 7 (Stevens et al., 1976).
Storage
Acetone should be used only in areas free of ignition sources, and quantities greater than 1 liter should be stored in tightly sealed metal containers in areas separate from oxidizers.
Shipping
UN1090 Acetone, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid
Purification Methods
The commercial preparation of acetone by catalytic dehydrogenation of isopropyl alcohol gives relatively pure material. Analytical reagent quality generally contains less than 1% of organic impurities but may have up to about 1% of H2O. Dry acetone is appreciably hygroscopic. The main organic impurity in acetone is mesityl oxide, formed by aldol condensation. It can be dried with anhydrous CaSO4, K2CO3 or type 4A Linde molecular sieves, and then distilled. Silica gel and alumina, or mildly acidic or basic desiccants cause acetone to undergo the aldol condensation, so that its water content is increased by passage through these reagents. This also occurs to some extent when P2O5 or sodium amalgam is used. Anhydrous MgSO4 is an inefficient drying agent, and CaCl2 forms an addition compound. Drierite (anhydrous CaSO4) offers minimum acid and base catalysis for aldol formation and is the recommended drying agent for this solvent [Coetzee & Siao Inorg Chem 14 2 1987, Riddick & Bunger Organic Solvents Wiley-Interscience, N.Y., 3rd edn, 1970]. Acetone can be shaken with Drierite (25g/L) for several hours before it is decanted and distilled from fresh Drierite (10g/L) through an efficient column, maintaining atmospheric contact through a Drierite drying tube. The equilibrium water content is about 10-2M. Anhydrous Mg(ClO4)2 should not be used as drying agent because of the risk of EXPLOSION with acetone vapour. Organic impurities have been removed from acetone by adding 4g of AgNO3 in 30mL of water to 1L of acetone, followed by 10mL of M NaOH, shaking for 10minutes, filtering, drying with anhydrous CaSO4 and distilling [Werner Analyst (London) 58 335 1933]. Alternatively, successive small portions of KMnO4 have been added to acetone at reflux, until the violet colour persists, followed by drying and distilling. Refluxing with chromium trioxide (CrO3) has also been used. Methanol has been removed from acetone by azeotropic distillation (at 35o) with methyl bromide, and treatment with acetyl chloride. Small amounts of acetone can be purified as the NaI addition compound, by dissolving 100g of finely powdered NaI in 400g of boiling acetone, then cooling in ice and salt to -8o. Crystals of NaI.3Me2CO are filtered off and, on warming in a flask, acetone distils off readily. [This method is more convenient than the one using the bisulfite addition compound.] It has also been purified by gas chromatography on a 20% free fatty acid phthalate (on Chromosorb P) column at 100o. For efficiency of desiccants in drying acetone see Burfield and Smithers [J Org Chem 43 3966 1978]. The water content of acetone can be determined by a modified Karl Fischer titration [Koupparis & Malmstadt Anal Chem 54 1914 1982]. [Beilstein 1 IV 3180.] Rapid procedure: Dry over anhydrous CaSO4 and distil.
Toxicity evaluation
Acetone evaporates rapidly, even from water and soil. Once entered the atmosphere, it is degraded by photolysis, a reaction in which free radicals are involved or removed by wet deposits. It is a significant groundwater contaminant because of its miscibility in water.
Incompatibilities
Acetone reacts violently with oxidizing agents, chlorinated solvents, and alkali mixtures. It reacts vigorously with sulfur dichloride, potassium t-butoxide, and hexachloromelamine. Acetone should not be used as a solvent for iodine, as it forms a volatile compound that is extremely irritating to the eyes.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Incineration.
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (inhalation solution; oral tablets; topical preparations). Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK.
Properties of Acetone
| Melting point: | -94 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 56 °C760 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 0.791 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 2 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 184 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 3326 | ACETONE |
| Flash point: | 1 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | Miscible with water and with ethanol (96 per cent). |
| appearance | Colorless liquid |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 19.3(at 25℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 0.79 (25/25℃) |
| color | Colorless, invisible vapor |
| Odor | Characteristic pungent odor detectable at 33 to 700 ppm (mean = 130 ppm) |
| PH | 5-6 (395g/l, H2O, 20°C) |
| Relative polarity | 0.355 |
| explosive limit | 2.6-12.8%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 42ppm |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| JECFA Number | 139 |
| Merck | 14,66 |
| BRN | 63580 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 2.27 at 14.9 °C, 3.03 at 25 °C, 7.69 at 35.1 °C, 11.76 at 44.9 °C (Betterton, 1991) |
| Dielectric constant | 1.0(0℃) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 1780 mg/m3 (750 ppm), STEL
2375 mg/m3 (ACGIH); 10 h–TWA 590
mg/m3 (250 ppm); IDLH 20,000 ppm
(NIOSH). |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 67-64-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetone(67-64-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Acetone (67-64-1) |
Safety information for Acetone
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P242:Use only non-sparking tools. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Acetone
Acetone manufacturer
Friedrich Organic Chemicals India Private Limited
New Products
Cyclopentane-1,2-dione 2,6-Dibromoaniline 5-Hydroxy-3,9-dimethyl-7H-benzo[c]fluoren-7-one Methyl 4-(acetyloxy)-6-methoxy-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2naphthalenecarboxylate 4-Hydroxy-6,7-dimethoxy-1-phenyl-2naphthalenecarboxylic acid (3,5-Dibromophenyl)[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methanone (4-butoxyphenyl)(4-fluorophenyl)methanone (4-Bromophenyl)(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methanone Cefuroxime EP Impurity-A N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity N-(8-Amino-6-fluoro-5-methyl-1-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl)acetamide 4-Ethyl-4-hydroxy-1,4,7,8-tetrahydro-3H,10H-spiro[pyrano[3,4-f]indolizine-6,2'-[1,3]dioxolane]-3,10-dione (E)-N'-(2-cyano-4-nitrophenyl)- N,N-dimethylformimidamide 2-Chloro-7-cyclopentyl-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-6-carboxylic acid Benzyl-N,4-dimethylpiperidine-3- amine dihydrochloride 5-bromopyridin-2-amine 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 3,4 Dimethoxy BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Acetone CAS 67-64-1View Details
Acetone CAS 67-64-1View Details
67-64-1 -
 Acetone CAS 67-64-1View Details
Acetone CAS 67-64-1View Details
67-64-1 -
 Acetone CAS 67-64-1View Details
Acetone CAS 67-64-1View Details
67-64-1 -
 Acetone CAS 67-64-1View Details
Acetone CAS 67-64-1View Details
67-64-1 -
 Acetone CAS 67-64-1View Details
Acetone CAS 67-64-1View Details
67-64-1 -
 Acetone CAS 67-64-1View Details
Acetone CAS 67-64-1View Details
67-64-1 -
 Acetone CASView Details
Acetone CASView Details -
 CDH Acetone AR GradeView Details
CDH Acetone AR GradeView Details
107-87-9
