CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Melting Point | 193.5 °C |
|---|---|
| Dissociation Constants | 7.7 |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 454.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | -6.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 10 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 14 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Exact Mass | 454.22749329 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 454.22749329 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 262 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 593 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 14 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
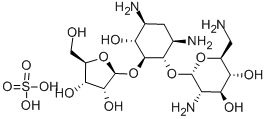
Ribostamycin is an amino cyclitol glycoside that is 4,6-diaminocyclohexane-1,2,3-triol having a 2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-alpha-D-glucosyl residue attached at position 1 and a beta-D-ribosyl residue attached at position 2. It is an antibiotic produced by Streptomyces ribosidificus (formerly S. thermoflavus). It has a role as a metabolite, an antimicrobial agent and an antibacterial drug. It is an amino cyclitol glycoside and an aminoglycoside antibiotic. It is a conjugate base of a ribostamycin(4+).