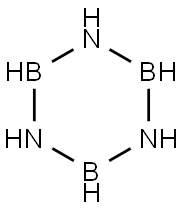
BORAZINE
- CAS NO.:6569-51-3
- Empirical Formula: B3H6N3
- Molecular Weight: 80.5
- MDL number: MFCD00047325
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-06 14:31:44
What is BORAZINE?
Description
Borazole (borazine) is a colourless liquid with an aromatic smell. With water, it decomposes to form boric acid, ammonia, and hydrogen. The reaction product of boron and ammonia at high temperatures is also known as inorganic benzene.
Description
Borazine, or?s-triazaborane, is an inorganic compound isoelectronic with benzene that exhibits some aromatic character. It was first described in 1926 by Alfred Stock and Erich Pohland in their ninth paper in a series on boron–hydrogen compounds. Borazine may be useful in hydrogen storage applications.
Chemical properties
inorganic analog of benzene; colorless liquid; preparation: heating equimolar mixture of ammonia and BH3 at 250°C–300°C for 30min [MER06] [HAW93]
The Uses of BORAZINE
Borazine can be useful in the study of structural stability and the low-lying singlet and triplet states of BN - n -acenes, n = 1-7.
What are the applications of Application
Films that were deposited thermally from borazine vapor were found to be too reactive to be suitable for fabricating masks for X-ray lithography. However, films containing predominately cubic boron nitride, CBN [10043-11-5], were deposited using ions extracted from a borazine plasma via an ion beam. Very hard, adherent films were deposited on ceramic, glass, stainless steel, etc. An obvious practical application is the hardening of tool surfaces to markedly extend their life. A thermally deposited film of hexagonal BN [10043-11-5], from B3N3Cl6 [19087-72-0] at 900 ℃, protected SiO2 tubes from halide corrosion. A copolymer between 2,4,6-tributylborazine [7325-06-6] and an unsaturated N,N'-hexamethylenebiscarboxamide was useful for hardening epoxy resins. Trichloroborazine was used as part of a catalyst mix for the polymerization of propene. Flexible BN coatings on copper or copperbase alloys were formed from gaseous 2,4,6- trichloroborazine. The films were stable to 700℃ in air.
General Description
Borazine can be prepared by
copyrolysis of NaBH4 and NH4Cl in a highboiling glyme, by reduction of trichloroborazine, or by pyrolysis of
ammonia borane in diglyme.
A large body of literature exists on the preparation and chemistry of symmetrically and unsymmetrically substituted borazines. B-Substituted trihaloborazines, readily prepared
from BX3 and NH4Cl, react with Grignard reagents to give symmetrical trialkyl- or triarylborazines. Symmetrically substituted N-trialkylor N-triarylborazines are readily prepared from
LiBH4 and RNH3Cl, or by pyrolysis of
RNH2BH3.
Borazine is thermally stable at 0 C, but decomposes slowly at ambient temperature. Borazine hydrolyzes slowly, but trihaloborazines
hydrolyze quite rapidly. Hydrogen halides form
1 : 3 adducts with borazine, which decompose to
trihaloborazines on warming.
Properties of BORAZINE
| Melting point: | -58° |
| Boiling point: | 55°C |
| Density | d40 0.824; d457 0.898 |
| refractive index | nD20 1.3821 |
| storage temp. | below 5° C |
| solubility | reacts with H2O |
| pka | -2.66±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | colorless liquid |
| color | colorless |
| Specific Gravity | 0.81 |
| Water Solubility | hydrolyzes, evolving boron hydrides [HAW93] |
| Hydrolytic Sensitivity | 9: reacts extremely rapidly with atmospheric moisture - may be pyrophoric - glove box or sealed system required |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 6569-51-3 |
Safety information for BORAZINE
Computed Descriptors for BORAZINE
New Products
1-Chloro-4-Methyl-2-Nitrobenzene 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile Benzethonium Chloride Trenbolone Enanthate Prednisolone acetate Cisplatin Chlorodehydromethyl testosterone Ketoconazole 2,4-Difluoro-5-nitrobenzoicacid Methyl 2-oxo-2,3-dihydrobenzo[d]oxazole-7-carboxylate 3-Hydroxy-4-nitrobromobenzene 4-(2-Aminoethyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromoen-2-one 2-Ethyl-1,4-diaminobenzene 2-Ethylhexyl 4-aminobenzoate Fmoc-N-Me-Ala-OH Boc-His-OH Fmoc-N-Me-Ile-OH tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Ethyl Resin Indole Methyl ResinRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
![tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate 98%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate 98%View Details
tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate 98%View Details
2640989-54-2 -
 Indole Ethyl Resin 98%View Details
Indole Ethyl Resin 98%View Details -
 Indole Methyl Resin 98%View Details
Indole Methyl Resin 98%View Details -
 N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) 99%View Details
N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) 99%View Details
538-75-0 -
 Boc-L-Ala-OH >98%View Details
Boc-L-Ala-OH >98%View Details
15761-38-3 -
 2-Methoxyphenothiazine >98%View Details
2-Methoxyphenothiazine >98%View Details
1771-18-2 -
![4-Chloropyrrolo[2,3-d]-pyrimidine 98%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 4-Chloropyrrolo[2,3-d]-pyrimidine 98%View Details
4-Chloropyrrolo[2,3-d]-pyrimidine 98%View Details
3680-69-1 -
 31972-52-8 >95%View Details
31972-52-8 >95%View Details
31972-52-8
