Cholecystokinin
Synonym(s):CCK;Cholecystokinin;RICK;RIP2;CARD3
- CAS NO.:9011-97-6
- Empirical Formula: C166H261N51O52S4
- Molecular Weight: 0
- MDL number: MFCD00131790
- Update Date: 2026-01-13 11:26:51
What is Cholecystokinin?
Toxicity
Ld 50 in rats : 2730 mg/kg (oral) .
Cholecystokinin has been associated with increased anxiety and panic attacks .
Description
Cholecystokinin is the most widespread and abundant peptide in the brain, with only the mature cerebellum possibly devoid of representation. Interest in this peptide also stems from its potency, prominent colocalization with dopamine, nonsynaptic associations influencing neuronal excitability and cerebral blood flow, and putative links to several neuropsychiatric disorders (Rehfeld 1992a, 1992b).
Indications
For use as a diagnostic aid for evaluation of gallbladder disorders. It is also used in conjunction with secretin in pancreatic insufficiency .
Background
Cholecystokinin ( also known as CCK or CCK-PZ) is a peptide hormone of the gastrointestinal system which is responsible for stimulating the digestion of fat and protein. Cholecystokinin, previously called pancreozymin, is synthesized and secreted by enteroendocrine cells in the duodenum (the first portion of the small intestine) and leads to the release of bile and digestive enzymes. CCK also acts as an appetite suppressant and has been studied for weight management regimens .
Normally, it is an endogenous hormone but is available commercially for diagnostic processes and replacement in pancreatic insufficiency . in the octapeptide form.
Cholecystokinin is one of the first gastrointestinal hormones discovered, identified more than 90 years ago due to its ability to stimulate gallbladder contraction in 1928. Soon after, it was recognized to be identical to the factor responsible for stimulating pancreatic exocrine secretion in 1943 . This hormone has also been shown to have positive effects on enteric smooth muscle contraction and on nerve activity at multiple locations in the peripheral and central nervous system. In addition to its roles in promoting smooth muscle cell contraction/exocrine cell secretion, CCK promotes cell growth, energy production, gene expression and protein synthesis, processes that have profound for drug development . This drug has also been investigated for possible antipsychotic properties, owing to its effect on CCK receptors in the brain .
Recent studies have suggested that cholecystokinin also plays a major role in inducing drug tolerance to opioids such as morphine and heroin, and is partially implicated in experiences of pain hypersensitivity during opioid withdrawal .
General Description
Receptor interacting serine/threonine kinase 2 (RIPK2) or RICK is a serine/threonine kinase. It contains a kinase domain at the amino-terminal, an intermediate domain and a caspase activation and recruitment domain (CARD) at the carboxy-terminal. The gene encoding RIPK2 is localized on human chromosome 8q21.3.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Receptor interacting serine/threonine kinase 2 (RIPK2) or RICK is activated during innate immune responses and acts as a scaffold for downstream effectors. It functions in nuclear factor-κB (NFκB) activation pathways. The protein also has roles in toll-like receptor (TLR)-signaling pathways and in the production of inflammatory cytokines.
Pharmacokinetics
Cholecystokinin (CCK) plays an imperative role in facilitating digestion within the small intestine. The activation of the CCK1 receptor by CCK has demonstrated to be responsible for a wide variety of important physiologic functions, including the stimulation of gallbladder, contraction and exocrine pancreatic enzyme secretion, delay of gastric emptying, relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi, inhibition of gastric acid secretion, and induction of satiety . Cholecystokinin is also produced by neurons in the enteric nervous system and is found to be widely distributed in the brain . An interesting function of CCK is the role it plays in stimulating the CCK receptor and subsequently regulating food consumption, which may prove to be a highly useful treatment for obesity . Exogenous administration CCK has been widely studied .
Diseases resulting from excessive or deficient secretion of cholecystokinin are rare. Cholecystokinin deficiency has been described in humans as part of autoimmune polyglandular syndrome, characterized as a malabsorption syndrome clinically similar to pancreatic exocrine insufficiency. Additionally, there is increasing evidence that alterations in expression of cholecystokinin or its receptor within the brain may possibly play a role in the pathogenesis of various types of anxiety disorders and schizophrenia .
Foodstuffs flowing into the small intestine are mostly made up of large macromolecules (proteins, polysaccharides, and triglyceride) that require digestion into small molecules (amino acids, monosaccharides, fatty acids) in order to be absorbed. Digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile salts from the liver (which are stored in the gallbladder) are necessary for digestion. Cholecystokinin is the primary stimulus for the release of pancreatic enzymes and bile secretion into the small intestine. Additionally, cholecystokinin, induces contraction of the gallbladder muscle, resulting in the reduction of gallbladder size and evacuation of bile .
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of Cholecystokinin
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| form | buffered aqueous glycerol solution |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for Cholecystokinin
Computed Descriptors for Cholecystokinin
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 RIPK2 (1-299), active, GST tagged human CASView Details
RIPK2 (1-299), active, GST tagged human CASView Details -
 2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 -
 1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) -
 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
27472-21-5 -
 Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
7252-83-7 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 -
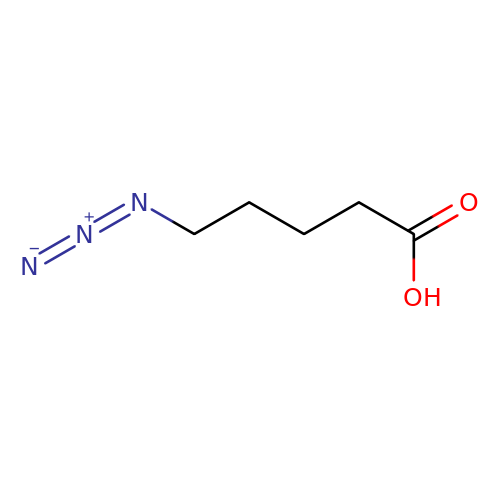 5-azidovalericacidView Details
5-azidovalericacidView Details
79583-98-5
