1,2-Diphenylhydrazine
Synonym(s):N,N′-Diphenylhydrazine;N,N′-Bianiline;Hydrazobenzene;NSC 3510
- CAS NO.:122-66-7
- Empirical Formula: C12H12N2
- Molecular Weight: 184.24
- MDL number: MFCD00003012
- EINECS: 204-563-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-13 11:19:13
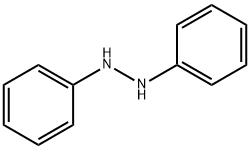
What is 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine?
Description
Diphenylhydrazine is a man-made chemical that occurs in two isomeric forms: 1,1-diphenylhydrazine and 1,2-diphenylhdrazine. Diphenylhydrazine is produced by the reduction of nitrobenzene. Little or no information is available for 1,1-diphenylhydrazine. Most toxicological and use data pertain to 1,2-diphenylhydrazine.
Chemical properties
yellow crystalline powder
The Uses of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine
Previously, 1,2-diphenylhydrazine was used for producing benzidine that was used in the synthesis of benzidine-based dyes. However, these dyes are no longer produced in the United States. The primary use of 1,2-diphenylhydrazine is in the production of the anti-inflammatory agent phenylbutazone and sulfinpyrazone, a uricosuric agent.
The Uses of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine
Impurity in the production of Phenylbutazone (P319570). Hydrazobenzene is a metabolic intermediate of Azobenzene Carcinogenic
The Uses of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine
Formerly used as a starting material in the production of benzidine for dyes; production of certain drugs.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 36, p. 1529, 1988 DOI: 10.1248/cpb.36.1529
Tetrahedron, 32, p. 2157, 1976 DOI: 10.1016/0040-4020(76)85128-9
General Description
Orange powder or a bright orange crystalline solid.
Air & Water Reactions
1,2-Diphenylhydrazine oxidizes in air. 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine decomposes in acid solutions. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
1,2-Diphenylhydrazine is a mild reducing agent. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, acid chlorides and acid anhydrides. Interaction with perchloryl fluoride in the presence of a dilutent below 32°F has caused separation of explosive solids. Is readily oxidized by nitric acid, silver nitrate or permanganate. Is reduced under alkaline conditions .
Health Hazard
1,2-Diphenylhydrazine is a liver toxin in rodents and appears to be carcinogenic in experimental animals.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine are not available; however, 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine is probably combustible.
Potential Exposure
Tumorigen,Mutagen. 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine (DPH) is a precursor inthe manufacture of benzidine, an intermediate in the production of dyes. 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine is used in the synthesis of phenylbutazone, a potent anti-inflammatory(antiarthritic) drug. Manufacturers of dyes and pharmaceuticals are subject to occupational exposure. Groups workingin the laboratory and forensic medicine may also be subjectto 1,2-diphenylhydrazine exposure.
First aid
Skin Contact: Flood all areas of body thathave contacted the substance with water. Do not wait toremove contaminated clothing; do it under the water stream.Use soap to help assure removal. Isolate contaminatedclothing when removed to prevent contact by others. EyeContact: Remove any contact lenses at once. Flush eyeswell with copious quantities of water or normal saline for atleast 2030 min. Seek medical attention. Inhalation: Leavecontaminated area immediately; breathe fresh air. Properrespiratory protection must be supplied to any rescuers. Ifcoughing, difficult breathing, or any other symptomsdevelop, seek medical attention at once, even if symptomsdevelop many hours after exposure. Ingestion: If convulsions are not present, give a glass or two of water or milk todilute the substance. Assure that the person’s airway isunobstructed and contact a hospital or poison center imm
Carcinogenicity
Hydrazobenzene is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Environmental Fate
Biological. When 5 and 10 mg/L of diphenylhydrazine was statically incubated in the dark at 25
°C with yeast extract and settled domestic wastewater inoculum, 80 and 72% biodegradation,
respectively, were observed after 7 d (Tabak et al., 1981).
Chemical/Physical. Wet oxidation of 1,2-diphenylhydrazine at 320 °C yielded formic and acetic
acids (Randall and Knopp, 1980). 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine will not hydrolyze (Kollig, 1993).
At influent concentrations of 1.0, 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001 mg/L, the GAC adsorption capacities
were 16,000, 160, 1.5, and 0.015 mg/g, respectively (Dobbs and Cohen, 1980).
Storage
Color Code—Green: General storage may be used.Prior to working with this chemical you should be trainedon its proper handling and storage. Store under nitrogenaway from oxidizers, strong acids, acid chlorides, acidanhydrides. A regulated, marked area should be establishedwhere this chemical is handled, used, or stored in compliance with OSHA Standard 1910.1045.
Shipping
The name of this material is not in the DOT listof materials for label and packaging standards. However,based on regulations, it may be classified as anEnvironmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s. Thischemical requires a shipping label of “CLASS 9.” It falls inHazard Class 9 and Packing Group III.[20,21]
Purification Methods
Crystallise hydrazobenzene from hot EtOH containing a little ammonium sulfide or H2SO3 (to prevent atmospheric oxidation), preferably under N2. Dry it in a vacuum desiccator, and store it in the dark or under N2. Alternatively, crystallise it from pet ether (b 60-100o) to constant absorption spectrum. It is almost colourless but in air it turns yellow, then red with the formation of azobenzene. The hydrochloride crystallises from EtOH and has m 163-164o(dec); however, hydrazobenzene readily rearranges to benzidine in the presence of acid. The picrate crystallises from *C6H6 and has m 123o(dec). [Beilstein 15 H 123.]
Toxicity evaluation
The mechanism of action of diphenylhydrazine is not known. It is possible that some toxic effects may be attributed to its major metabolites, aniline and azobenzene, both of which are known carcinogens. Results of metabolism studies reporting aniline, benzidine, hyroxybenzidines, and aminophenols as metabolites in rats following multiple routes of administration suggest that the diphenylhydrazine metabolism may be similar to that of azobenzene and aniline. It is also possible that conversion of 1,2-diphenylhydrazine to aniline in the gastrointestinal tract may occur due to intestinal microflora and via acid hydrolysis.
Incompatibilities
Not compatible with oxidizers, strongacids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, and mineral acidsforming benzidine. Store under nitrogen.
Properties of 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine
| Melting point: | 123-126 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 308.2°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1,158 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 2.6 x 10-5 mmHg at 25 °C (Mabey et al., 1982) |
| refractive index | 1.6266 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Soluble in ethanol (Weast, 1986). |
| form | neat |
| pka | 3.02±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | Colorless to pale yellow to orange crystals |
| Water Solubility | 221 mg/L at 25 °C (U.S. EPA, 1980a) |
| BRN | 639793 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 122-66-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Hydrazine, 1,2-diphenyl-(122-66-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine (122-66-7) |
Safety information for 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H350:Carcinogenicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for 1,2-Diphenylhydrazine
| InChIKey | YBQZXXMEJHZYMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
1,2-Diphenylhydrazine manufacturer
Clickchem Research LLP
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 122-66-7 N,N'-Diphenylhydrazine 98%View Details
122-66-7 N,N'-Diphenylhydrazine 98%View Details
122-66-7 -
 Hydrazobenzene CAS 122-66-7View Details
Hydrazobenzene CAS 122-66-7View Details
122-66-7 -
 Hydrazobenzene pure CAS 122-66-7View Details
Hydrazobenzene pure CAS 122-66-7View Details
122-66-7 -
 Hydrazobenzene CAS 122-66-7View Details
Hydrazobenzene CAS 122-66-7View Details
122-66-7 -
 Hydrazobenzene pure CAS 122-66-7View Details
Hydrazobenzene pure CAS 122-66-7View Details
122-66-7 -
 Hydrazobenzene CAS 122-66-7View Details
Hydrazobenzene CAS 122-66-7View Details
122-66-7 -
 HYDRAZOBENZENEView Details
HYDRAZOBENZENEView Details
122-66-7 -
 Hydrazobenzene (N N Diphenylhydrazine) CAS NO. 122-66-7View Details
Hydrazobenzene (N N Diphenylhydrazine) CAS NO. 122-66-7View Details
122-66-7
