DICUMAROL
Synonym(s):3,3ʹ-Methylenebis(4-hydroxycoumarin), Bishydroxycoumarin, Dicumarol;Bishydroxycoumarin;Dicoumarol;Dicoumarol - CAS 66-76-2 - Calbiochem;Dicumarol
- CAS NO.:66-76-2
- Empirical Formula: C19H12O6
- Molecular Weight: 336.3
- MDL number: MFCD00006857
- EINECS: 200-632-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-02-02 18:10:39
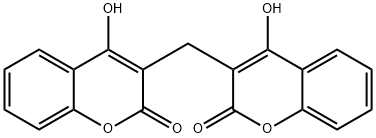
What is DICUMAROL?
Toxicity
LD50=233 mg/kg (orally in mice); LD50=250 mg/kg (orally in rats)
Description
The plants containing dicoumarol mainly include red carnation grass (Trifolium pratense L., hongchezhoucao), rotten alfalfa (Medicago sativa L., zimuxu), rotten white vanilla rhinoceros (Melilotus albus Desr., baixiangcaomuxi), and other plants in Leguminosae.
Description
Dicoumarol is a natural compound found in several leguminous plants, including spoiled sweet clover (Melilotus spp.), alfalfa (Medicago sativa), and red clover (Trifolium pratense). Biochemically, dicoumarol is a potent, competitive inhibitor of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), with a reported IC50 value of 2.6 nM in the absence of bovine serum albumin (BSA). In cell-based assays, dicoumarol demonstrates broad antiproliferative and signaling-modulatory activities. It inhibits the growth of various cancer cell lines, including pancreatic (MIA PaCa-2) and colon (HCT116) carcinoma cells, with IC50 values of 52 μM and 19 μM, respectively. Furthermore, it interferes with key cellular signaling pathways by inhibiting stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK) and suppressing the activation of NF-κB and JNK, which contributes to its antiproliferative effects.
Chemical properties
white fine crystalline powder
Physical properties
Appearance: white or milky white crystalline powder, slightly fragran; Solubility: not dissolved in water, ethanol, and ether, slightly dissolved in chloroform, dissolved in alkali solution; Melting point: 287–293?°C.?It can be bluer or with purple fluorescence in the ultraviolet light.
History
In 1940, Karl Paul Link, a fertile scientist from the University of Wisconsin in the
United States, first isolated the anticoagulant substance from the moldy alfalfa
(Melilotus) and determined its structure. It is a kind of dicoumaroloid substance,
combined by two molecules of coumarin substances. Since this material was found
in the first few years, it has been used as a rodenticide .
In 1979, Conrad et?al. reacted p-nitrobenzene ketone with 4-hydroxycoumarin to
obtain vinegar coumarin, which is basically the same as warfarin in anticoagulant,
but its metabolites also have anticoagulant effect, so the duration of anticoagulation
is longer than warfarin.
The Uses of DICUMAROL
Dicoumarol is a naturally occurring coumarin derivative that functions as a vitamin K antagonist. It is clinically employed as an anticoagulant for the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic disorders, including thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, and thromboembolism. It is also used prophylactically to prevent thrombus formation in the postoperative period.
Indications
For decreasing blood clotting. Often used along with heparin for treatment of deep vein thrombosis.
Background
Dicoumarol is an oral anticoagulant agent that works by interfering with the metabolism of vitamin K. In addition to its clinical use, it is also used in biochemical experiments as an inhibitor of reductases.
What are the applications of Application
Dicoumarol is an inhibitor of reductase
Definition
ChEBI: A hydroxycoumarin that is methane in which two hydrogens have each been substituted by a 4-hydroxycoumarin-3-yl group.
Indications
Intravascular thromboembolic diseases include postoperative or postoperative thrombotic phlebitis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, and atrial fibrillation caused by embolism.
General Description
Dicumarol, 3,3'-methylenebis[4-hydroxycoumarin],is a white or creamy white crystalline powderwith a faint, pleasant odor and a slightly bitter taste. It ispractically insoluble in water or alcohol, slightly soluble inchloroform, and dissolved readily by solutions of fixed alkalies.The effects after administration require 12 to 72 hours todevelop and persist for 24 to 96 hours after discontinuance.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Prototype of the 4-hydroxycoumarin class of anticoagulants, which act as vitamin K antagonists, preventing formation of prothrombin. There are many reports that dicumarol also inhibits NADPH:quinone oxidoreductase (NQO(1)). In one, it inhibited NQO(1) in a pancreatic cancer cell line, causing increased formation of superoxide and inhibiting cell growth.
Pharmacokinetics
Dicumarol is an coumarin-like compound found in sweet clover. It is used as an oral anticoagulant and acts by inhibiting the hepatic synthesis of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors (prothrombin and factors VII, IX, and X).
Pharmacokinetics
Dicoumarol is not completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, often is associated with gastrointestinal discomfort, and is very rarely used clinically. Today, the only coumarin used in the United States is warfarin, but phenprocoumon and acenocomumarol are used in Europe.
Pharmacology
Dicoumarin is an oral anticoagulant drug and is invalid in?vitro . Dicoumarin is a coumarin derivative, and its common mechanism is to inhibit synthesis of the coagulation factor in the liver. The structure of dicoumarin is similar to that of vitamin K and is an antagonist or a competitive inhibitor of vitamin K.?It binds to the vitamin K epoxide reductase in the liver, inhibits the conversion of vitamin K from epoxide to hydroquinone, and inhibits the recycling of vitamin K, resulting in that the glutamate side chain of vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors II, VII, IX, and X cannot be carboxylated by γ-carboxy glutamate groups, affecting the binding of coagulation factor with calcium ion, and thereby inhibiting coagulation, reducing platelet adhesion, and prolonging thrombosis time . Dicoumarol drugs have no direct confrontation with synthesized prothrombin and coagulation factor, so it is ineffective in?vitro. After withdrawal of dicoumarin, prothrombin and coagulation factors II, IV, IX, and X gradually restore to a certain level, and hence the anticoagulant effect disappear, so its efficacy can be maintained for a long time .
Clinical Use
Dicoumarol is utilized either as a monotherapy or as an adjunct to heparin for the prophylaxis and treatment of intravascular clotting disorders. Its clinical indications include postoperative thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism, acute embolic and thrombotic peripheral artery occlusion, and recurrent idiopathic thrombophlebitis. While it does not affect existing thrombi, it is administered to prevent further clot propagation and embolization, which is particularly relevant in conditions like acute coronary thrombosis. It has also been used to prevent the progression of gangrene following frostbite. Treatment is initiated and monitored based on the patient's prothrombin time. The typical oral dosage ranges from 25 to 200 mg, administered as capsules or tablets, with subsequent doses adjusted to maintain a target prothrombin time of approximately 30 seconds. In the event of hemorrhage, treatment involves the administration of menadione sodium bisulfite (a form of vitamin K) and, if necessary, a blood transfusion.
Side Effects
The most serious adverse reaction of warfarin is bleeding, which can be against by vitamin K, and if necessary, fresh plasma or whole blood can be injected into the body to confront bleeding .
Synthesis
Dicoumarol, 3,3??-methylene-bis(4-hydroxycoumarin) (24.1.8), is synthesized from 4-hydroxycoumarine (24.1.7), which is in turn synthesized from salicylic acid methyl ester by cyclization to a chromone derivative using sodium or sodium methoxide; or from o-oxyacetophenone by reacting it with diethylcarbonate in the presence of sodium ethoxide. Condensation of the resulting 4-hydroxycoumarin with formaldehyde as a phenol component gives dicoumarol.

Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of DICUMAROL
| Melting point: | 290-292 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 392.79°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2864 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4450 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | DMSO:3.06(Max Conc. mg/mL);9.1(Max Conc. mM) DMSO:PBS (pH 7.2) (1:1):0.5(Max Conc. mg/mL);1.49(Max Conc. mM) DMF:1.25(Max Conc. mg/mL);3.72(Max Conc. mM) Water:50.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);148.68(Max Conc. mM) |
| form | Fine Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 4.20±1.00(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in aqueous alkaline solutions, organic bases, 0.1 N NaOH (15 mg/ml), Pyridine (50 mg/ml), chloroform (slightly soluble), and benzene (slightly soluble). Insoluble in water, and alcohols. |
| Merck | 14,3090 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2H-1-Benzopyran-2-one, 3,3'-methylenebis[4-hydroxy- (66-76-2) |
Safety information for DICUMAROL
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for DICUMAROL
New Products
N,O-Dimethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Imatinib Impurity Brivaracetam Racemic Acid Balcofen S- isomer/(S)-Baclofen Lansoprazole S-Isomer R,S,S-diketopiperazine (EP & USP)/Lisinopril EP Impurity D Vildagliptin N-Nitroso-L-Proline Methyl Ester 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile 4-Fluorothiophenol (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 4-Bromo BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![4-HYDROXY-3-[(4-HYDROXY-2-OXO-2H-CHROMEN-3-YL)(2-HYDROXYPHENYL)METHYL]-2H-CHROMEN-2-ONE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure5/GIF/CB0355209.gif)
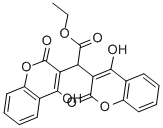
![2H-1-BENZOPYRAN-2-ONE, 3,3'-[(2,3,4-TRIMETHOXYPHENYL)METHYLENE]BIS[4-HYDROXY]-](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/215118-76-6.gif)

You may like
-
 Dicumarol 98% (HPLC) CAS 66-76-2View Details
Dicumarol 98% (HPLC) CAS 66-76-2View Details
66-76-2 -
 Dicoumarol CAS 66-76-2View Details
Dicoumarol CAS 66-76-2View Details
66-76-2 -
 Dicumarol 98% CAS 66-76-2View Details
Dicumarol 98% CAS 66-76-2View Details
66-76-2 -
 Dicoumarol CAS 66-76-2View Details
Dicoumarol CAS 66-76-2View Details
66-76-2 -
 3,3′-Methylene-bis(4-hydroxycoumarin) CAS 66-76-2View Details
3,3′-Methylene-bis(4-hydroxycoumarin) CAS 66-76-2View Details
66-76-2 -
 Bendamustine deschloroethyl acid ethyl ester 2517968-40-8 NLT 95%View Details
Bendamustine deschloroethyl acid ethyl ester 2517968-40-8 NLT 95%View Details
2517968-40-8 -
 Acebutolol EP Impurity K NLT 95%View Details
Acebutolol EP Impurity K NLT 95%View Details
74143-33-2 -
 90717-17-2 Ketamine Impurity-C NLT 95%View Details
90717-17-2 Ketamine Impurity-C NLT 95%View Details
90717-17-2
