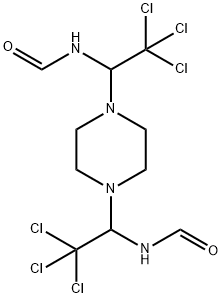
TRIFORINE
- CAS NO.:26644-46-2
- Empirical Formula: C10H14Cl6N4O2
- Molecular Weight: 434.96
- MDL number: MFCD00055521
- EINECS: 247-872-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-13 11:12:54
What is TRIFORINE?
Description
Triforine is a clear light yellow colour with an ethanol (alcohol) odour and a highly flammable liquid. It is used as a fungicide for the control of black spot, powdery mildew, and diseases of rust in roses, fruits, vegetables, cereals, and ornamentals. Application of triforine acts both as a preventative and a curative fungicide and is known to destroying diseases already in the plant and also preventing disease infestations. It is also used as a post-harvest control of brown rot on peaches, nectarines, apricots, cherries, and plums.
The Uses of TRIFORINE
Triforine is used to control powdery mildews on cereals, fruits, vines, hops, ornamentals, cucurbits and some vegetables, rusts on cereals, fruit, ornamentals and beans. It also controls Munilia spp. on stone fruit, Ascochyta blight on chrysanthemums, black spot on roses, scab on apples and fairy rings on turf. Triforine also suppresses tetranychid mite activity.
The Uses of TRIFORINE
food additive; fungicide; agricultural chemical.
The Uses of TRIFORINE
This pesticide is widely used in flower growing. Cross reactions are expected to diehlorvos.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of N-alkylpiperazines in which the two amino groups of piperazine are replaced by 1-formamido-2,2,2-trichloroethyl groups. A fungicide active against a range of diseases including powdery mildew, scab and rust.
General Description
Colorless crystals. Non corrosive. Used as a fungicide.
Reactivity Profile
A piperazine, trichloromethylformamide derivative. Decomposed in strong acid to trichloroacetaldehyde and piperazine salts, and in strongly alkaline media to chloroform and piperazine.
Hazard
Low toxicity by ingestion, inhalation, and skin contact. Human systemic effects.
Agricultural Uses
Fungicide: Triforine is a systemic fungicide with protectant, eridicant, and curative activity. It is locally systemic, is quickly absorbed by the plant and should be applied on or before an infection occurs. Triforine is used for control of black spot, brown rot, scab, petal blight, rust and other diseases on fruits such as apples, peaches, plumbs, nectarines, apricots, and strawberry; in hops, vegetables, cereals, and ornamentals such as roses and chrysanthemums. Triforine breaks down rapidly in the environment. Not approved for use in EU countries . Registered for use in the U.S.
Trade name
CELA50®; CW524®; DENARIN® FUNGINEX®; SAPROL®; TRIFORIN®; W524®
Contact allergens
This pesticide is widely used in flower growing. Cross- reactions are expected to dichlorvos.
Safety Profile
Low toxicity by ingestion, inhalation, and skin contact. Human systemic effects: change in taste function. When heated to decomposition emits toxic fumes of NOx and Cl-.
Metabolic pathway
Thermal reaction of triforine with several alcohols in a closed glass tube gives N-(1-alkoxy-2,2,2- trichloroethyl) formamides.
Degradation
Triforine (1) is stable up to 180°C. It decomposes in aqueous solution
when exposed to daylight or UV light. In strongly acid media, it is
decomposed to trichloroacetaldehyde and piperazine salts. In strongly
basic media, triforine decomposes to give chloroform and piperazine
(DT50 3.5 days at pH 5-7, 25 °C). From an unbuffered aqueous solution
stored for 13 weeks, four hydrolysis products of triforine, 5, 6, 7 and 3,
were isolated by preparative thin-layer chromatography. After 6 months
at room temperature in an unbuffered solution, 7 was the major product.
These products indicate that stepwise removal of substituents from the
nitrogen atoms of the ring occurred and the composition of the mixtures
produced by hydrolysis was shown to be pH- and time-dependent
(Scheme 1).
When solid triforine was irradiated with UV light (254 nm) for 1, 16
or 64 hours, analysis of the products showed that one side chain was
removed preferentially and the second was attacked more slowly.
Products 2, 3, 4 [N-(2,2-dichlorovinyl)formamide], 12 (probably formed
by reaction of 2 with chloral, a photoproduct) and 2,2,2-trichloroethane-
1,1-diol were identified and minor amounts of six other products were
detected by thin-layer chromatography. Compound 2 is probably the
major photolytic product. When triforine was irradiated in solution in
deionised water with a quartz high pressure lamp (maximum energy at
366 nm), 4 was isolated and identified as a product of photolysis but was
itself photolabile and could no longer be detected after 5 hours irradiation
(Darda et al., 1977).
Properties of TRIFORINE
| Melting point: | 155℃ (decomposition) |
| Boiling point: | 561.5±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.5269 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 8 x 10-2 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly) |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 9 mg l-1 (20 °C) |
| pka | 10.6 (base) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Merck | 13,9762 |
| BRN | 626358 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 26644-46-2 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Triforine (26644-46-2) |
Safety information for TRIFORINE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. |
Computed Descriptors for TRIFORINE
New Products
DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate N,O-Dimethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE Levothyroxine Impurity-F Montelukast EP Impurity-D/Montelukast USP Related Compound C Atorvastatin FXA Impurity/Atorvastatin Cyclic 6-Hydroxy Impurity Sodium Salt Isosulfan blue Keto N-Oxide Impurity Ivermectin Impurity F N-Nitroso des Methyl Tramadol/N-Nitroso-N-Desmethyl-Tramadol (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 1,4-bis(methylsulfonyl)butane 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene CSA (DL-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid) 2-Hydroxy-4-methylnicotinic acid 3-iodo-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine (2S)-1-((2S,3S)-3-(2-methylbutyl)-4-oxooxetan-2-yl)pentadecan-2-yl formylleucinate 1-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethane-1-sulfonyl chloride S-(1-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) ethanethioateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Triforin CAS 26644-46-2View Details
Triforin CAS 26644-46-2View Details
26644-46-2 -
 Triforin CAS 26644-46-2View Details
Triforin CAS 26644-46-2View Details
26644-46-2 -
 674783-97-2 98+View Details
674783-97-2 98+View Details
674783-97-2 -
 H-D-TRP(FOR)-OH HCL 98+View Details
H-D-TRP(FOR)-OH HCL 98+View Details
367453-01-8 -
 49830-37-7 98+View Details
49830-37-7 98+View Details
49830-37-7 -
 3-Amino-3-(4-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
3-Amino-3-(4-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
325-89-3 -
 1428243-26-8 98+View Details
1428243-26-8 98+View Details
1428243-26-8 -
 1-aminocyclopentane carbonitrile, HCl 98+View Details
1-aminocyclopentane carbonitrile, HCl 98+View Details
16195-83-8
