CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Solubility | 0.008 mg/mL at 25°C (77°F ) |
|---|---|
| LogP | log Kow = 5.0 |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Vandetanib solid is found to be stable to both thermal and hydrolytic degradation but a small degree of degradation is observed under stressed photolytic conditions. In solution, vandetanib is degraded under acidic, oxidative and light stress conditions but it is stable under basic conditions. |
| Decomposition | Thermal decomposition may produce toxic gases such as carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 475.4 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 4.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 474.10667 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 474.10667 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 59.5 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 539 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
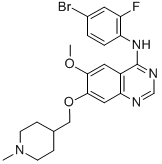
Vandetanib is a quinazoline that is 7-[(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)methoxy]quinazoline bearing additional methoxy and 4-bromo-2-fluorophenylamino substituents at positions 6 and 4 respectively. Used for the treatment of symptomatic or progressive medullary thyroid cancer in patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease. It has a role as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent. It is an aromatic ether, a secondary amine, a member of quinazolines, a member of piperidines, an organobromine compound and an organofluorine compound.