CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 209-211 °C |
| Solubility | 2.51e-01 g/L |
| LogP | 2.4 |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 291.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 2.4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 291.18344366 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 291.18344366 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 58.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 350 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
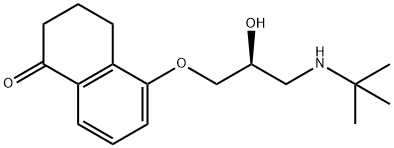
Levobunolol is a cyclic ketone that is 3,4-dihydronaphthalen-1-one substituted at position 5 by a 3-(tert-butylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy group (the S-enantiomer). A non-selective beta-adrenergic antagonist used (as its hydrochloride salt) for treatment of glaucoma. It has a role as an antiglaucoma drug and a beta-adrenergic antagonist. It is a propanolamine, a cyclic ketone and an aromatic ether. It is a conjugate acid of a levobunolol(1+). It derives from a hydride of a tetralin.