Sevelamer
- CAS NO.:52757-95-6
- Empirical Formula: C6H12ClNO
- Molecular Weight: 149.62
- MDL number: MFCD09260188
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-21 10:59:17
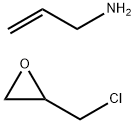
What is Sevelamer?
Absorption
Not absorbed following oral administration, however no absorption studies have been performed in patients with renal disease. Sevelamer may bind to dietary phosphates and prevent its gastrointestinal absorption when sevelamer is administered in combination with food.
Toxicity
Sevelamer has been given to normal healthy volunteers in doses of up to 14 grams per day for eight days with no adverse effects. Sevelamer has been given in average doses up to 13 grams per day to hemodialysis patients. There are no reported overdosages of sevelamer in patients. Since sevelamer is not absorbed, the risk of systemic toxicity is low.
The Uses of Sevelamer
Antihyper-phosphatemic.
Indications
For the control of serum phosphorus in patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) on hemodialysis.
Background
Sevelamer is a phosphate binding drug used to prevent hyperphosphataemia in patients with chronic renal failure. It is marketed by Genzyme under the trade name Renagel.
brand name
Renagel (Genzyme).
Pharmaceutical Applications
In patients on dialysis, Sevelamer or lanthanum salts can be used to maintain normal phosphate blood levels. Sevelamer is a polymer containing amine groups. These protonated amine groups can react with the negatively charged phosphate groups via ionic binding and prevent absorption of phosphate from the gut. Sevelamer is a hydrogel containing cross-linked polyallylamine chains. The negatively charged phosphate can be bound to the positively charged amine groups of the hydrogel in the intestines and removed via the faeces.
Pharmacokinetics
Patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) retain phosphorus and can develop hyperphosphatemia. High serum phosphorus can precipitate serum calcium resulting in ectopic calcification. When the product of serum calcium and phosphorus concentrations (Ca x P) exceeds 55 mg2/dL2, there is an increased risk that ectopic calcification will occur. Hyperphosphatemia plays a role in the development of secondary hyperparathyroidism in renal insufficiency. An increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels is characteristic of patients with chronic renal failure. Increased levels of PTH can lead to osteitis fibrosa, a bone disease. A decrease in serum phosphorus may decrease serum PTH levels. Treatment of hyperphosphatemia includes reduction in dietary intake of phosphate, inhibition of intestinal phosphate absorption with phosphate binders, and removal of phosphate with dialysis. Sevelamer taken with meals has been shown to decrease serum phosphorus concentrations in patients with ESRD who are on hemodialysis. In vitro studies have shown that the capsule and tablet formulations bind phosphate to a similar extent. Sevelamer treatment also results in a lowering of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and total serum cholesterol levels.
Clinical Use
Phosphate-binding agent
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: reduces bioavailability of
ciprofloxacin.
Ciclosporin: possibly reduces ciclosporin
concentration.
Calcitriol: absorption may be impaired by sevelamer.
Mycophenolate: may reduce mycophenolate levels.
Tacrolimus: possibly reduces tacrolimus
concentration.
Thyroid hormones: possibly reduces levothyroxine
concentration.
Metabolism
Not Available
Metabolism
Sevelamer is not systemically absorbed.
Properties of Sevelamer
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
Safety information for Sevelamer
Computed Descriptors for Sevelamer
New Products
1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Dorzolamide trans isomer Ritonavir - Impurity U Doultegravir isomer 1 N-Nitroso Dextromethorphan EP-A Dolutegravir Isopropyl Analogue (14R dextromethorphan) 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 4-Fluorothiophenol 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideYou may like
-
 PhosGood Sevelamer 800 Mg TabletsView Details
PhosGood Sevelamer 800 Mg TabletsView Details
52757-95-6 -
 Clidinium Bromide Related Compound B 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details
Clidinium Bromide Related Compound B 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details -
 N-Nitroso Atenolol EP Impurity I 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details
N-Nitroso Atenolol EP Impurity I 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details -
 N-Nitroso Atenolol EP Impurity I 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details
N-Nitroso Atenolol EP Impurity I 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details -
 Clidinium Bromide Related Compound B 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details
Clidinium Bromide Related Compound B 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details -
 N-Nitroso Atenolol EP Impurity I 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details
N-Nitroso Atenolol EP Impurity I 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details -
 N-Nitraso Atenolol EP Impurity G 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details
N-Nitraso Atenolol EP Impurity G 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details -
 N-Nitroso Atenolol EP Impurity I 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details
N-Nitroso Atenolol EP Impurity I 25 MG 50 MG 100 MG 250 MG EXTRAView Details
