Calcium carbonate
Synonym(s):Calcii carbonas;Calcium carbonate;Carbonic Acid Calcium Salt;Carbonic Acid Calcium Salt, Calcium Carbonate
- CAS NO.:471-34-1
- Empirical Formula: CCaO3
- Molecular Weight: 100.0869
- MDL number: MFCD00010906
- EINECS: 207-439-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-15 13:03:24
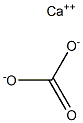
What is Calcium carbonate?
Absorption
Maximal absorption occurs at doses of 500 mg or less taken with food. Oral bioavailability depends on intestinal pH, the presence of food and dosage.
Description
Calcium carbonate is an inorganic salt primarily used to manage and treat low calcium conditions, GERD, CKD, and other indicated conditions. Calcium carbonate is classified as a calcium supplement, antacid, and phosphate binder.

Chemical properties
Calcium carbonate occurs as an odorless and tasteless white powder or crystals. It exists in two forms: hexagonal calcite and orthorhombic aragonite. Calcite decomposes upon heating at 825°C, while aragonite melts at 1339°C (102.5 atm). Density: calcite 2.71 g/cm3, aragonite 2.83 g/cm3; insoluble in water (15 mg/L at 25°C); Ksp 4.8 x 10–9; soluble in dilute mineral acids.
Physical properties
Calcium carbonate is a naturally occurring compound found in living organisms and throughout the Earth's crust. Its molecular formula is CaCO3, with a molecular weight of 100.0924 g/mol. It appears as a white powder or crystals that is soluble in acid but insoluble in water. It occurs in various mineral forms: calcite, aragonite, and vaterite. Calcite is the most common calcium carbonate mineral, while vaterite is very rare. CaCO3 is commonly found in the shells of many marine organisms (such as snails and conchs), birds, and oyster pearls. It occurs naturally in various forms of limestone, such as marble, chalk, and coral. Calcium carbonate, or precipitated chalk, has excellent absorption properties. It provides a matte finish and moderate coverage. However, excessive use of this material can result in an unpleasant dry, powdery feel and should be avoided.
Occurrence
Calcium carbonate occurs in nature as limestone in various forms, such as marble, chalk, and coral. It is probably the most widely-used raw material in the chemical industry. It has numerous applications, primarily to produce cement, mortars, plasters, refractories, and glass as building materials. It also is used to produce quicklime, hydrated lime and a number of calcium compounds. It is produced either as powdered or precipitated calcium carbonate. The latter consists of finer particles of greater purity and more uniform size. They also have many important commercial applications. Various grades of precipitated calcium carbonate are used in several products, such as textiles, papers, paints, plastics, adhesives, sealants, and cosmetics.
The Uses of Calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is the most widely used raw material in the chemical industry.
(1) It is mainly used in the production of building materials such as cement, mortar, plaster, refractories and glass.
(2) It is used in the production of quicklime, slaked lime and various calcium compounds.
(3) It is widely used as a filler and coating pigment in papermaking to whiten paper. It can replace more expensive fluorescent whitening agents in paper and as a filler to replace more expensive wood pulp fibers; it also helps to control the pH value in the alkaline range.
(4) It is used in the production of plastics; it is used in the production of polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), thermosetting polyesters and polyolefins. It can be used to replace more expensive resins.
(5) It is used as a filler in baking powder, a calcium fortifier, a mild buffer in dough, a source of calcium ions in dry mix desserts, and a neutralizer in antacids.
(6) It is used as an additive in paints and coatings for a wide range of applications including particle size distribution, opacity control, weather resistance, pH control and corrosion protection.
(7) It can be used to buffer acidic soils; to mitigate the effects of acid precipitation on water bodies; and to desulfurize gases in scrubbers to reduce sulfur emissions from air pollution sources.
(8) It is used to neutralize gold toners and as a fine abrasive added to water and alcohol for cleaning glass plates before applying photographic adhesive.
Background
Calcium carbonate is an inorganic salt used as an antacid. It is a basic compound that acts by neutralizing hydrochloric acid in gastric secretions. Subsequent increases in pH may inhibit the action of pepsin. An increase in bicarbonate ions and prostaglandins may also confer cytoprotective effects. Calcium carbonate may also be used as a nutritional supplement or to treat hypocalcemia.
Indications
Calcium carbonate is indicated for conditions with low serum calcium, such as osteoporosis, osteomalacia, hypothyroidism, hypoparathyroidism, pseudohypoparathyroidism, DiGeorge syndrome, renal insufficiency, pancreatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, Fanconi syndrome, pregnancy, nursing mothers, postmenopausal women, and when using certain medications (e.g., rifampin, plicamycin). For relief of heartburn and acid indigestion. May also be used as a nutritional supplement or to treat hypocalcemia.
Production Methods
Calcium carbonate is obtained from natural limestone deposits. The purified compound, known as precipitated calcium carbonate, is synthesized from limestone. Limestone is calcined to calcium oxide and carbon dioxide in a kiln. The products are recombined after purification. Calcium oxide is hydrated with water to give a slurry called milk of lime, which is then carbonated by bubbling CO2 through it. The reactions involved in the process are as follows:
CaCO3 CaO + CO2
CaO + H2O Ca(OH)2
Ca(OH)2+ CO2→CaCO3+ H2O
The crystal sizes required for various commercial applications may be controlled by temperature, pH, concentrations, and mixing rate.
Calcium carbonate also may be precipitated by mixing solutions of calcium chloride and sodium carbonate.
Definition
calcium carbonate: A white solid,CaCO3, which is only sparingly solublein water. Calcium carbonatedecomposes on heating to give calciumoxide (quicklime) and carbondioxide. It occurs naturally as theminerals calcite (rhombohedral; r.d.2.71) and aragonite (rhombic; r.d.2.93). Rocks containing calcium carbonatedissolve slowly in acidifiedrainwater (containing dissolved CO2)to cause temporary hardness. In thelaboratory, calcium carbonate is precipitatedfrom limewater by carbondioxide. Calcium carbonate is used inmaking lime (calcium oxide) and isthe main raw material for theSolvay process.
Preparation
Calcium carbonate may also be produced by mixing solutions of calcium chloride and sodium carbonate. In some cases, the presence of sodium is objectionable so that the ammonium carbonate salt is preferable.
What are the applications of Application
Calcium carbonate is used as a very mild abrasive for hand polishing nickel, gold, silver, or plated ware, buttons, and similar materials.
Reactions
Calcium carbonate decomposes to calcium oxide and CO2 on heating. Treatment with dilute mineral acids produces corresponding calcium salts with liberation of CO2:
CaCO3+ 2HCl →CaCl2+ H2O + CO2
In the presence of CO2 it dissolves in water with the formation of bicarbonate:
CaCO3+ H2O + CO2→Ca2++ 2HCO3 ¯
It is reduced to calcium carbide when heated with coke or anthracite in an electric furnace:
2CaCO3+ 5C→(high temperature)→2CaC2+ 3CO2
brand name
Cal-Sup (3M Pharmaceuticals); Children’s Mylanta Upset Stomach Relief (Johnson & Johnson-Merck Consumer); Chooz (Schering- Plough HealthCare); Mylanta Soothing Lozenges (Johnson & Johnson-Merck Consumer).
General Description
Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) is a naturally found material in chalk, limestone, and marble. It is composed of three elements which include carbon, oxygen, and calcium. It is formed by reacting carbon dioxide with slaked or burnt lime. It can be used for a variety of applications ranging from industrial, food to agriculture.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Pharmaceutical Applications
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) can be found in clinical applications such as antacids, but not that an excessive intake can be hazardous.
A variety of calcium salts are used for clinical application, including calcium carbonate, calcium chloride,
calcium phosphate, calcium lactate, calcium aspartate and calcium gluconate. Calcium carbonate is the most
common and least expensive calcium supplement. It can be difficult to digest and may cause gas in some
people because of the reaction of stomach HCl with the carbonate and the subsequent production of CO2.
Calcium carbonate is recommended to be taken with food, and the absorption rate in the intestine depends
on the pH levels. Taking magnesium salts with it can help prevent constipation. Calcium carbonate consists
of 40% Ca2+, which means that 1000 mg of the salt contains around 400 mg of Ca2+. Often, labels will only
indicate the amount of Ca2+ present in each tablet and not the amount of calcium carbonate.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Calcium carbonate is a naturally occurring compound that reduces T4 absorption and enhancess serum thyrotropin levels. It also precludes osteoporosis induced by thyrotropin-suppressive doses of levothyroxine in postmenopausal women. Additionally, it reduces diarrhea in individuals with protease inhibitor-induced HIV-infection.
Pharmacokinetics
Gastric-peptic disease occurs as a result of an imbalance between protective factors, such as mucus, bicarbonate, and prostaglandin secretion, and aggressive factors, such as hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). Antacids work by restoring acid-base balance, attenuating the pepsin activity and increasing bicarbonate and prostaglandin secretion. The acid-neutralizing capacity of calcium carbonate is 58 mEq/15 ml. When used as a nutritional supplement, calcium carbonate acts by directly increasing calcium stores within the body.
Safety
Calcium carbonate is mainly used in oral pharmaceutical formulations
and is generally regarded as a nontoxic material. However,
calcium carbonate administered orally may cause constipation and
flatulence. Consumption of large quantities (4–60 g daily) may also
result in hypercalcemia or renal impairment. Therapeutically, oral
doses of up to about 1.5 g are employed as an antacid. In the
treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic renal
failure, oral daily doses of 2.5–17 g have been used. Calcium
carbonate may interfere with the absorption of other drugs from the
gastrointestinal tract if administered concomitantly.
LD50 (rat, oral): 6.45 g/kg
Potential Exposure
PrimaryIrritant (monocarbonate). Calcium carbonate is used as asource of lime, as a neutralizing agent, in manufacturing ofrubber, plastics, paint and coatings, sealants, paper, dentifrices, ceramics, putty, polishes and cleaners, insecticides,inks and cosmetics, whitewash, Portland cement, antacids,in analytical chemistry, and others.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Can impair absorption of some drugs, e.g. iron,
ciprofloxacin.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Metabolism
Under the influence of gastric acid, any residual carbonate will be converted to carbon dioxide and water. Any unbound calcium not involved in the binding of phosphate will be variable and may be absorbed. Calcium is absorbed mainly from the small intestine by active transport and passive diffusion. About one-third of ingested calcium is absorbed although this can vary depending upon dietary factors and the state of the small intestine. 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol (calcitriol), a metabolite of vitamin D, enhances the active phase of absorption. Excess calcium is mainly excreted renally. Unabsorbed calcium is eliminated in the faeces, together with that secreted in the bile and pancreatic juice. Minor amounts are lost in the sweat, skin, hair, and nails.
Storage
Calcium carbonate is stable and should be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry place.
Shipping
Scoop up and place in suitable container.Discard with regular trash.
Structure and conformation
The space lattice of CaCO3 belongs to the triagonal system, and the sodium nitric acid structure has a space group of D63d. It isarhombohedron crystal, with a basis comprising two molecules, and it has a lattice constant of a=0.636 nm, a=46°6'. Ca1 positions (1/4, 1/4, 1/4), Ca2 (3/4, 3/4, 3/4), C3 (0, 0, 0) and C4 (1/2, 1/2, 1/2), andCtakes the middle of Ca–Ca. The O atom positions the corner of the triangle, the plane of which is perpendicular to the optical axis, Ca–C–Ca–. This includes C and O3, as C4 shift position by 60° with the O3 of C3. The behavior of CO 2K 3 is different for light oscillating perpendicularly to the optical axis (O-ray) and light oscillating parallel to the axis (E-ray), which is the origin of the uniaxial negative crystal.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with acids and ammonium salts.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (buccal chewing gum, oral capsules and tablets; otic solutions; respiratory inhalation solutions). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Calcium carbonate
| Melting point: | 825 °C |
| Boiling point: | 800 °C |
| Density | 2.93 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | 1.6583 |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | 5 M HCl: 0.1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | random crystals |
| color | White-beige to slightly beige-gray |
| Specific Gravity | 2.93 |
| PH Range | 8 |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 9.91(1 mM solution);9.91(10 mM solution);9.91(100 mM solution); |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.09 λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.06 |
| Merck | 14,1657 |
| BRN | 8008338 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 8.54 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH: TWA 10 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 6.1(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with acids, fluorine, ammonium salts, alum. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 471-34-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Calcium carbonate (471-34-1) |
Safety information for Calcium carbonate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Calcium carbonate
| InChIKey | VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
Calcium carbonate manufacturer
Remark Chemical Enterprises
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile valeronitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Calcium Carbonate Precipitated 98%View Details
Calcium Carbonate Precipitated 98%View Details -
 CALCIUM CARBONATE LIGHT 99%View Details
CALCIUM CARBONATE LIGHT 99%View Details -
 Calcium Carbonate 99%View Details
Calcium Carbonate 99%View Details -
 Activated Calcium Carbonate 99%View Details
Activated Calcium Carbonate 99%View Details -
 Limestone 99%View Details
Limestone 99%View Details -
 Calcium Carbonate 99%View Details
Calcium Carbonate 99%View Details -
 Calcium carbonate 99%View Details
Calcium carbonate 99%View Details -
 Calcium carbonate 98%View Details
Calcium carbonate 98%View Details
