Potassium chloride
Synonym(s):Potassium chloride;KCl;Potassium chloride solution;CLK;CLK1
- CAS NO.:7447-40-7
- Empirical Formula: KCl
- Molecular Weight: 74.55
- MDL number: MFCD00011360
- EINECS: 231-211-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:39
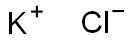
What is Potassium chloride ?
Absorption
The potassium in Potassium chloride is a normal dietary constituent and under steady-state conditions the amount of potassium absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract is equal to the amount excreted in the urine.
Toxicity
Potassium chloride has low toxicity. The administration of oral potassium salts to persons with normal excretory mechanisms for potassium rarely causes serious hyperkalemia. However, if excretory mechanisms are impaired, of if potassium is administered too rapidly intravenously, potentially fatal hyperkalemia can result.
Description
Potassium chloride (KCl) is a metal halide salt that is used in a variety of areas. The dominant application of potassium chloride is to serve as a fertilizer, which offers potassium to plants and prevents them from certain diseases. Besides, it can be applied in food and medical industry. As a treatment for hypokalemia, potassium chloride pills are taken to balance the blood's potassium levels and prevent potassium deficiency in the blood. In food industry, it serves as a electrolyte replenisher and a good salt substitute for food, as well as a firming agent to give consistent texture to food, thus to strengthen its structure.
Chemical properties
Potassium chloride occurs as odorless, colorless crystals or a white crystalline powder, with an unpleasant, saline taste. The crystal lattice is a face-centered cubic structure. It occurs naturally as the mineralsylvite (KCl) and as carnallite(KCl·MgCl2·6H2O); It has the interesting property of being more soluble than sodium chloride in hot water but less soluble in cold.
The Uses of Potassium chloride
Potassium Chloride is a common laboratory reagent and calibration standard for measuring electrical conducivity. Potassium chloride is a widely used reagent in biochemistry and molecular biology. It is also used in studies of ion transport and potassium channels. KCl is also utilized in the solubilization, extraction, purification, and crystallization of proteins.
Background
A white crystal or crystalline powder, Potassium chloride is used as an electrolyte replenisher, in the treatment of hypokalemia, in buffer solutions, and in fertilizers and explosives. The FDA withdrew its approval for the use of all solid oral dosage form drug products containing potassium chloride that supply 100 mg or more of potassium per dosage unit, except for controlled-release dosage forms and those products formulated for preparation of solution prior to ingestion.
Indications
Potassium chloride is used as an electrolyte replenisher and in the treatment of hypokalemia.
Definition
ChEBI: Potassium chloride is a metal chloride salt with a K(+) counterion. It has a role as a fertilizer. It is a potassium salt, an inorganic chloride and an inorganic potassium salt.
Production Methods
Potassium chloride occurs naturally as the mineral sylvite or sylvine; it also occurs in other minerals such as sylvinite, carnallite, and kainite. Commercially, potassium chloride is obtained by the solar evaporation of brine or by the mining of mineral deposits.
brand name
Apo-k;Celeka;Durules-k;Kadalex;Kalinorm;Kalipor;Kalium durules;K-long;Miopotasio;Plenish-k;Potasion;Roychlor;Rum-k;Swiss-kal sr;Ultra-k-chlor.
World Health Organization (WHO)
Potassium chloride has been used for many years to correct potassium deficiency. The use of fast-acting tablets has been associated with lesions of the gastro-intestinal mucosa, which have led to their general withdrawal.
General Description
Potassium chloride (KCl) is a water-soluble metal salt that comprises of potassium and chlorine. It can be extracted from minerals and salt water. KCl can be used in industries such as cosmetics, food, biomedical, chemical and fertilizer.
Air & Water Reactions
Hygroscopic. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Potassium chloride is not in general strongly reactive. Violent reaction with BrF3 and with a mixture of sulfuric acid potassium permanganate mixture . Reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid to generate fumes of hydrogen chloride.
Health Hazard
Potassium chloride is an essential constituent of the body for intracellular osmotic pressure and buffering, cell permeability, acid-base balance, muscle contraction and nerve function.
SYMPTOMS: Large doses of Potassium chloride usually induce vomiting, so acute intoxication by mouth is rare. If no pre-existing kidney damage, it is rapidly excreted. Poisoning disturbs the rhythm of heart. Large doses by mouth can cause gastrointestinal irritation, purging, weakness, and circulatory disturbances.
Fire Hazard
Flammability data is not available, but Potassium chloride is probably nonflammable.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Agricultural Uses
Muriate of potash or potassium chloride (KCl), is a major potash fertilizer. It is water soluble and is generally blended with other components to make it a multi-nutrient fertilizer. It has a higher salt index than potassium sulphate and is recommended for most crops except tobacco, potato and grapes, which are sensitive to chloride ions.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Potassium chloride is widely used in a variety of parenteral and nonparenteral pharmaceutical formulations. Its primary use, in parenteral and ophthalmic preparations, is to produce isotonic solutions.It is also used therapeutically in the treatment of hypokalemia.
Experimentally, potassium chloride is frequently used as a model drug in the development of new solid-dosage forms, particularly for sustained-release or modified-release products.
Industrial uses
Potassium chloride is a colorless or white crystallinecompound of the composition KCl, usedfor molten salt baths for the heat treatment ofsteels.
Potassium chloride is used in the porcelainenamel industry as a setting-up agent in titaniumcover coats. In general, the quantities ofpotassium chloride, when used as an electrolyte,will be approximately the same as sodiumnitrite, which it replaces.
Pharmacokinetics
The potassium ion is in the principle intracellular cation of most body tissues. Potassium ions participate in a number of essential physiological processes including the maintenance of intracellular tonicity, the transmission of nerve impulses, the contraction of cardiac, skeletal and smooth muscle, and the maintenance of normal renal function. The intracellular concentration of potassium is approximately 150 to 160 mEq per liter. The normal adult plasma concentration is 3.5 to 5 mEq per liter. An active ion transport system maintains this gradient across the plasma membrane. Potassium is a normal dietary constituent and under steady-state conditions the amount of potassium absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract is equal to the amount excreted in the urine. The usual dietary intake of potassium is 50 to 100 mEq per day.
Clinical Use
Hypokalaemia
Safety Profile
A human poison by ingestion. Poison experimentally by ingestion, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: nausea, blood clotting changes, carhac arrhythmias. An eye irritant. Mutation data reported. Explosive reaction with BrF3; sulfuric acid + potassium permanganate. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of K2O and Cl-.
Safety
Potassium chloride is used in a large number of pharmaceutical formulations, including oral, parenteral, and topical preparations, both as an excipient and as a therapeutic agent.
Parenterally, rapid injection of strong potassium chloride solutions can cause cardiac arrest; in the adult, solutions should be infused at a rate not greater than 750 mg/hour.
Therapeutically, in adults, up to 10 g orally, in divided doses has been administered daily, while intravenously up to 6 g daily has been used.
(guinea pig, oral): 2.5 g/kg
(mouse, IP): 1.18 g/kg
(mouse, IV): 0.12 g/kg
(mouse, oral): 0.38 g/kg
(rat, IP): 0.66 g/kg
(rat, IV): 0.14 g/kg
(rat, oral): 2.6 g/kg
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II antagonists:
increased risk of hyperkalaemia.
Ciclosporin: increased risk of hyperkalaemia.
Potassium-sparing diuretics: increased risk of
hyperkalaemia.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of hyperkalaemia.
Metabolism
Potassium is excreted mainly by the kidneys; it is secreted in the distal tubules in exchange for sodium or hydrogen ions. Some potassium is excreted in the faeces and small amounts may also be excreted in sweat.
Storage
Potassium chloride tablets become increasingly hard on storage at
low humidities. However, tablets stored at 76% relative humidity
showed no increase or only a slight increase in hardness.The
addition of lubricants, such as 2% w/w magnesium stearate,
reduces tablet hardness and hardness on aging.Aqueous
potassium chloride solutions may be sterilized by autoclaving or
by filtration.
Potassium chloride is stable and should be stored in a well-closed
container in a cool, dry place.
Purification Methods
Dissolve it in conductivity water, filter it, and saturate it with chlorine (generated from conc HCl and KMnO4). Excess chlorine is boiled off, and the KCl is precipitated by HCl (generated by dropping conc HCl into conc H2SO4). The precipitate is washed with water, dissolved in conductivity water at 90-95o, and crystallised by cooling to about -5o. The crystals are drained at the centrifuge, dried in a vacuum desiccator at room temperature, then fused in a platinum dish under N2, cooled and stored in a desiccator. Potassium chloride has also been sublimed in a stream of pre-purified N2 gas and collected by electrostatic discharge [Craig & McIntosh Can J Chem 30 448 1952].
Incompatibilities
Potassium chloride reacts violently with bromine trifluoride and
with a mixture of sulfuric acid and potassium permanganate. The
presence of hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride, and magnesium
chloride decreases the solubility of potassium chloride in water.
Aqueous solutions of potassium chloride form precipitates with
lead and silver salts.
Intravenous aqueous potassium chloride solutions are incompatible
with protein hydrolysate.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (injections, ophthalmic preparations, oral capsules, and tablets). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
References
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Potassium_chloride
https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00761
http://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-potassium-chloride-uses-formula-side-effects.html
Properties of Potassium chloride
| Melting point: | 770 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1420°C |
| Density | 1.98 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 1500°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | random crystals |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 1.984 |
| PH Range | 7 |
| PH | 5.5-8.0 (20℃, 50mg/mL in H2O) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | 340 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.02 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Merck | 14,7621 |
| Sublimation | 1500 ºC |
| BRN | 1711999 |
| Dielectric constant | 4.6(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids. Protect from moisture. Hygroscopic. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7447-40-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Potassium chloride(7447-40-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Potassium chloride (7447-40-7) |
Safety information for Potassium chloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H303:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Potassium chloride
| InChIKey | WCUXLLCKKVVCTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Potassium chloride manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 POTASSIUM CHLORIDE 99%View Details
POTASSIUM CHLORIDE 99%View Details -
 Potassium Chloride Ar 98%View Details
Potassium Chloride Ar 98%View Details -
 Potassium Chloride 99%View Details
Potassium Chloride 99%View Details -
 Potassium chloride 99%View Details
Potassium chloride 99%View Details -
 Potassium chloride 98%View Details
Potassium chloride 98%View Details -
 Potassium chloride 98%View Details
Potassium chloride 98%View Details -
 Potassium chloride,99% 99%View Details
Potassium chloride,99% 99%View Details -
 Borate Buffered Saline CASView Details
Borate Buffered Saline CASView Details
