Tungsten
Synonym(s):Tungsten;W;W 00BO35;W 00BO55;W 00BO65
- CAS NO.:7440-33-7
- Empirical Formula: W
- Molecular Weight: 183.84
- MDL number: MFCD00011461
- EINECS: 231-143-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-13 11:25:41
What is Tungsten?
Description
Tungsten was recognized as a distinct element in 1779 by Peter Woulfe, but not isolated until 1783, by Jose and Fausto d’Elhuyar. The average tungsten concentration in the earth’s crust is ~0.006%. Tungsten occurs naturally as tungstate, mainly in compounds such as wolframites and scheelites.
Chemical properties
Tungsten is a hard, brittle, steel-gray to tinwhite metal or fine powder.
Physical properties
Extremely pure samples of tungsten are rather soft and can be cut easily with a simple saw.Pure tungsten can be drawn into fine wires (ductile). On the other hand, if there are even a fewimpurities in the sample, the metal becomes very hard and brittle. It is a very dense metal witha whitish-to-silvery-grayish color when freshly cut. It has the highest melting point of all metalsat 3,422°C, making it a useful metal where high temperatures are required. Incidentally,the transition metals on both sides of it in period 6 (73Ta and 75Re) have the second- and thirdhighestmelting points. Tungsten’s boiling point is also high at 5,927°C.
Isotopes
There are 36 isotopes of tungsten. Five are naturally stable and therefore contributeproportionally to tungsten’s existence on Earth, as follows: W-180 = 0.12%, W-182 = 26.50%, W-183 = 14.31%, W-184 = 30.64%, and W-186 = 28.43%. The other31 isotopes are man-made in nuclear reactors and particle accelerators and have halflivesranging from fractions of a second to many days.
Origin of Name
Tungsten was originally named “Wolfram” by German scientists, after the mineral in which it was found, Wolframite—thus, its symbol “W.” Later, Swedish scientists named it tung sten, which means “heavy stone,” but it retained its original symbol of “W.”
Occurrence
Tungsten is the 58th most abundant element found on Earth. It is never found in 100%pure form in nature. Its major ore is called wolframite or tungsten tetroxide, (Fe,Mn)WO4,which is a mixture of iron and manganese and tungsten oxide. During processing, the ore ispulverized and treated with strong alkalis resulting in tungsten trioxide (WO3), which is thenheated (reduced) with carbon to remove the oxygen. This results in a variety of bright colorchanges and ends up as a rather pure form of tungsten metal: 2WO3 + 3C → 2WO + 3CO2.Or, if hydrogen is used as the reducing agent, a more pure form of metal is produced: WO3+ 3H2 → W + 3H2O.
Tungsten ores (oxides) are found in Russia, China, South America, Thailand, and Canada.In the United States, the ores are found in Texas, New Mexico, Colorado, California, Arizona,and Nebraska.
History
In 1779 Peter Woulfe examined the mineral now known as wolframite and concluded it must contain a new substance. Scheele, in 1781, found that a new acid could be made from tung sten (a name first applied about 1758 to a mineral now known as scheelite). Scheele and Berman suggested the possibility of obtaining a new metal by reducing this acid. The de Elhuyar brothers found an acid in wolframite in 1783 that was identical to the acid of tungsten (tungstic acid) of Scheele, and in that year they succeeded in obtaining the element by reduction of this acid with charcoal. Tungsten occurs in wolframite, (Fe, Mn)WO4; scheelite, CaWO4; huebnerite, MnWO4; and ferberite, FeWO4. Important deposits of tungsten occur in California, Colorado, Bolivia, Russia, and Portugal. China is reported to have about 75% of the world’s tungsten resources. Natural tungsten contains five stable isotopes. Thirty-two other unstable isotopes and isomers are recognized. The metal is obtained commercially by reducing tungsten oxide with hydrogen or carbon. Pure tungsten is a steel-gray to tin-white metal. Very pure tungsten can be cut with a hacksaw, and can be forged, spun, drawn, and extruded. The impure metal is brittle and can be worked only with difficulty. Tungsten has the highest melting point of all metals, and at temperatures over 1650°C has the highest tensile strength. The metal oxidizes in air and must be protected at elevated temperatures. It has excellent corrosion resistance and is attacked only slightly by most mineral acids. The thermal expansion is about the same as borosilicate glass, which makes the metal useful for glass-to-metal seals. Tungsten and its alloys are used extensively for filaments for electric lamps, electron and television tubes, and for metal evaporation work; for electrical contact points for automobile distributors; X-ray targets; windings and heating elements for electrical furnaces; and for numerous spacecraft and high-temperature applications. High-speed tool steels, Hastelloy?, Stellite?, and many other alloys contain tungsten. Tungsten carbide is of great importance to the metal-working, mining, and petroleum industries. Calcium and magnesium tungstates are widely used in fluorescent lighting; other salts of tungsten are used in the chemical and tanning industries. Tungsten disulfide is a dry, high-temperature lubricant, stable to 500°C. Tungsten bronzes and other tungsten compounds are used in paints. Zirconium tungstate has found recent applications (see under Zirconium). Tungsten powder (99.999%) costs about $2900/kg.
Characteristics
Tungsten is considered part of the chromium triad of group six (VIB), which consists of24Cr, 42Mo, and 74W. These elements share many of the same physical and chemical attributes.Tungsten’s high melting point makes it unique insofar as it can be heated to the point thatit glows with a very bright white light without melting. This makes it ideal as a filamentfor incandescent electric light bulbs. Most metals melt long before they reach the point ofincandescence.
Chemically, tungsten is rather inert, but it will form compounds with several other elementsat high temperatures (e.g., the halogens, carbon, boron, silicon, nitrogen, and oxygen).Tungsten will corrode in seawater.
The Uses of Tungsten
Tungsten, also known as wolfram, occurs as wolframite (FeWO4). It can be found in the earth’s crust but not in its pure metal form. It combines with other chemicals and compounds within the rocky earth’s crust. It is a transitional hard metal with physicochemical properties and can also be manufactured commercially (Lassner and Schnubert, 1999; Gbaruko and Igwe, 2007; Stefaniak, 2010; Strigul et al., 2010).
Tungsten is most commonly used to increase the hardness of steel. It is available commercially in the form of powder, single crystal, and ultrapure granule grades. It is also used in the manufacturing of alloys, light filaments, and X-ray tubes. A recent use for tungsten is as a lead substitute during the manufacturing of ammunition and sporting good products. Another recent commercial use for tungsten is in the production of wedding bands. It is also used as a catalyst in chemical reactions (Lassner and Schnubert, 1999; Gbaruko and Igwe, 2007; Stefaniak, 2010; Strigul et al., 2010).
To increase hardness, toughness, elasticity, and tensile strength of steel; manufacture of alloys; manufacture of filaments for incandescent lamps and in electron tubes; in contact points for automotive, telegraph, radio and television apparatus; in phonograph needles. Tungsten carbides (W2C, WC) used in rock drills, metal-cutting tools, wire-drawing dies. WC used as catalyst instead of platinum: Bennett et al., Science 184, 563 (1974).
The Uses of Tungsten
Since its melting temperature is over 3,400°C, tungsten is one of the few metals that canglow white hot when heated without melting. This factor makes it the second most frequentlyused industrial metal (the first is iron). Tungsten is used in the filaments of common lightbulbs, as well as in TV tubes, cathode ray tubes, and computer monitors. Its ability to be“pulled” into thin wire makes it useful in the electronics industry. It is also used in solarenergy products and X-ray equipment. Its ability to withstand high temperatures makes itideal for rocket engines and electric-heater filaments of all kinds. Tungsten carbide is used as asubstitute for diamonds for drills and grinding equipment. This attribute is important in themanufacture of exceptionally hard, high-speed cutting tools.
The Uses of Tungsten
Ferrous and nonferrous alloys, filaments in incandescent lamps, heating elements, welding electrodes, manufacture of abrasives and tools, manufacture of textiles and ceramics.
Definition
A transition metal occurring naturally in wolframite ((Fe,Mn)WO4) and scheelite (CaWO4). It was formerly called wolfram. It is used as the filaments in electric lamps and in various alloys. Symbol: W; m.p. 3410 ± 20°C; b.p. 5650°C; r.d. 19.3 (20°C); p.n. 74; r.a.m. 183.84.
Definition
tungsten: Symbol W. A white orgrey metallic transition element(formerly called wolfram); a.n. 74;r.a.m. 183.85; r.d. 19.3; m.p. 3410°C;b.p. 5660°C. It is found in a numberof ores, including the oxides wolframite,(Fe,Mn)WO4, and scheelite,CaWO4. The ore is heated with concentratedsodium hydroxide solutionto form a soluble tungstate. Theoxide WO3 is precipitated from thisby adding acid, and is reduced to themetal using hydrogen. It is used invarious alloys, especially high-speedsteels (for cutting tools) and in lampfilaments. Tungsten forms a protectiveoxide in air and can be oxidizedat high temperature. It does not dissolvein dilute acids. It forms compoundsin which the oxidation stateranges from +2 to +6. The metal wasfirst isolated by Juan d’Elhuyer andFausto d’Elhuyer (1755–1833) in1783.
Production Methods
Tungsten occurs principally in the minerals wolframite (Fe,Mn)WO4, scheelite (CaWO4), ferberite (FeWO4), and hubnerite (MnWO4). These ores are found in China, Russia, Canada, Austria, Africa, Bolivia, Columbia, and Portugal. Wolframite is the most important oreworldwide; scheelite is the principal domestic U.S. ore. Scheelite, when pure, contains 80.6% WO3, the most common impurity being MoO3. The percentages of FeO and MnO in wolframite vary considerably; hubnerite is the term applied to ore containing more than 20% MnO and ferberite and to ore containing more than 20% FeO. Intermediate samples are called wolframite.
Reactivity Profile
Tungsten is stable at room temperature. Very slowly attacked by nitric acid, sulfuric acid, and aqua regia. Dissolved by a mixture of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid. No reaction with aqueous bases. Attacked rapidly by motlen alkaline melts such as Na2O2 or KNO3/NaOH. Vigorous reactions with bromine trifluoride and chlorine trifluoride. Becomes incandescent upon heating with lead oxide; becomes incandescent in cold fluorine and with iodine pentafluoride. Combustible in the form of finely divided powder and may ignite spontaneously.
Hazard
Tungsten dust, powder, and fine particles will explode, sometimes spontaneously, in air.The dust of many of tungsten’s compounds is toxic if inhaled or ingested.
Health Hazard
The soluble compounds of tungsten are distinctly more toxic than the insoluble forms.
Flammability and Explosibility
Flammable
Safety Profile
An inhalation hazard. Mildly toxic by an unspecified route. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. A skin and eye irritant. Flammable in the form of dust when exposed to flame. The powdered metal may ignite on contact with air or oxidants (e.g., bromine pentafluoride, bromine, chlorine trifluoride, potassium perchlorate, potassium dichromate, nitryl fluoride, fluorine, oxygen difluoride, iodine pentafluoride, hydrogen sulfide, sodlum peroxide, lead (IV)oxide). See also TUNGSTEN COMPOUNDS and POWDERED METALS.
Potential Exposure
Tungsten is used in ferrous and nonferrous alloys, and for filaments in incandescent lamps. It has been stated that the principal health hazards from tungsten and its compounds arise from inhalation of aerosols during mining and milling operations. The principal compounds of tungsten to which workers are exposed are ammonium paratungstate, oxides of tungsten (WO3, W2O5, WO2); metallic tungsten; and tungsten carbide. In the production and use of tungsten carbide tools for machining, exposure to the cobalt used as a binder or cementing substance may be the most important hazard to the health of the employees. Since the cemented tungsten carbide industry uses such other metals as tantalum, titanium, niobium, nickel, chromium, and vanadium in the manufacturing process, the occupational exposures are generally to mixed dust.
Carcinogenicity
Tungsten has been suspected to be involved in the occurrence of childhood leukemia, with the discovery of a cluster of diseases in Fallon, Nevada, associated with elevated levels of tungsten in urine and drinking water. The exact environmental source of exposure to tungsten was not clearly identi?ed and there is little evidence for an etiological role of tungsten in eliciting leukemia.
Environmental Fate
Tungsten in the environment largely exists as ions in compounds and primarily insoluble solids. The potential for particulate matter to spread is low as wet and dry deposition removes it from the atmosphere. If released to air, most tungsten compounds have low vapor pressures and are expected to exist solely in the particulate phase in the ambient atmosphere. Volatization is not expected to be an important fate process.
Shipping
UN3089 Metal powders, flammable, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 4.1; Labels: 4.1-Flammable solid. UN3189 Metal powder, self heating, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 4.2; Labels: 4.2-Spontaneously combustible material.
Purification Methods
Clean the solid with conc NaOH solution, rub it with very fine emery paper until its surface is bright, wash it with previously boiled and cooled conductivity water and dry it with filter paper. [Hein & Herzog in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol II p 1417 1965.]
Toxicity evaluation
Reported inhalation effects are probably due to cobalt in exposures, a competitive inhibitor of molybdenum utilization.
Incompatibilities
Tungsten: The finely divided powder is combustible and may ignite spontaneously in air. Incompatible with bromine trifluoride; chlorine trifluoride; fluorine, iodine pentafluoride.
Waste Disposal
Recovery of tungsten from sintered metal carbides, scrap and spent catalysts has been described as an alternative to disposal.
Properties of Tungsten
| Melting point: | 3410 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 5660 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 19.3 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 3000℃ |
| Flash point: | -23 °C |
| storage temp. | no restrictions. |
| form | wire |
| color | Silver-gray |
| Specific Gravity | 19.3 |
| Resistivity | 4.9 μΩ-cm, 20°C |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Merck | 13,9884 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2 ppm; STEL 4 ppm OSHA: TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3) NIOSH: IDLH 25 ppm; TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3); STEL 4 ppm(10 mg/m3) |
| Stability: | Stable. Dust is flammable, though not likely to present a hazard if normal good practice is used. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7440-33-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Tungsten(7440-33-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tungsten (7440-33-7) |
Safety information for Tungsten
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H228:Flammable solids H252:Self-heating substances and mixtures |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P235:Keep cool. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P370+P378:In case of fire: Use … for extinction. |
Computed Descriptors for Tungsten
Tungsten manufacturer
Parmanu Dhatu Nigam
New Products
Cyclopentane-1,2-dione 2,6-Dibromoaniline (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid 1-AMino-cyclobutaneMethanol HCl TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 3-Amino-3-(3-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 3-Amino-3-(4-methylphenyl)propionic acid 3-AMINO-3-(3-CHLORO-PHENYL)-PROPIONIC ACID Cefuroxime EP Impurity-A N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity 4 - fluoro- 2 - methoxy- 5 - nitroaniline 1-(2-amino-5-hydroxy phenyl)propan-1-one tert-butyl 4-(6-((7-cyclo pentyl -6-(dimethyl carbamoyl) -7H-pyrrolo [2,3-d]pyrimidin-2-yl) amino)pyridin-3-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylate 2-amino-5-nitrobenzonitrile (4-Fluoro-2-methoxy-5-nitro- phenyl)-[4- (1-methyl-1H- indol-3- yl)-pyrimidin-2-yl]- amine (3R,4R)-1-benzyl-N,4-dimethylpiperidin-3- amine 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
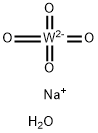

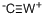
![[1,2-BIS(DIPHENYLPHOSPHINO)ETHANE]TUNGSTEN TETRACARBONYL](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/29890-05-9.gif)

You may like
-
 Tungsten wire CASView Details
Tungsten wire CASView Details -
 Tungsten wire CASView Details
Tungsten wire CASView Details -
 Tungsten wire CASView Details
Tungsten wire CASView Details -
 Tungsten wire CASView Details
Tungsten wire CASView Details -
 Tungsten wire CASView Details
Tungsten wire CASView Details -
 Tungsten wire CASView Details
Tungsten wire CASView Details -
 Tungsten wire CASView Details
Tungsten wire CASView Details -
 Tungsten (0.18 m2/g) (nitrogen BET specific surface area) CASView Details
Tungsten (0.18 m2/g) (nitrogen BET specific surface area) CASView Details
