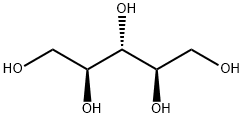
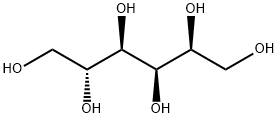
Sorbitol
Synonym(s):D -Glucitol;D -Sorbitol;D-Glucitol;Parteck Sorbitol
- CAS NO.:50-70-4
- Empirical Formula: C6H14O6
- Molecular Weight: 182.17
- MDL number: MFCD00004708
- EINECS: 200-061-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-02-02 18:10:39
What is Sorbitol?
Chemical properties
Sorbitol occurs as an odorless, white or almost colorless, crystalline, hygroscopic powder.
Occurrence
Sorbitol is one of the most widely found sugar alcohols in nature with relatively high concentrations occurring in apples, pears, plums, peaches and apricots. Also reported found in several varieties of berries, seaweed and algae.
The Uses of Sorbitol
Sorbitol is highly hygroscopic and has a pleasant, sweet taste. It maintains moistness in shredded coconut, pet foods, and candy. In sugarless frozen desserts, it depresses the freezing point, adds solids, and contributes some sweetness. It is used in low-calorie beverages to provide body and taste. It is used in dietary foods such as sugarless candy, chewing gum, and ice cream. It is also used as a crystallization modifier in soft sugar-based confections.
Besides, it can be used in manufacture of sorbose, ascorbic acid, propylene glycol, synthetic plasticizers and resins; as humectant (moisture conditioner) on printing rolls, in leather, tobacco. In writing inks to insure a smooth flow and to prevent crusting on the point of the pen. In antifreeze mixtures with glycerol or glycols.
Background
A polyhydric alcohol with about half the sweetness of sucrose. Sorbitol occurs naturally and is also produced synthetically from glucose. It was formerly used as a diuretic and may still be used as a laxative and in irrigating solutions for some surgical procedures.
Production Methods
Sorbitol occurs naturally in the ripe berries of many trees and
plants. It was first isolated in 1872 from the berries of the Mountain
Ash (Sorbus americana).
Industrially, sorbitol is prepared by high-pressure hydrogenation
with a copper–chromium or nickel catalyst, or by electrolytic
reduction of glucose and corn syrup. If cane or beet sugars are used
as a source, the disaccharide is hydrolyzed to dextrose and fructose
prior to hydrogenation.
Definition
Sorbitol is a hexahydric alcohol that occurs in rose hips and rowan berries. It can be synthesized by the reduction of glucose. Sorbitol is used to make vitamin C (ascorbic acid) and surfactants. It is also used in medicines and as a sweetener (particularly in foods for diabetics). It is an isomer of mannitol.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Sorbitol is widely used as an excipient in pharmaceutical formulations. It is also used extensively in cosmetics and food products. It may also be used analytically as a marker for assessing liver blood flow.
Safety Profile
Mildly toxic by ingestion. Human systemic effects by ingestion: hypermotility and diarrhea. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Safety
Sorbitol is better tolerated by diabetics than sucrose and is widely used in many sugar-free liquid vehicles. However, it is not considered to be unconditionally safe for diabetics.
Reports of adverse reactions to sorbitol are largely due to its action as an osmotic laxative when ingested orally,(17–19) which may be exploited therapeutically. Ingestion of large quantities of sorbitol (>20 g/day in adults) should therefore be avoided.
Side Effects
There are no formal recommendations for sorbitol intake. Fermentation of sorbitol in the large intestine can create gastrointestinal discomfort including bloating, gas and diarrhea. But these effects are not the same for everyone. Therefore, the FDA requires a label statement regarding potential laxative effects for foods that might lead to eating 50 grams of sorbitol in a day.
For those following a low Fermentable Oligosaccharides Disaccharides Monosaccharides And Polyols (FODMAP) diet, food sources of sorbitol are monitored because sorbitol is a type of polyol.
Storage
Sorbitol is chemically relatively inert and is compatible with most excipients. It is stable in air in the absence of catalysts and in cold, dilute acids and alkalis. Sorbitol does not darken or decompose at elevated temperatures or in the presence of amines. It is nonflammable, noncorrosive, and nonvolatile.
Incompatibilities
Sorbitol will form water-soluble chelates with many divalent and
trivalent metal ions in strongly acidic and alkaline conditions.
Addition of liquid polyethylene glycols to sorbitol solution, with
vigorous agitation, produces a waxy, water-soluble gel with a
melting point of 35–40℃. Sorbitol solutions also react with iron
oxide to become discolored.
Sorbitol increases the degradation rate of penicillins in neutral
and aqueous solutions.
Properties of Sorbitol
| Melting point: | 98-100 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | bp760 105° |
| alpha | 4 º (per eur. pharm.) |
| Density | 1.28 g/mL at 25 °C |
| vapor density | <1 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <0.1 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 3029 | D-SORBITOL |
| Flash point: | >100°C |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | Very soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol |
| form | liquid |
| pka | pKa (17.5°): 13.6 |
| Specific Gravity | 1.28 |
| color | White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 5.0-7.0 (25℃, 1M in H2O) |
| PH Range | 5 - 7 at 182 g/l at 25 °C |
| optical activity | [α]20/D 1.5±0.3°, c = 10% in H2O |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.04 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.045 |
| Merck | 14,8725 |
| BRN | 1721899 |
| Dielectric constant | 33.5(27℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Avoid strong oxidizing agents. Protect from moisture. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 50-70-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Sorbitol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Sorbitol
| InChIKey | FBPFZTCFMRRESA-JGWLITMVSA-N |
Sorbitol manufacturer
Gangwal Healthcare Pvt Ltd
New Products
Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Rifaximin EP Impurity-G N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile 4-Fluorothiophenol (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 4-Bromo BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Sorbitol 99%View Details
Sorbitol 99%View Details -
 Sorbitol 99%View Details
Sorbitol 99%View Details -
 D-Sorbitol CAS 50-70-4View Details
D-Sorbitol CAS 50-70-4View Details
50-70-4 -
 D-Sorbitol CAS 50-70-4View Details
D-Sorbitol CAS 50-70-4View Details
50-70-4 -
 Sorbitol Liquid ChemicalView Details
Sorbitol Liquid ChemicalView Details
50-70-4 -
 Liquid Sorbitol Chemical, Maize, 300 KgView Details
Liquid Sorbitol Chemical, Maize, 300 KgView Details
50-70-4 -
 Sorbitol Cas 50 70 4, Grade: Technical GradeView Details
Sorbitol Cas 50 70 4, Grade: Technical GradeView Details
50-70-4 -
 Sorbitol Liquid (Sorbitol)View Details
Sorbitol Liquid (Sorbitol)View Details
50-70-4