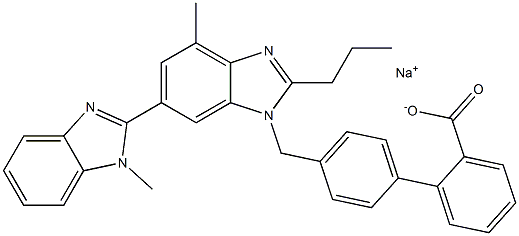
Telmisartan
Synonym(s):4′[(1,4′-Dimethyl-2′-propyl[2,6′-bi-1H-benzimidazol]-1′-yl)methyl][1,1′-biphenyl]-2-carboxylic acid;BIBR 277;Telmisartan
- CAS NO.:144701-48-4
- Empirical Formula: C33H30N4O2
- Molecular Weight: 514.62
- MDL number: MFCD00918125
- EINECS: 620-494-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-28 14:58:11
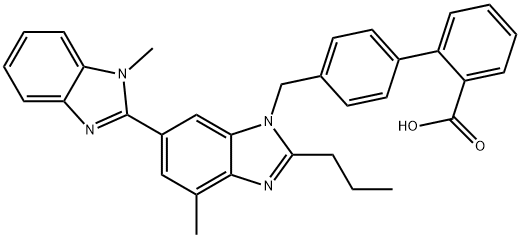
What is Telmisartan?
Absorption
Oral telmisartan follows nonlinear pharmacokinetics over the dose range of 20 mg to 160 mg. Both Cmax and AUC present greater than proportional increases at higher doses. With once-daily dosing, telmisartan has trough plasma concentrations of about 10% to 25% of peak plasma concentrations. The absolute bioavailability of telmisartan depends on the dosage. At 40 mg and 160 mg, the bioavailability was 42% and 58%, respectively. Food slightly decreases bioavailability. For instance, when the 40 mg dose is administered with food, a decrease of about 6% is seen, and with the 160 mg dose, there is a decrease of about 20%.
Toxicity
Intravenous LD50 in rats is 150-200 mg/kg in males and 200 to 250 mg/kg in females. Acute oral toxicity is low: no deaths and no changes occurred in rats or dogs at 2000 mg/kg, the highest dose tested. Limited data are available with regard to overdosage in humans.
Description
Telmisartan was launched in the US for the treatment of hypertension. Telmisartan blocks the action of angiotensin II (Ang II), the primary effector molecule of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). It is the sixth of this class of 《sartans》 to be marketed after the lead compound Losartan.
Chemical properties
White or off white crystalline powder
Originator
Boehringer Ingelheim (Germany)
The Uses of Telmisartan
Telmisartan, an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, is an effective medication for the treatment of hypertension. It can be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs. Additionally, it is beneficial in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy in hypertensive individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Telmisartan is also used to address congestive heart issues.
Background
Telmisartan is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist (ARB) used in the management of hypertension. Recent studies suggest that telmisartan may also have PPAR-gamma agonistic properties that could potentially confer beneficial metabolic effects.
Indications
Used alone or in combination with other classes of antihypertensives for the treatment of hypertension. Also used in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, as well as the treatment of congestive heart failure (only in patients who cannot tolerate ACE inhibitors).
What are the applications of Application
Telmisartan is a nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor type 1 antagonist
Definition
ChEBI: Telmisartan is a member of the class of benzimidazoles used widely in the treatment of hypertension. It has a role as an antihypertensive agent, an angiotensin receptor antagonist, an EC 3.4.15.1 (peptidyl-dipeptidase A) inhibitor, a xenobiotic and an environmental contaminant. It is a member of biphenyls, a member of benzimidazoles and a carboxybiphenyl.
brand name
Micardis (Boehringer Ingelheim).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Telmisartan is a non-peptide AT1 angiotensin receptor antagonist.
Pharmacokinetics
Telmisartan is an orally active nonpeptide angiotensin II antagonist that acts on the AT1 receptor subtype. It has the highest affinity for the AT1 receptor among commercially available ARBs and has minimal affinity for the AT2 receptor.
New studies suggest that telmisartan may also have PPARγ agonistic properties that could potentially confer beneficial metabolic effects, as PPARγ is a nuclear receptor that regulates specific gene transcription, and whose target genes are involved in the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism, as well as anti-inflammatory responses.
Angiotensin II is formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE, kininase II). Angiotensin II is the principal pressor agent of the renin-angiotensin system, with effects that include vasoconstriction, stimulation of synthesis and release of aldosterone, cardiac stimulation, and renal reabsorption of sodium. Telmisartan works by blocking the vasoconstrictor and aldosterone secretory effects of angiotensin II.
Clinical Use
Angiotensin-II antagonist:
Hypertension
Prevention of cardiovascular events
Synthesis
Telmisartan can be prepared in eight steps starting with methyl 4-amino-3-methyl benzoate; the first and second cyclization into a benzimidazole ring occur at steps 4 and 6 respectively.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Analgesics: antagonism of hypotensive effect and
increased risk of renal impairment with NSAIDs;
hyperkalaemia with ketorolac and other NSAIDs.
Antihypertensives: increased risk of hyperkalaemia,
hypotension and renal impairment with ACE-Is and
aliskiren.
Cardiac glycosides: concentration of digoxin
increased.
Ciclosporin: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and
nephrotoxicity.
Diuretics: enhanced hypotensive effect;
hyperkalaemia with potassium-sparing diuretics.
ESAs: increased risk of hyperkalaemia; antagonism
of hypotensive effect.
Lithium: reduced excretion (possibility of enhanced
lithium toxicity).
Potassium salts: increased risk of hyperkalaemia.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of hyperkalaemia and
nephrotoxicity.
Metabolism
Minimally metabolized by conjugation to form a pharmacologically inactive acyl-glucuronide, the glucuronide of the parent compound is the only metabolite that has been identified in human plasma and urine. The cytochrome P450 isoenzymes are not involved in the metabolism of telmisartan.
Overdose
The most likely manifestations of overdosage with telmisartan would be hypotension, dizziness and tachycardia; bradycardia could occur from parasympathetic (vagal) stimulation. Supportive treatment should be instituted if symptomatic hypotension occurs.
Properties of Telmisartan
| Melting point: | 261-263°C |
| Boiling point: | 771.9±70.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.16 |
| RTECS | DV2037500 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: >5 mg/mL at 60 °C |
| pka | 3.86±0.36(Predicted) |
| form | solid |
| color | white |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Merck | 14,9129 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 144701-48-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Telmisartan
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P312:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician if you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. |
Computed Descriptors for Telmisartan
| InChIKey | RMMXLENWKUUMAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(C2=CC=C(CN3C(CCC)=NC4=C(C)C=C(C5N(C)C6=CC=CC=C6N=5)C=C43)C=C2)=CC=CC=C1C(O)=O |
Telmisartan manufacturer
Gangwal Healthcare Pvt Ltd
CEFA CILINAS BIOTICS PVT LTD
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile valeronitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![4'-(Hydroxymethyl)-[1,1'-Biphenyl]-2-Carboxylic Acid](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/158144-54-8.gif)
![4'-(Dibromomethyl)-[1,1'-Biphenyl]-2-Carbonitrile](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/209911-63-7.gif)
You may like
-
 Telmisartan 99%View Details
Telmisartan 99%View Details -
 144701-48-4 Telmisartan-USP 98%View Details
144701-48-4 Telmisartan-USP 98%View Details
144701-48-4 -
 Telmisartan 99%View Details
Telmisartan 99%View Details -
 Telmisartan 99%View Details
Telmisartan 99%View Details -
 144701-48-4 Telmisartan 98%View Details
144701-48-4 Telmisartan 98%View Details
144701-48-4 -
 Telmisartan 98%View Details
Telmisartan 98%View Details -
 Telmisartan 95% CAS 144701-48-4View Details
Telmisartan 95% CAS 144701-48-4View Details
144701-48-4 -
 Telmisartan API PowderView Details
Telmisartan API PowderView Details
144701-48-4
