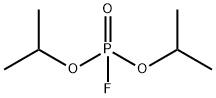
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Isofluorphate appears as oily liquid. Clear, colorless or faintly yellow liquid. This material is used as a research tool in neuroscience for its ability to inhibit cholinesterase (by phosphorylation) on an acute/sub-acute basis and to produce a delayed neuropathy. An insecticide. Used in Germany as a basis for "nerve gases". (EPA, 1998) |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Liquid |
| Odor | Very weak fruity odor |
| Boiling Point | 144 °F at 9 mmHg (EPA, 1998) |
| Melting Point | -116 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Solubility | 15400 mg/L (at 25 °C) |
| Density | 1.055 (EPA, 1998) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Vapor Density | 6.4 (Air= 1) |
| Vapor Pressure | 0.579 mmHg at 68 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| LogP | 1.17 |
| Stability/Shelf Life | ANHYDROUS CMPD OR OIL SOLUTIONS ARE STABLE IN GLASS CONTAINERS AT ROOM TEMPERATURES. |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /Fluoride and Phosporous Oxide/ |
| Refractive Index | Index of refraction: 1.3830 @ 25 °C/D |
| Kovats Retention Index | 926 927 929 |
| Other Experimental Properties | Forms hydrogen fluoride in presence of moisture; decomp in water @ pH about 2.5 |
| Chemical Classes | Pesticides -> Organophosphate Insecticides |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 184.15 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 1.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Exact Mass | 184.06645946 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 184.06645946 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 35.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 144 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Isofluorphate appears as oily liquid. Clear, colorless or faintly yellow liquid. This material is used as a research tool in neuroscience for its ability to inhibit cholinesterase (by phosphorylation) on an acute/sub-acute basis and to produce a delayed neuropathy. An insecticide. Used in Germany as a basis for "nerve gases". (EPA, 1998)