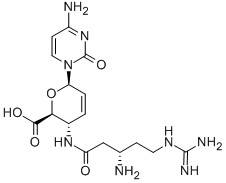
BLASTICIDIN S
- CAS NO.:2079-00-7
- Empirical Formula: C17H26N8O5
- Molecular Weight: 422.44
- MDL number: MFCD02091639
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-13 11:16:58
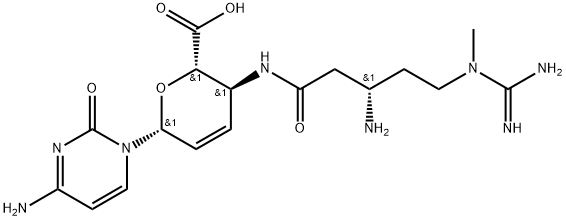
What is BLASTICIDIN S?
Description
Nucleoside antibiotic produced by Streptomyces griseochromogenes (1). Biosynthesized from cytosine, glucose, arginine, and methionine (2).
The Uses of BLASTICIDIN S
Blasticidin S is a nucleoside produced by several species of Streptomyces, first reported in the late 1950s. Blasticidin S is an antifungal agent with particularly potent activity against the rice pathogen, Piricularia oryzae, for which it was used commercially for some time in Japan. Blasticidin S inhibits protein synthesis and is active against bacteria, tumour cell lines and nematodes. More recently, blasticidin S has been used as a marker for strain manipulations. Blasticidin S provided by BioAustralis is presented as the free base to avoid problems associated with the use of the hydrochloride.
The Uses of BLASTICIDIN S
Blasticidin-S is used for the control of rice blast (PyricuZuria oryzae) by foliar application.
Definition
ChEBI: A blasticidin that is an antibiotic obtained from Streptomyces griseochromogene.
Production Methods
Blasticidin S is produced by Streptomyces griseochromogenes, and has a wide range of antimicrobial activity (4). This antibiotic was utilized in the Far East beginning in 1961 against the rice blast pathogen Pyricularia oryzae, with effective control achieved at rates of 10–40 ppm (4).
General Description
Blasticidin S was found in the culture broth of Streptomyces griseochromogenes by Yonehara et al. of the University of Tokyo in 1958. It has a nucleoside-analogue structure and shows strong activity against phytopathogenic fungi, especially Pericularia oryzae, the pathogen causing rice blast. Blasticidin S has been used to protect rice plants.
Pharmacology
Inhibits protein synthesis both in eukaryotes and in prokaryotes (5,6). Interacts with ribosomal RNA in large subunit, interfering with the transpeptidation step. Inhibits cell-free protein synthesis in P. oryzae and Escherichia coli.
Metabolic pathway
Several blasticidin S-resistant microorganisms are found to produce blasticidin S deaminase which catalyzes the hydrolytic deamination of the cytosine moiety in blasticidin S to give a non-toxic deaminohydroxy derivative.
Metabolism
3H-blasticidin S administered to mice was excreted in the urine and feces within 24 h. Cytomycin and cytosin were identified as the main metabolites in and on rice plants, respectively (7). In soil, DT50 < 5 d. Metabolized to nontoxic deaminohydroxy blasticidin S by Aspergillus sp. and resistant Bacillus cereus. Novel deaminase and coding genes, BSD and bsr, were isolated as selectable marker genes for genetic engineering (8).
Degradation
Blasticidin-S is obtained as white needle crystals which are very soluble in water. The compound is stable in the pH range 5-7 but it is unstable under alkaline conditions. It is readily degraded by sunlight when on the surface of rice plants with the main degradation product being cytosine (2) (Yamaguchi et al., 1972) as shown in Scheme 1.
Toxicity evaluation
Acute oral LD50 for male rats: 56.8, female rats: 55.9, male mice: 51.9, and female mice: 60.1 mg/kg. Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >500 mg/kg. Eye: severe irritation.
Properties of BLASTICIDIN S
| Melting point: | 235°C |
| Boiling point: | 539.06°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D11 +108.4° (water) |
| Density | 1.1690 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | Low |
| refractive index | 1.6910 (estimate) |
| solubility | DMF: soluble; DMSO: soluble; Ethanol: soluble; Methanol: soluble; Water: soluble |
| form | A solid |
| pka | 2.4 (carboxyl), 4.6,8.0 and>12.5 (three bases) |
| Water Solubility | >30 g l-1(20 °C) |
| Stability: | Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Blasticidin S (2079-00-7) |
Safety information for BLASTICIDIN S
Computed Descriptors for BLASTICIDIN S
New Products
Cyclopentane-1,2-dione 2,6-Dibromoaniline (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid 1-AMino-cyclobutaneMethanol HCl TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 3-Amino-3-(3-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 3-Amino-3-(4-methylphenyl)propionic acid 3-AMINO-3-(3-CHLORO-PHENYL)-PROPIONIC ACID Cefuroxime EP Impurity-A N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity 4 - fluoro- 2 - methoxy- 5 - nitroaniline 1-(2-amino-5-hydroxy phenyl)propan-1-one tert-butyl 4-(6-((7-cyclo pentyl -6-(dimethyl carbamoyl) -7H-pyrrolo [2,3-d]pyrimidin-2-yl) amino)pyridin-3-yl) piperazine-1-carboxylate 2-amino-5-nitrobenzonitrile (4-Fluoro-2-methoxy-5-nitro- phenyl)-[4- (1-methyl-1H- indol-3- yl)-pyrimidin-2-yl]- amine (3R,4R)-1-benzyl-N,4-dimethylpiperidin-3- amine 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 10442-39-4 TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 98+View Details
10442-39-4 TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 98+View Details
10442-39-4 -
 68208-21-9 98+View Details
68208-21-9 98+View Details
68208-21-9 -
 3-Amino-3-(3-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
3-Amino-3-(3-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
117391-51-2 -
 3-Amino-3-(4-methylphenyl)propionic acid 68208-18-4 98+View Details
3-Amino-3-(4-methylphenyl)propionic acid 68208-18-4 98+View Details
68208-18-4 -
 10442-39-4 TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 98+View Details
10442-39-4 TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 98+View Details
10442-39-4 -
 68208-21-9 98+View Details
68208-21-9 98+View Details
68208-21-9 -
 3-Amino-3-(3-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
3-Amino-3-(3-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
117391-51-2 -
 3-Amino-3-(4-methylphenyl)propionic acid 68208-18-4 98+View Details
3-Amino-3-(4-methylphenyl)propionic acid 68208-18-4 98+View Details
68208-18-4
