Tetrahydrofuran
Synonym(s):THF;Tetrahydrofuran;Oxolane;Butylene oxide;PTHF
- CAS NO.:109-99-9
- Empirical Formula: C4H8O
- Molecular Weight: 72.11
- MDL number: MFCD00005356
- EINECS: 203-726-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-13 11:24:20
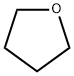
What is Tetrahydrofuran?
Description
Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a colorless, miscible, polar organic heterocyclic compound with a strong odor. THF is a versatile solvent and chemical intermediate used in a variety of industrial applications, including the manufacture of polymers, inks and coatings, as well as pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
Chemical properties
Tetrahydrofuran is a colorless, clear liquid with a strong ethereal odor and an odor threshold concentration of 2 ppm. Its density is less than that of water, its boiling point is 66°C (17°F), and its flash point is 6°F (17°C). Its vapor is heavier than air. It is highly flammable but relatively mildly toxic. Tetrahydrofuran may explode in contact with strong oxidants. It may polymerize in the presence of cationic initiators. Contact with lithium aluminum hydride, other lithium-aluminum alloys, or sodium or potassium hydroxide may be hazardous.
The Uses of Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran is a widely used industrial solvent. It is used as a solvent for resins, vinyls, and polymers; as a reaction medium in Grignard and metal hydride reactions; and in the synthesis of butyrolactone, succinic acid, and 1,4-butanediol diacetate. It is also used as a fumigant and in combination with other compounds. It is also used to stabilize fuel color and sludge formation.
Definition
ChEBI: A cyclic ether that is butane in which one hydrogen from each methyl group is substituted by an oxygen.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with an ethereal odor. Less dense than water.Flash point 6°F. Vapors are heavier than air.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Oxidizes readily in air to form unstable peroxides that may explode spontaneously [Bretherick, 1979 p.151-154, 164]. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Tetrahydrofuran reacts violently with oxidizing agents leading to fires and explosions [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980. p. 891]. Subject to peroxidation in the air. Peroxides or their products react exothermically with lithium aluminum hydride [MCA Guide for Safety 1973]. Thus, use as a solvent for lithium aluminum hydride has led to fires. Using potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide to dry impure Tetrahydrofuran that contains peroxides has resulted in explosions. A violent explosion occurred during the preparation of sodium aluminum hydride from sodium and aluminum in a medium of Tetrahydrofuran [Chem. Eng. News 39(40):57. 1961]. THF forms explosive products with 2-aminophenol [Lewis 3227].
Health Hazard
The toxicity of tetrahydrofuran is of loworder in animals and humans. The targetorgans are primarily the respiratory systemand central nervous system. It is an irritantto the upper respiratory tract and eyes.At high concentrations it exhibits anestheticproperties similar to those of many loweraliphatic ethers. Exposure to concentrationsabove 25,000 ppm in air can cause anesthesiain humans. Other effects noted were strongrespiratory stimulation and fall in bloodpressure (ACGIH 1986). Kidney and liverinjuries occurred in experimental animalsexposed to 3000 ppm for 8 hours/day for20 days (Lehman and Flury 1943). Inhalationof high concentrations of vapors or ingestionof the liquid also causes nausea, vomiting,and severe headache. The acute oraltoxicity is low; the LD50 value in rats is in therange of 2800 mg/kg. The inhalation LC50value in rats is 21,000 ppm/3 h.
Flammability and Explosibility
THF is extremely flammable (NFPA rating = 3), and its vapor can travel a
considerable distance to an ignition source and "flash back." A 5% solution of THF
in water is flammable. THF vapor forms explosive mixtures with air at
concentrations of 2 to 12% (by volume). Carbon dioxide or dry chemical
extinguishers should be used for THF fires.
THF can form shock- and heat-sensitive peroxides, which may explode on
concentration by distillation or evaporation. Always test samples of THF for the
presence of peroxides before distilling or allowing to evaporate. THF should never
be distilled to dryness.
Industrial uses
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), the saturated derivative of furan, when used as a solvent for high molecular weight polyvinyl chloride (PVC), vinyl chloride copolymers, and polyvinylidene chloride copolymers at ambient temperatures yields solutions of high solids content. Blends of THF and methyl ethyl ketone are often used for increased solvency in certain polymer compositions. Applications for THF polymer solutions include PVC top coatings of automotive upholstery, audio tape coatings of polyurethane/metal oxides on polyester tape, polyurethane coatings for fabric finishes, water-vapor barrier film coatings of PVC, and polyvinylidene chloride copolymers onto cellophane film. Tetrahydrofuran is an excellent solvent for many inks used for printing on PVC film and on PVC plastic articles. Polyvinyl chloride pipe welding cements are made by dissolving the resin in THF solvent. Other adhesive applications include cements for leather, plastic sheeting, and for molded plastic assemblies. Other uses of THF are as a chemical intermediate and as a complexing solvent for various inorganic, organometallic, and organic compounds. These THF complexes are important as Grignard reagents, catalysts for organic reactions, and in stereo-specific polymerizations. Tetrahydrofuran is the solvent of choice in many pharmaceutical reactions and applications. The excellent solvency of THF makes this solvent ideal for solvent cleaning of polymer manufacturing and processing equipment.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Mildly toxic by inhalation. Human systemic effects by inhalation: general anesthesia. Mutation data reported. Irritant to eyes and mucous membranes. Narcotic in high concentrations. Reported as causing injury to liver and kidneys. Flammable liquid. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flames, oxidizers. Explosive in the form of vapor when exposed to heat or flame. In common with ethers, unstabilized tetrahydrofuran forms thermally explosive peroxides on exposure to air. Stored THF must always be tested for peroxide prior to distdlation. Peroxides can be removed by treatment with strong ferrous sulfate solution made slightly acidic with sodium bisulfate. Caustic alkalies deplete the inhibitor in THF and may subsequently cause an explosive reaction. Explosive reaction with KOH, NaAlH2, NaOH, sodium tetrahydroaluminate. Reacts with 2-aminophenol + potassium dioxide to form an explosive product. Reacts with lithium tetrahydroaluminate or borane to form explosive hydrogen gas. Violent reaction with metal halides (e.g., hafnium tetrachloride, titanium tetrachloride, zirconium tetrachloride). Vigorous reaction with bromine, calcium hydride + heat. Can react with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use foam, dry chemical, COa. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See also 2TETRAHYDROFURYL HYDROPEROXIDE
Potential Exposure
The primary use of tetrahydrofuran is as a solvent to dissolve synthetic resins, particularly polyvinyl chloride and vinylidene chloride copolymers. It is also used to cast polyvinyl chloride films, to coat substrates with vinyl and vinylidene chloride; and to solubilize adhesives based on or containing polyvinyl chloride resins. A second large market for THF is as an electrolytic solvent in the Grignard reaction-based production of tetramethyl lead. THF is used as an intermediate in the production of polytetramethylene glycol.
Hazard
Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a very hazardous substance due primarily to its flammable and explosive properties. Toxicity is also of concern and must be considered in the safe handling and storage of THF. Irritation from dermal contact with THF warrants the wearing of gloves and safety glasses for protection during the routine handling of this substance.
Carcinogenicity
THF showed little evidence of mutagenic activity in a variety of in vitro and in vivo assays.
Source
Leaches from PVC cement used to join tubing (Wang and Bricker, 1979)
Applications
Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a cyclic ether with two primary industrial uses. The major use is as a monomer in the production of polytetramethylene ether glycol (PTMEG), a component of cast and thermoplastic urethane elastomers, polyurethane stretch fibers (spandex), and high-performance copolyester-polyether elastomers (COPE). A smaller amount of THF is used as a solvent in polyvinyl chloride (PVC) cements, pharmaceuticals, and coatings; precision magnetic tape manufacture; and as a reaction solvent.
Producttion
In 1956, W. W. Gilbert and B. W. Howk at Du Pont patented the catalytic hydrogenation of maleic anhydride to produce THF. Du Pont later patented a process for hydrogenating furan to THF. Today the predominant THF manufacturing process is the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 1,4-butanediol. More than two dozen US patents on this process were issued between 1975 and 2007.
Storage
THF should be used only in areas free of ignition sources, and quantities greater than 1 liter should be stored in tightly sealed metal containers in areas separate from oxidizers. Containers of THF should be dated when opened and tested periodically for the presence of peroxides.
Purification Methods
It is obtained commercially by catalytic hydrogenation of furan from pentosan-containing agricultural residues. It was purified by refluxing with, and distilling from LiAlH4 which removes water, peroxides, inhibitors and other impurities [Jaeger et al. J Am Chem Soc 101 717 1979]. Peroxides can also be removed by passage through a column of activated alumina, or by treatment with aqueous ferrous sulfate and sodium bisulfate, followed by solid KOH. In both cases, the solvent is then dried and fractionally distilled from sodium. Lithium wire or vigorously stirred molten potassium have also been used for this purpose. CaH2 has also been used as a drying agent. Several methods are available for obtaining the solvent almost anhydrous. Ware [J Am Chem Soc 83 1296 1961] dried it vigorously with sodium-potassium alloy until a characteristic blue colour was evident in the solvent at Dry-ice/cellosolve temperatures. The solvent is kept in contact with the alloy until distilled for use. Worsfold and Bywater [J Chem Soc 5234 1960], after refluxing and distilling from P2O5 and KOH, in turn, refluxed the solvent with sodium-potassium alloy and fluorenone until the green colour of the disodium salt of fluorenone was well established. [Alternatively, instead of fluorenone, benzophenone, which forms a blue ketyl, can be used.] The tetrahydrofuran was then fractionally distilled, degassed and stored above CaH2. p-Cresol or hydroquinone inhibit peroxide formation. The method described by Coetzee and Chang [Pure Appl Chem 57 633 1985] for 1,4-dioxane also applies here. Distillations should always be done in the presence of a reducing agent, e.g. FeSO4. [Beilstein 17 H 10, 17 I 5, 17 II 15, 17 III/IV 24, 17/1 V 27.] It irritates the skin, eyes and mucous membranes, and the vapour should never be inhaled. It is HIGHLY FLAMMABLE, and the necessary precautions should be taken. Rapid purification: Purification as for diethyl ether.
Toxicity evaluation
The principal target organs in rodents receiving repeated exposures to THF are the central nervous system (CNS), kidney, and liver. The CNS effects caused by THF are thought to be mediated via the THF metabolites tetrahydro-2-furanone and 4-hydroxybutanoic acid. This is consistent with the CNS effects associated with these metabolites as well as the higher narcotic potency of THF in mice than in comparably exposed rats and the shorter half-life of THF in the presence of mouse versus rat hepatic microsomes. In contrast to the CNS effects, the male rat kidney tumors and female mouse liver tumors appear to be induced by the parent compound, not a metabolite. Lifetime exposures of rodents to tetrahydro-2-furanone, 4-hydroxybutanoic acid, and sodium succinate have not resulted in treatment-related carcinogenic effects, and a mechanistic study demonstrated that hepatocellular proliferation in female mice exposed to THF is actually enhanced by CYP450 inhibition, not decreased as one would predict if proliferation is mediated by a THF metabolite. The THF database has been reviewed against potential mode of action (MoA) candidates including direct DNA reactivity, cytotoxicity followed by regenerative cell proliferation, excessive accumulation of alpha 2u-globulin, exacerbation of rat chronic progressive nephropathy (CPN), and nuclear receptor (e.g., constitutive androstane receptor) activation leading to enzyme induction and enhanced cell proliferation. While the tumorigenic MoAs have not been identified, exacerbation of CPN (rat kidney) and nuclear receptor activation (mouse liver) are currently the more favored. BothMoAs are thought to involve nongenotoxic (i.e., threshold) events. CPN has no known counterpart in humans.
Incompatibilities
Forms thermally explosive peroxides in air on standing (in absence of inhibitors). Peroxides can be detonated by heating, friction, or impact. Reacts violently with strong oxidizers, strong bases and some metal halides. Attacks some forms of plastics, rubber and coatings.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Concentrated waste containing peroxides-perforation of a container of the waste from a safe distance followed by open burning.
Properties of Tetrahydrofuran
| Melting point: | -108°C |
| Boiling point: | 66 °C |
| Density | 0.887 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor density | 2.5 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <0.01 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | water: soluble |
| form | Liquid |
| appearance | Colorless liquid |
| color | <10(APHA) |
| Specific Gravity | 0.89 |
| PH Range | 7 |
| Relative polarity | 0.207 |
| PH | 7-8 (200g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | Ethereal, detectable at 2 to 50 ppm |
| explosive limit | 1.5-12.4%(V) |
| Water Solubility | miscible |
| FreezingPoint | -108℃ |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive & Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 245 nm Amax: ≤0.26 λ: 275 nm Amax: ≤0.046 λ: 315 μm Amax: ≤0.0044 |
| Merck | 14,9211 |
| BRN | 102391 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.54 (static headspace-GC, Welke et al., 1998) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 200 ppm (590 mg/m3) (ACGIH,
MSHA, and OSHA); STEL 250 ppm
(ACGIH); IDLH 20,000 ppm (NIOSH). |
| Dielectric constant | 11.6(-70℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with halogens, strong oxidizing agents, strong reducing agents, strong bases, oxygen. May generate explosive peroxides in storage if in contact with air. Highly flammable. Store at room temperature under nitrogen. Hazardous polymerisation may occur. Light sensitive. May contain 2,6-di-tertbutyl-4-methylphenol (BHT) as a s |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 109-99-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 119) 2019 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Furan, tetrahydro-(109-99-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tetrahydrofuran (109-99-9) |
Safety information for Tetrahydrofuran
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H302:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H351:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Tetrahydrofuran
| InChIKey | WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Tetrahydrofuran manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Rifaximin EP Impurity-G N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile 4-Fluorothiophenol (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 4-Bromo BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Tetrahydrofuran 99%View Details
Tetrahydrofuran 99%View Details -
 Tetrahydrofuran 98%View Details
Tetrahydrofuran 98%View Details -
 Tetrahydrofuran 98%View Details
Tetrahydrofuran 98%View Details -
 Tetrahydrofuran 99%View Details
Tetrahydrofuran 99%View Details -
 THF Tetrahydrofuran CASView Details
THF Tetrahydrofuran CASView Details -
 THF Tetrahydrofuran CASView Details
THF Tetrahydrofuran CASView Details -
 Tetrahydrofuran CASView Details
Tetrahydrofuran CASView Details -
 Tetra Hydro Furan. CASView Details
Tetra Hydro Furan. CASView Details
