D-GALACTOSAMINE
- CAS NO.:7535-00-4
- Empirical Formula: C6H13NO5
- Molecular Weight: 179.17
- MDL number: MFCD01941613
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-08-28 13:53:27
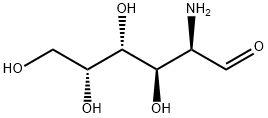
What is D-GALACTOSAMINE?
Description
Galactosamine is a model hepatotoxicant, induces hepatitis
characterized by neutrophilic infiltration, and kills the animal
by fulminant hepatic failure. Galactosamine, an amino derivative
of sugar galactose, has been used as a model hepatotoxicant
since the first reports of hepatotoxicity in late 1970s by
Keppler and associates. Galactosamine-induced hepatitis has
been a model of choice to study various aspects of liver disease,
including mechanisms of toxicant-induced apoptosis and
necrosis, liver tissue repair, neutrophil infiltration and transmigration,
and the role of endotoxin or lipopolysaccharide
(LPS) in initiating liver injury.
Humans and animals synthesize galactosamine in the body.
Galactosamine (a type of hexosamine) is formed when an
amino group replaces one of the hydroxy groups of a sixcarbon
sugar, or hexose. The human body utilizes uridine
diphosphate (UDP)-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine or glucosamine as
a precursor to synthesize this compound, and is most often
found in the form N-acetyl-D-galactosamine (often referred to
as N-acetylgalactosamine). Most importantly, galactosamine is
a constituent of hyaluronic acid, a powerful water-binding
agent. Many different types of tissues in human body contain
hyaluronic acid, which acts as a lubricating agent in the synovial
fluid of joints and in connective tissues. Hyaluronic acid
also acts as a lubricating agent in the vitreous humor of the
eyeball. Hyaluronic acid has considerable medicinal value; it is
often used in wound healing, burn dressings, osteoarthritis
treatment, cataract or corneal transplantation surgery, and
various types of plastic surgeries.
Definition
ChEBI: The pyranose form of D-galactosamine.
Toxicity evaluation
Galactosamine induces liver injury by interfering with the uridine pool in the cell, which is essential for RNA and protein synthesis. Galactosamine ismetabolized via the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, which leads to the generation of uridine derivatives of galactosamine. The two enzymes of the Leloir pathway, galactokinase and UDP-galactose uridyltransferase, convert galactosamine into galactosamine-1-phosphate and UDP-galactosamine, respectively,due to their lowsubstrate specificity.UDPgalactosamine blocks the final enzyme in Leloir pathway, the UDP-galactose-40 epimerase, resulting in the accumulation of UDP-galactosamine in the cells. This results in the depletion of uridine triphosphate (UTP), UDP, uridine monophosphate (UMP), and the sugar derivative of uridine such as UDP-glucose and UDP-galactose essential for RNA and protein synthesis. Orotate, a precursor of the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway, has been used as an antidote to galactosamine toxicity.
Properties of D-GALACTOSAMINE
| Melting point: | 185 °C |
| Boiling point: | 532.5±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.491±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | under inert gas (nitrogen or Argon) at 2–8 °C |
| pka | 11.21±0.45(Predicted) |
Safety information for D-GALACTOSAMINE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for D-GALACTOSAMINE
New Products
4-Iodo-3,5-dimethylbenzonitrile 2-fluoro-4-iodoaniline 2-(3-Methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)acetic acid (as potassium salt) 6,6'-methylenebis(9-methyl-3-((2-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-carbazol-4(9H)-one) 3-Bromo-2-fluorobenzoic acid Quinuclidine-4-carbonitrile N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate N,O-Dimethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Bupropian related compound F Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 1,4-bis(methylsulfonyl)butane 4-Cyano-N-Methacryloyl-3-Trifluoromethyl Aniline 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzeneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




![GALACTOSAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE, D-, [1-14C]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB1474082.gif)
![ACETYL-D-GALACTOSAMINE, N-[GALACTOSAMINE-1-3H]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB2411075.gif)
You may like
-
![6,6'-bis(difluoromethoxy)-2,2'-bis((3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methylsulfinyl)-1H,1'H-5,5'-bibenzo[d]imidazole 98%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 6,6'-bis(difluoromethoxy)-2,2'-bis((3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methylsulfinyl)-1H,1'H-5,5'-bibenzo[d]imidazole 98%View Details
6,6'-bis(difluoromethoxy)-2,2'-bis((3,4-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methylsulfinyl)-1H,1'H-5,5'-bibenzo[d]imidazole 98%View Details
2115779-15-0 -
 4-bromo-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid 98%View Details
4-bromo-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid 98%View Details
13745-17-0 -
 230971-72-9 (1-((2'-(2-((1-((2'-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl)-2-butyl-4-chloro-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl)-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl)-2-butyl-4-chloro-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methanol 98%View Details
230971-72-9 (1-((2'-(2-((1-((2'-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl)-2-butyl-4-chloro-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl)-2H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl)-2-butyl-4-chloro-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methanol 98%View Details
230971-72-9 -
 1941177-45-2 98%View Details
1941177-45-2 98%View Details
1941177-45-2 -
 Isopropyl amine Hydrochloride 99%View Details
Isopropyl amine Hydrochloride 99%View Details
15572-56-2 -
 19501-58-7 99%View Details
19501-58-7 99%View Details
19501-58-7 -
 Cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxylic acid 99%View Details
Cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxylic acid 99%View Details
598-10-7 -
 230971-71-8 (1-((2'-(1-((1-((2'-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl)-2-butyl-4-chloro-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl)-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl)-2-butyl-4-chloro-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methanol 98%View Details
230971-71-8 (1-((2'-(1-((1-((2'-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl)-2-butyl-4-chloro-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl)-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl)methyl)-2-butyl-4-chloro-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methanol 98%View Details
230971-71-8
