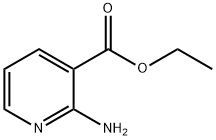
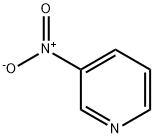
Nicotinic acid
Synonym(s):Nicotinic acid;Niacin;Pyridine-3-carboxylic acid;3-Picolinic acid;Niacin, 3-Pyridinecarboxylic acid
- CAS NO.:59-67-6
- Empirical Formula: C6H5NO2
- Molecular Weight: 123.11
- MDL number: MFCD00006391
- EINECS: 200-441-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-30 18:09:56
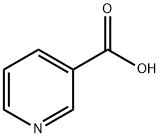
What is Nicotinic acid?
Description
Nicotinic acid is an additive to food on the basis of its nutrient supplement qualities as a vitamin (as an enzyme co-factor). This water-soluble vitamin of the B complex occurs in various animal and plant tissues. It is required by the body for the formation of coenzymes NAD and NADP. A deficiency of niacin results in the disease, pellagra.
Physical properties
Nicotinic acid and nicotinamide are colorless crystalline substances. Each is insol uble or only sparingly soluble in organic solvents. Nicotinic acid is slightly soluble
in water and ethanol; nicotinamide is very soluble in water and moderately soluble
in ethanol
Nicotinic acid is amphoteric and forms salts with acids as well as bases. Its car boxyl group can form esters and anhydrides and can be reduced.
History
Huber first synthesized nicotinic acid in 1867. In 1914, Funk isolated nicotinic acid from rice polishings. Goldberger, in 1915, demonstrated that pellagra is a nutritional deficiency. In 1917, Chittenden and Underhill demonstrated that canine blacktongue is similar to pellagra. In 1935, Warburg and Christian showed that niacinamide is essential in hydrogen transport as diphosphopyridine nucleotide (DPN). In the following year, Euler et al. isolated DPN and determined its structure. In 1937, Elvhehjem et al. cured blacktongue by administration of niacinamide derived from liver. In the same year, Fouts et al. cured pellagra with niacinamide. In 1947, Handley and Bond established conversion of tryptophan to niacin by animal tissues.
The Uses of Nicotinic acid
Nicotinic acid is also known as niacin and vitamin B3. It is a water-soluble conditioning agent that improves rough, dry, or flaky skin, helping smooth the skin and improve its suppleness. niacin enhances the appearance and feel of hair, by increasing body, suppleness, or sheen, or by improving the texture of hair that has been damaged physically or by chemical treatment. When used in the formulation of skin care products, niacinamide and nicotinic acid enhance the appearance of dry or damaged skin by reducing flaking and restoring suppleness.
Background
Niacin is a B vitamin used to treat vitamin deficiencies as well as hyperlipidemia, dyslipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and to reduce the risk of myocardial infarctions.
Indications
Nicotinic acid is indicated to prevent vitamin deficiencies in pediatric and adult patients receiving parenteral nutrition as part of multivitamin intravenous injections. Niacin oral tablets are indicated as a monotherapy or in combination with simvastatin or lovastatin to treat primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia. It can also be used to reduce the risk of nonfatal myocardial infarctions in patients with a history of myocardial infarction and hyperlipidemia. Niacin is also indicated with bile acid binding resins to treat atherosclerosis in patients with coronary artery disease and hyperlipidemia or to treat primary hyperlipidemia. Finally niacin is indicated to treat severe hypertriglyceridemia.
What are the applications of Application
Nicotinic Acid is a major chemical component of coenzymes NAD+ and NADP+
brand name
Niacor (Upsher Smith); Niaspan (KOS); Nicolar (Sanofi Aventis); Wampocap (Medpointe).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Nicotinic acid is an antioxidant and acts as a coenzyme in the form of nicotinamide adenine nucleotides(NAD). It modulates lipid metabolism and may be useful in treating dyslipidemia. Nicotinic acid reduces the low-density lipoprotein (LDL) synthesis and improves high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels. Deficiency of niacin leads to enhanced lipid peroxidation and is implicated in Crohn′s disease Deficiency also impacts DNA repair and also leads to skin and gastrointestinal disorder pellagra.
Mechanism of action
Nicotinic acid decreases formation and secretion of VLDL by the liver.This action appears secondary to its ability to inhibit fatty acid mobilization from adipose tissue. Circulating free fatty acids provide the main source of fatty acids for hepatic triglyceride synthesis, and lowering triglyceride synthesis lowers VLDL formation and secretion by the liver. Since plasma VLDL is the source of LDL, lowering VLDL can ultimately lower LDL. In addition, nicotinic acid shifts LDL particles to larger (more buoyant) sizes. The larger LDL particles are thought to be less atherogenic.
Pharmacokinetics
Niacin is a B vitamin used to treat vitamin deficiencies as well as hyperlipidemia, dyslipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and to reduce the risk of myocardial infarctions. Niacin acts to decrease levels of very low density lipoproteins and low density lipoproteins, while increasing levels of high density lipoproteins. Niacin has a wide therapeutic window with usual oral doses between 500mg and 2000mg. Patients with diabetes, renal failure, uncontrolled hypothyroidism, and elderly patients taking niacin with simvastatin or lovastatin are at increased risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis.
Toxicity
Overdose of niacin may present with severe prolonged hypotension. Patients experiencing an overdose should be treated with supportive measures which may include intravenous fluids.
The oral LD50 in the mouse is 3720mg/kg, in the rabbit is 4550mg/kg, in the rat is 7000mg/kg, and the dermal LD50 in the rat is >2000mg/kg.
Side Effects
Nicotinic acid can cause gastrointestinal (GI) distress,liver dysfunction (especially at high doses), decreased glucose tolerance, hyperglycemia, and hyperuricemia. Thus, it is contraindicated in patients with hepatic dysfunction, peptic ulcer, hyperuricemia, or diabetes mellitus.
Synthesis
Nicotinic acid, pyridine-3-carboxylic acid (20.2.9) is synthesized industrially by heating a paraldehyde trimer of acetaldehyde, under pressure with ammonia, which leads to the formation of 2-methyl-5-ethylpyridine, followed by oxidation with nitric acid which gives the desired product.

Absorption
In patients with chronic kidney disease, the Cmax is 0.06μg/mL for a 500mg oral dose, 2.42μg/mL for a 1000mg oral dose, and 4.22μg/mL for a 1500mg oral dose. The Tmax is 3.0 hours for a 1000mg or 1500mg oral dose. The AUC is 1.44μg*h/mL for a 500mg oral dose, 6.66μg*h/mL for a 1000mg oral dose, and 12.41μg*h/mL for a 1500mg oral dose. These values did not drastically differ in patients requiring dialysis.
Metabolism
The metabolism of niacin is poorly described in the literature, but the metabolites niacinamide, niacinamide N-oxide, nicotinuric acid, N1-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide, N1-methyl-4-pyridone-5-carboxamide, and trigonelline have been identified in human urine.
Properties of Nicotinic acid
| Melting point: | 236-239 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 260C |
| Density | 1.473 |
| refractive index | 1.5423 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 193°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 18g/l |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 4.85(at 25℃) |
| color | White to off-white |
| PH | 2.7 (18g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | odorless to sl. odor, sour taste |
| Water Solubility | 1-5 g/100 mL at 17 ºC |
| Merck | 14,6525 |
| BRN | 109591 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. May be light sensitive. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 59-67-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Niacin(59-67-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Nicotinic acid (59-67-6) |
Safety information for Nicotinic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Nicotinic acid
| InChIKey | PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Nicotinic acid manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile valeronitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Nicotinic acid 98%View Details
Nicotinic acid 98%View Details -
 Nicotinic Acid CAS 59-67-6View Details
Nicotinic Acid CAS 59-67-6View Details
59-67-6 -
 Nicotinic Acid (SQ) CAS 59-67-6View Details
Nicotinic Acid (SQ) CAS 59-67-6View Details
59-67-6 -
 Nicotinic Acid Powder, Grade Standard: USPView Details
Nicotinic Acid Powder, Grade Standard: USPView Details
59-67-6 -
 Vitamin B3, 5Kg BagView Details
Vitamin B3, 5Kg BagView Details
59-67-6 -
 96% Nicotinic Acid EP Impurity GView Details
96% Nicotinic Acid EP Impurity GView Details
494-52-0 -
 Nicotinic Acid Powder, 5Kg BagView Details
Nicotinic Acid Powder, 5Kg BagView Details
59-67-6 -
 Niacin API PowderView Details
Niacin API PowderView Details
59-67-6
