Linzagolix
- CAS NO.:935283-04-8
- Empirical Formula: C22H15F3N2O7S
- Molecular Weight: 508.42
- Update Date: 2025-10-29 15:43:00
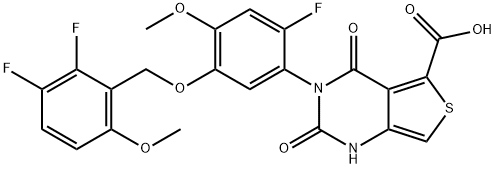
What is Linzagolix?
Absorption
Linzagolix is quickly absorbed following oral administration, with Cmax occurring approximately 2 hours following administration.
Toxicity
No data regarding overdosage with linzagolix are available. In the event of a suspected overdose, patients should be monitored closely. Institute symptomatic and supportive measures as clinically indicated.
Background
Linzagolix is a non-peptide, selective antagonist of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) receptor. It has been studied for the treatment of estrogen-dependent conditions such as uterine fibroids and endometriosis. It is similar to other GnRH receptor antagonists like cetrorelix, relugolix, and elagolix.
Uterine fibroids occur in >70% of women of reproductive age, and when symptomatic are associated with heavy menstrual bleeding, anemia, abdominal pain and pressure, bloating, increased urinary frequency, and reproductive dysfunction. As these fibroids are essentially estrogen-dependent phenomena, hormone therapies which suppress estrogen activity - including GnRH receptor antagonists like linzagolix - are thought to be beneficial by preventing intramyometrial growths in the endometrial glands.
Linzagolix was approved for use in the European Union in June 2022 for the management of symptoms caused by uterine fibroids.
Indications
Linzagolix is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe symptoms of uterine fibroids in adult women of reproductive age.
Pharmacokinetics
The administration of linzagolix results in a dose-dependent suppression of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone, and a subsequent decrease in circulating estradiol concentrations. The median serum estradiol levels across all studied patients was in the range of 20 to 60 pg/mL, and progesterone levels were maintained ≤3.1 ng/mL in 83% of women receiving the 200mg dose of linzagolix and 68% of women receiving the 100mg dose.
Linzagolix should be avoided in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) and in patients with moderate, severe, or end-stage renal disease (eGFR ≤59 mL/min). Some patients experienced a reduction in bone mineral density, varying from 3 to 8% - patients with an increased risk of fracture or osteoporosis should be monitored closely and should receive regular bone density scans to assess any on-going loss.
Metabolism
Up to seven metabolites of linzagolix have been quantified in patient plasma, urine, and feces, although plasma metabolites represent less than 10% of the total linzagolix-related exposure. Two primary demethylated metabolites - KP017 and KP046 - have been identified, with CYP2C9 primarily responsible for the formation of KP017 and CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP3A4 are primarily responsible for the formation of KP046. Unchanged parent drug is the predominant circulating component in human plasma and in the urine, and one of the major components in the feces.
Properties of Linzagolix
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO : 125 mg/mL (245.86 mM; Need ultrasonic) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to light brown |
Safety information for Linzagolix
Computed Descriptors for Linzagolix
Linzagolix manufacturer
LUPA PHARMACEUTICALS
New Products
Cyclopentane-1,2-dione 2,6-Dibromoaniline (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid 1-AMino-cyclobutaneMethanol HCl TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 3-Amino-3-(3-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 3-Amino-3-(4-methylphenyl)propionic acid 3-AMINO-3-(3-CHLORO-PHENYL)-PROPIONIC ACID Cefuroxime EP Impurity-A N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity 4 - fluoro- 2 - methoxy- 5 - nitroaniline 1-(2-amino-5-hydroxy phenyl)propan-1-one tert-butyl 4-(6-((7-cyclo pentyl -6-(dimethyl carbamoyl) -7H-pyrrolo [2,3-d]pyrimidin-2-yl) amino)pyridin-3-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylate 2-amino-5-nitrobenzonitrile (4-Fluoro-2-methoxy-5-nitro- phenyl)-[4- (1-methyl-1H- indol-3- yl)-pyrimidin-2-yl]- amine (3R,4R)-1-benzyl-N,4-dimethylpiperidin-3- amine 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanideYou may like
-
 Linzagolix Choline 98+View Details
Linzagolix Choline 98+View Details
935283-04-8 -
 10442-39-4 TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 98+View Details
10442-39-4 TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 98+View Details
10442-39-4 -
 3-Amino-3-(3-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
3-Amino-3-(3-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
117391-51-2 -
 3-Amino-3-(4-methylphenyl)propionic acid 68208-18-4 98+View Details
3-Amino-3-(4-methylphenyl)propionic acid 68208-18-4 98+View Details
68208-18-4 -
 10442-39-4 TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 98+View Details
10442-39-4 TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 98+View Details
10442-39-4 -
 68208-21-9 98+View Details
68208-21-9 98+View Details
68208-21-9 -
 3-Amino-3-(3-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
3-Amino-3-(3-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
117391-51-2 -
 3-Amino-3-(4-methylphenyl)propionic acid 68208-18-4 98+View Details
3-Amino-3-(4-methylphenyl)propionic acid 68208-18-4 98+View Details
68208-18-4
