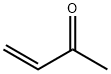
Trimethylsilylketene
- CAS NO.:4071-85-6
- Empirical Formula: C5H10OSi
- Molecular Weight: 114.22
- MDL number: MFCD00054882
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-31 14:38:37
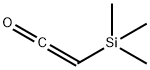
What is Trimethylsilylketene?
Physical properties
bp 81–82 °C; d 0.80 g cm?3.
The Uses of Trimethylsilylketene
Trimethylsilylketene is a reactive acylating agent for amines and alcohols; building block for synthesis of coumarins; synthesis of α-silyl ketones via the addition of organocerium reagents; treatment with stabilized ylides forms trimethylsilyl-substituted allenes;a cycloaddition with aldehydes affords β-lactones; forms small rings with diazomethane; treatment with n-BuLi forms a ketene enolate. It participates in the reactions of Trimethylsilylacetylation of Alcohols and Amines, Synthesis of Coumarins via Cyclization–Elimination, One-pot Formation of α-Silyl Ketones, Preparation of Trimethylsilyl-Substituted Allenes, Preparation of β-Lactones, Reaction with Diazomethane to Form Silylated Cyclopropanes and Cyclobutanones, Synthesis of Heterocycles, Formation of the Ketene Enolate, and other uses.
Preparation
Most often prepared (eq 1) by pyrolysis of ethoxy(trimethylsilyl)acetylene at 120??C (100 mmol scale, 65% yield).Recently, pyrolysis of t-butoxy(trimethylsilyl) acetylene has been shown to be a convenient alternative for the preparation of trimethylsilylketene (1). Thermal decomposition of t-butoxy(trimethylsilyl)acetylene causes elimination of 2-methylpropene slowly at temperatures as low as 50??C and instantaneously at 100¨C110??C (30 mmol scale, 63% yield). The main advantage of this method is that it is possible to generate trimethylsilylketene in the presence of nucleophiles, leading to in situ trimethylsilylacetylation (eq 2). Increased shielding of the triple bond prevents problems such as polymerization and nucleophilic attack that occur when the ketene is generated in situ from (trimethylsilyl)ethoxyacetylene. Trimethylsilylketene can also be prepared (eq 3) via the dehydration of commercially available trimethylsilylacetic acid with 1,3- dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) in the presence of a catalytic amount of triethylamine (100 mmol scale, 63%). Other typical methods used for ketene generation such as dehydrohalogenation of the acyl chloride and pyrolysis of the anhydride have been applied to the preparation of (1); however, both methods afford low yields.

Properties of Trimethylsilylketene
| Boiling point: | 80-82 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.813 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 3 °F |
| solubility | Sol CH2Cl2, CHCl3, CCl4, THF, diethyl ether, and
most standard organic solvents; reacts with alcoholic and amine
solvents. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ethenone, (trimethylsilyl)- (4071-85-6) |
Safety information for Trimethylsilylketene
Computed Descriptors for Trimethylsilylketene
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile valeronitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 -
 1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) -
 1529-41-5 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 99%View Details
1529-41-5 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 99%View Details
1529-41-5 -
 2856-63-5 99%View Details
2856-63-5 99%View Details
2856-63-5 -
 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
27472-21-5 -
 Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
7252-83-7 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8
