CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Dissociation Constants | 8.5 |
|---|---|
| Collision Cross Section | 232.9 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW, Method: calibrated with Waters Major Mix] |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 539.6 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | -7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 11 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 16 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 539.28025714 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 539.28025714 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 284 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 37 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 760 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 17 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
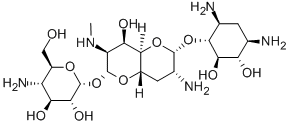
Apramycin is an aminoglycoside that is 2-deoxystreptamine that is substituted on the oxygen at position 4 by an (8R)-2-amino-8-O-(4-amino-4-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl)-2,3,7-trideoxy-7-(methylamino)-D-glycero-alpha-D-allo-octodialdo-1,5:8,4-dipyranos-1-yl) group. It has a role as an antimicrobial agent and an antibacterial drug. It is a 2-deoxystreptamine derivative, an organic heterobicyclic compound and an aminoglycoside.