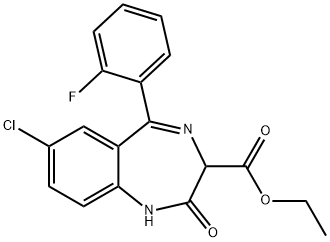
7-chloro-2,3-dihydro-2,2-dihydroxy-5-phenyl-1H-1,4-benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid
- CAS NO.:23887-31-2
- Empirical Formula: C16H11ClN2O3
- Molecular Weight: 314.72
- EINECS: 245-926-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2022-12-21 16:56:50
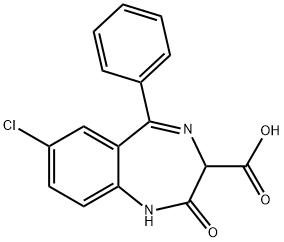
What is 7-chloro-2,3-dihydro-2,2-dihydroxy-5-phenyl-1H-1,4-benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid?
Absorption
Clorazepate is a prodrug for nordiazepam, and this conversion occurs almost entirely before entering systemic circulation. Therefore, the pharmacokinetic parameters of clorazepate are based on nordiazepam concentrations. In healthy volunteers given a 20 mg oral dose of clorazepate, nordiazepam had a peak plasma level of 356 ng/mL, which was reached approximately 0.9 h after the administration of clorazepate. The plasma levels of nordiazepam increase proportionally with the clorazepate dose and show moderate accumulation with repeated administration. The oral bioavailability of clorazepate is 91%.
Toxicity
The overdosage of benzodiazepines, such as clorazepate, is characterized by central nervous system (CNS) depression ranging from drowsiness to coma. In mild to moderate cases, symptoms can include drowsiness, confusion, dysarthria, lethargy, hypnotic state, diminished reflexes, ataxia, and hypotonia. Paradoxical or disinhibitory reactions are rare but may occur. In severe cases, patients experiencing a benzodiazepine overdose may develop respiratory depression and coma. Overdosage of benzodiazepines in combination with other CNS depressants may be fatal. General supportive measures, including intravenous fluids and airway management, should be used to manage a benzodiazepine overdose. The use of flumazenil for the complete or partial reversal of benzodiazepine-sedative effects during an overdose can lead to withdrawal and adverse reactions. Refer to the product label of clorazepate for additional overdosage management recommendations.
In rats, the oral LD50 of clorazepate is 1320 mg/kg, and in monkeys, it exceeds 1600 mg/kg. In animal reproduction studies, clorazepate did not affect fertility indices or the reproductive capacity of adult animals.
Background
Clorazepic acid (clorazepate) is a water-soluble benzodiazepine with muscle-relaxant and anticonvulsant actions effective in the treatment of anxiety. Following administration, clorazepate is rapidly converted to nordiazepam (N-desmethyldiazepam), its active metabolite, before entering systemic circulation. Similar to other benzodiazepines, the active metabolite of clorazepate enhances the binding of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) to the GABA type A (GABA-A) receptor, which promotes channel opening and neuronal hyperpolarization. The concomitant use of clorazepate and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Also, the use of clorazepate exposes users to users to the risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction, and its continued use may lead to significant physical dependence. In September 2020, a black box warning describing these risks was included on the product label of benzodiazepines as per FDA regulation. Clorazepate and its active metabolite, nordiazepam, are present in breast milk.
Indications
Clorazepate is indicated for the management of anxiety disorders or the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety. It is also used as adjunctive therapy in the management of partial seizures and for the symptomatic relief of acute alcohol withdrawal.
Definition
ChEBI: A 1,4-benzodiazepinone in which the oxo group is at position 2, and which is substituted at positions 3, 5, and 7 by carboxy, phenyl and chloro groups, respectively.
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacologically, clorazepate has the characteristics of benzodiazepines. Studies in healthy men have shown that clorazepate has depressant effects on the central nervous system. Since orally administered clorazepate dipotassium is rapidly decarboxylated to form nordiazepam, there is essentially no circulating parent drug. The use of benzodiazepines, including clorazepate, exposes users to abuse, misuse, and addiction risks, which can lead to overdose and death. Patients treated with clorazepate may also develop suicidal behavior and ideation, and the use of clorazepate may cause interference with psychomotor performance. The concomitant use of clorazepate with opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death.
Metabolism
Clorazepate is metabolized in the liver and excreted mainly through urine. Following oral administration, clorazepate is decarboxylated by the gastric acid of the stomach before absorption. The primary metabolite, nordiazepam, is further metabolized by hydroxylation. The major urinary metabolite is conjugated oxazepam (3-hydroxynordiazepam), and smaller amounts of conjugated p-hydroxynordiazepam and nordiazepam are also found in the urine.
Properties of 7-chloro-2,3-dihydro-2,2-dihydroxy-5-phenyl-1H-1,4-benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid
| Boiling point: | 563.9±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.46±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 0.80±0.40(Predicted) |
Safety information for 7-chloro-2,3-dihydro-2,2-dihydroxy-5-phenyl-1H-1,4-benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid
Computed Descriptors for 7-chloro-2,3-dihydro-2,2-dihydroxy-5-phenyl-1H-1,4-benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid
New Products
DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate Amlodipine EP Impurity-C Budesonide Impurity-K/Budesonide 21-Acetate (Epimers) Gabapentine Impurity 72 Bicalutamide Impurity-B Betahistine EP Impurity C Carbamazepine EP Impurity G 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 3-Hydroxypropionitrile 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![3-[(4-chlorophenyl)amino]propanoic acid](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/21617-19-6.gif)


You may like
-
 Bendamustine deschloroethyl acid ethyl ester NLT 95%View Details
Bendamustine deschloroethyl acid ethyl ester NLT 95%View Details
2517968-40-8 -
 110-59-8 valeronitrile 99%View Details
110-59-8 valeronitrile 99%View Details
110-59-8 -
 93-17-4 99%View Details
93-17-4 99%View Details
93-17-4 -
 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
26451-08-1 -
 3-Hydroxypropionitrile 109-78-4 99%View Details
3-Hydroxypropionitrile 109-78-4 99%View Details
109-78-4 -
 1529-41-5 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 99%View Details
1529-41-5 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 99%View Details
1529-41-5 -
 2856-63-5 99%View Details
2856-63-5 99%View Details
2856-63-5 -
 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
27472-21-5
