CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Solubility | 6.67e-03 g/L |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 416.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 4.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Exact Mass | 416.24369293 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 416.24369293 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 98.1 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 520 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
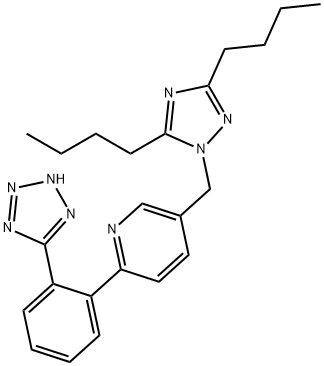
Forasartan is a member of the class of pyridines that is pyridine which is substituted at positions 2 and 5 by o-(tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl and (3,5-dibutyl-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl groups, respectively. It is a nonpeptide antagonist of angiotensin II, type 1 (AT1) receptors, used for the treatment of hypertension. It has a role as an angiotensin receptor antagonist and an antihypertensive agent. It is a member of tetrazoles, a member of pyridines, a member of triazoles and a member of benzenes.