VITAMINS
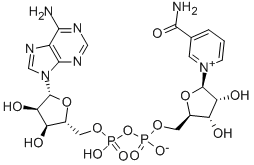
- Empirical Formula: C21H27N7Na2O14P2.xH2O
- Molecular Weight: 0
- MDL number: MFCD00284863
What is VITAMINS?
The Uses of VITAMINS
Organic compounds that are essential for normal body growth and maintenance. They are classified into two groups: fat-soluble ( A, D, E, and K) vitamins, and water-soluble vitamins ( B and C). Vitamins are measured in very low concentrations, such as 1–100 mg. Through biochemical action, they perform various functions in such processes as cell growth, normal digestion, manufacture of red blood cells, and absorption of calcium and phosphorus. Inadequate vitamin intake can be the result of food deficiency, increased vitamin requirements, and increased vitamin loss. The vitamins of determined importance include: A (retinol), B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B5 (pantothenic acid), B6 (pyridoxine), B12 (cyanocobalamin), C (ascorbic acid), D2 (calciferol), E (tocopherol), K, niacin, folic acid, and biotin.
Agricultural Uses
Vitamins are a class of organic substances required in
small amounts by living organisms to maintain normal
health.
Some well-identified vitamins are (a) vitamin A
(retinol), (b) vitamin B complex which are water-soluble
vitamins [for example, vitamin B1 (thiamin), B2
(riboflavin), B6 (pyridoxine) and B12 (cyanocobalamin)],
(c) vitamin C (ascorbic acid), (d) vitamin D, (found in the
liver and in fish oils), which is important for the
absorption of calcium and for the prevention of diseases
like rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults, (e)
vitamin E (tocopherol), (f) vitamin H (biotin), (g) vitamin
K, found mainly in green leaves, and essential in treating
blood-clotting, (h) vitamin M (folic acid), and (i) vitamin
P. Bioflavanoides are regarded as a vitamin in the USA.
Most B and C vitamins occur in plants, animals and
micro-organisms. The vitamin D group includes vitamin
D2 (calciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). The vitamin K
group includes K1, (phylloquinone) and K2
(menaquinone).
Animals cannot synthesize many vitamins and these
must, therefore, be supplied in their food through plants
and microbes. Vitamin A, D, E and K are fat-soluble and
are stored in fat bodies. Vitamins B and C are watersoluble
and cannot be stored, and have to be regularly
supplied through the diet.
All animals contain gut bacteria capable of producing
sufficient amount of B vitamins. The livestock are able to
produce adequate supplies of vitamin D in their coats and
skin, irradiated during the summer months.
Foods may contain vitamin precursors (called
provitamins) , and they change chemically in the body to
form actual vitamins. Many vitamins are destroyed by
light and heat, (e. g , , during cooking). When brown rice
is milled, it is deprived of about 80% of thiamin, 56% of
riboflavin, 65% of niacin, 60% of pantothenic acid and
55 % pyridoxine.
Many people depend on rice for a major part of
energy intake (almost 80 %). But highly polished rice is
deficient in B complex, which is subsequently made up
by the addition of thiamin, niacin and iron.
Vitamins and minerals reduce the incidence of
diseases like beriberi, pellagra, scurvy, etc. Milled rice
can be enriched by coating it with enriching ingredients.
Par boiling can be considered as a form of enrichment as
some vitamins and minerals are retained in the process.
Deficiencies of some vitamins can cause ill health. To
overcome these deficiencies in animals, livestock feed
must contain synthetic vitamin supplements, added in
balanced amounts according to the needs of the animals.
Vitamins function as coenzymes. Active parts of the
enzyme systems catalyze many anabolic and catabolic
reactions of living organisms, necessary for producing
energy, synthesizing tissue components, hormones and
chemical regulators, and detoxification and degradation
of waste products. Owing to their role in metabolism,
vitamins are generally concentrated in metabolically
most active tissues of animals and plants; for example, in
the liver or kidneys, and in seed germ.
Properties of VITAMINS
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
Safety information for VITAMINS
Computed Descriptors for VITAMINS
New Products
Mirtazapine Impurity C/Mirtazapine Lactam Impurity N,O-Dimethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile 4-Fluorothiophenol (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 4-Bromo BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Bendamustine deschloroethyl acid ethyl ester 2517968-40-8 NLT 95%View Details
Bendamustine deschloroethyl acid ethyl ester 2517968-40-8 NLT 95%View Details
2517968-40-8 -
 Acebutolol EP Impurity K NLT 95%View Details
Acebutolol EP Impurity K NLT 95%View Details
74143-33-2 -
 Clidinium Bromide Impurity NLT 95%View Details
Clidinium Bromide Impurity NLT 95%View Details
.6581-06-2 -
 192110-67-2 NLT 95%View Details
192110-67-2 NLT 95%View Details
192110-67-2 -
 Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity NLT 95%View Details
Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity NLT 95%View Details
59872-62-1 -
 90717-17-2 Ketamine Impurity-C NLT 95%View Details
90717-17-2 Ketamine Impurity-C NLT 95%View Details
90717-17-2 -
 .2005-04-1 N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A NLT 95%View Details
.2005-04-1 N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A NLT 95%View Details
.2005-04-1 -
 145773-22-1 Lantanoprost rc B NLT 95%View Details
145773-22-1 Lantanoprost rc B NLT 95%View Details
145773-22-1