Phenol
Synonym(s):Phenol;Phenol solution;Hydroxybenzene;C?H?O;Tris-equilabrated Phenol
- CAS NO.:108-95-2
- Empirical Formula: C6H6O
- Molecular Weight: 94.11
- MDL number: MFCD00002143
- EINECS: 203-632-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-13 11:21:50
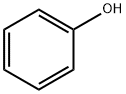
What is Phenol?
Description
Phenol, C6H5OH, also known as carbolic acid and phenylic acid, is a stable chemical substance and appear as colourless/white crystals with a characteristic, distinct aromatic/acrid odour. Phenol is used in the manufacture or production of explosives, fertiliser, coke, illuminating gas, lampblack, paints, paint removers, rubber, perfumes, asbestos goods, wood preservatives, synthetic resins, textiles, drugs, and pharmaceutical preparations. It is also extensively used as a disinfectant in the petroleum, leather, paper, soap, toy, tanning, dye, and agricultural industries.
Chemical properties
Phenol is a stable chemical substance. It is reactive and incompatible with strong oxidising agents, strong bases, strong acids, alkalis, and calcium hypochlorite. Phenol is flammable and may discolour in light. Phenol is soluble in water,alcohol,and ether. It is used in the production of resins,germicides,weedkillers,pharmaceuticals, and as a solvent in the refining of lubricating oils.
Physical properties
Phenol is a colorless or white crystalline solid with a characteristic, distinct aromatic/acrid odour that is slightly soluble in water. It is soluble in water,alcohol,and ether.
Occurrence
It is reported found in over 150 natural products including apricot, sour cherry, black currant, bilberry, cranberry, other berries, grapes, guava fruit, peach, pineapple, asparagus, onion, cooked potato, tomato, cinnamon bark, cassia leaf, ginger, pennyroyal oil, many cheeses, butter, milk, milk powder, boiled egg, fish and fish oil, cooked and cured meats, beer, wheaten bread, crisp bread, cognac, rose wine, cocoa, coffee, tea, whiskies, roasted filbert, roasted peanut, soybean, pecans, honey, avocado, Arctic bramble, passion fruit, beans, mushrooms, burley tobacco, cooked beef and chicken, fermented soy sauce, trassi, roasted almonds, sesame seed, fenugreek, mango, tamarind, Brazil nut, rice, rhubarb, licorice, buckwheat, watercress, malt, wort, dried bonito, loquat, myrtle berry, rosemary, Tahiti and Bourbon vanilla, endive, shrimp, crab, crayfish, clam, squid, truffle and Chinese quince.
The Uses of Phenol
Phenol is used in the manufacture of variousphenolic resins; as an intermediate in the production of many dyes and pharmaceuticals;as a disinfectant for toilets, floors, and drains;as a topical antiseptic; and as a reagentin chemical analysis.
In addition to the construction industry,phenol has many other applications.It isused in pharmaceuticals,in herbicides and pesticides,and as a germicide in paints.It can beused to produce caprolactam,which is the monomer used in the production of nylon 6.Another important industrial compound produced from phenol is bisphenol A,which ismade from phenol and acetone.
Background
Phenol is an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is active against a wide range of micro-organisms including some fungi and viruses, but is only slowly effective against spores. Phenol has been used to disinfect skin and to relieve itching. Phenol is also used as an oral analgesic or anesthetic in products such as Chloraseptic to treat pharyngitis. Additionally, phenol and its related compounds are used in surgical ingrown toenail treatment, a process termed phenolization. Research indicates that parental exposure to phenol and its related compounds are positively associated with spontaneous abortion. During the second world war, phenol injections were used as a means of execution by the Nazis. Phenol is a toxic compound whose vapours are corrosive to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract.
Indications
Phenol is primarily indicated for minor sore throat pain, sore mouth, minor mouth irritation, and pain associated with canker sores. Additionally, phenol is indicated in the treatment of focal spasticity.
Definition
ChEBI: Phenol is an organic hydroxy compound that consists of benzene bearing a single hydroxy substituent. The parent of the class of phenols. It has a role as a disinfectant, an antiseptic drug, a human xenobiotic metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a conjugate acid of a phenolate.
Production Methods
Historically, phenol was produced by the distillation of coal tar. Today, phenol is prepared by one of several synthetic methods, such as the fusion of sodium benzenesulfonate with sodium hydroxide followed by acidification; the hydrolysis of chlorobenzene by dilute sodium hydroxide at high temperature and pressure to give sodium phenate, which on acidification liberates phenol (Dow process); or the catalytic vapor-phase reaction of steam and chlorobenzene at 500°C (Raschig process).
Indications
Phenol in dilute solution (0.5% to 2%) decreases itch by anesthetizing the cutaneous nerve endings. Phenol should never be used on pregnant women or infants younger than 6 months of age.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 5.5 ppm. Aroma characteristics at 1.0%: medicinal, creosote, smoky, spicy, phenolic, leatherlike with notes of fried meat and coffee.
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 3 ppm: spicy, phenolic, tobacco, musty, woody, medicinal, smoky, tarlike and slightly spicy clovelike.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 107, p. 2153, 1985 DOI: 10.1021/ja00293a054
Synthetic Communications, 19, p. 453, 1989 DOI: 10.1080/00397918908050686
Air & Water Reactions
Decomposes slowly in air. Mixtures of 9-10% phenol in air are explosive. Soluble in water
Reactivity Profile
PHENOL is a weak acid. Reacts exothermically with bases. Reacts with strong oxidizing agents. Emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes when heated to decomposition. Undergoes, in the presence of aluminum chloride, potentially explosive reactions with nitromethane, butadiene, formaldehyde, peroxodisulfuric acid, peroxosulfuric acid, and sodium nitrite . Reacts violently with sodium nitrate in the presence of trifluoroacetic acid [Bretherick, 5th ed., 1995, p. 770]. May corrode lead, aluminum and its alloys, certain plastics, and rubber. Phenol may explode in contact with peroxodisulfuric acid (Dns, J. Ber., 1910, 43, 1880; Z. Anorg. Chem., 1911, 73, 1911.) or peroxomonosulfuric acid. (Sidgwick, 1950, 939)
Health Hazard
Phenol and its vapors are corrosive to the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract. The corrosive effect on skin and mucous membranes is due to a protein-degenerating effect. Repeated or prolonged skin contact with phenol may cause dermatitis, and potentially second and third-degree burns. Inhalation of phenol vapor may cause lung edema. Phenol may adversely effect the central nervous system and heart. Long-term, or repeated exposure, to phenol may have harmful effects on the liver and kidneys.
While there is no evidence that phenol causes cancer in humans it is readily absorbed through the skin; systemic poisoning can occur in addition to the local caustic burns. Resorptive poisoning by a large quantity of phenol can occur even with only a small area of skin, rapidly leading to paralysis of the central nervous system and a severe drop in body temperature. Phenol is also a reproductive toxin causing increased risk of abortion and low birth weight indicating retarded development in utero.
Chemical burns from skin exposures can be decontaminated by washing with polyethylene glycol or isopropyl alcohol; flushing with copious amounts of water will help to remediate the burn. Removal of contaminated clothing is required, as well as immediate hospital treatment for large splashes.
https://ehs.ucsc.edu/lab-safety-manual/specialty-chemicals/phenol.html
Fire Hazard
Flammable vapors when heated. Runoff from fire control water may give off poisonous gases and cause pollution. Mixtures of 9-10% phenol in air are explosive. Avoid aluminum chloride/nitrobenzene mixture, peroxodisulfuric acid, peroxomonosulfuric acid and strong oxidizing agents. Decomposes slowly on air contact. Avoid contact with strong oxidizing agents.
Flammability and Explosibility
Phenol is a combustible solid (NFPA rating = 2). When heated, phenol produces flammable vapors that are explosive at concentrations of 3 to 10% in air. Carbon dioxide or dry chemical extinguishers should be used to fight phenol fires.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Phenol is used mainly as an antimicrobial preservative in parenteral
pharmaceutical products. It has also been used in topical
pharmaceutical formulations and cosmetics;
Phenol is widely used as an antiseptic, disinfectant, and
therapeutic agent, although it should not be used to preserve
preparations that are to be freeze-dried.
Potential Exposure
Phenol is used as a pharmaceutical, in the production of fertilizer; coke, illuminating gas; lampblack, paints, paint removers; rubber, asbestos goods; wood preservatives; synthetic resins; textiles, drugs, pharmaceutical preparations; perfumes, bakelite, and other plastics (phenolformaldehyde resins); polymer intermediates (caprolactam, bisphenol-A and adipic acid). Phenol also finds wide use as a disinfectant and veterinary drug.
Carcinogenicity
Phenol had been investigated for carcinogenicity in animals by the oral and dermal routes. IARC and IRIS determined that animal human evidence for carcinogenicity was inadequate.
Metabolism
Phenyl sulfate, phenyl glucuronide, quinol sulfate, and quinol glucuronide were detected in human beings as phenol metabolites.
Absorption
Phenol is rapidly absorbed through the skin and into the lungs.
Health hazards
Phenol and its vapors are corrosive to the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract. The corrosive effect on skin and mucous membranes is due to a protein-degenerating effect. Repeated or prolonged skin contact with phenol may cause dermatitis, and potentially second and third-degree burns. Inhalation of phenol vapor may cause lung edema. Phenol may adversely effect the central nervous system and heart. Long-term, or repeated exposure, to phenol may have harmful effects on the liver and kidneys.
Toxicity
Mouse, Subcutaneous, LD50: 0.3-0.35 g/kg. (Duplay and Cazin, 1891; Tollens, 1905).Rat, Subcutaneous, LD50: 0.45. (Deichmann and Witherup, 1944).Rat, Oral, LD50: 0.53. (Deichmann and Witherup, 1944).Rat, Oral, LD50: 0.65. (Flickinger, 1976).Rat, Cutaneous, LD50: 0.67. (Conning and Hayes, 1970).
Storage
When exposed to air and light, phenol turns a red or brown color, the color being influenced by the presence of metallic impurities. Oxidizing agents also hasten the color change. Aqueous solutions of phenol are stable. Oily solutions for injection may be sterilized in hermetically sealed containers by dry heat. The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed, light-resistant container at a temperature not exceeding 15°C.
Incompatibilities
Phenol, available in solid or liquid form, is colorless to light pink and has a sweet aromatic odor. It is stable under normal conditions of storage and use. The liquid and vapor are combustible. Phenol is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, calcium hypochlorite, halogens, halogenated compounds, aluminum chloride, and nitrobenzene. Hot phenol can attack aluminum, lead, magnesium and zinc. It can react exothermally with peroxymonosulfuric acid, sodium nitrate, 1,3-butadiene and boron trifluoride diethyl ether. When phenol is heated to decomposition (ca. 715 °C), decomposition products include carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.
https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0493.html
http://www51.honeywell.com/sm/common/documents/Public_Risk_Summary_-_GPS0075_Phenol_Dec_2012.pdf
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Incineration.
Precautions
Acute poisoning of phenol by ingestion, inhalation or skin contact may lead to death. Phenol is readily absorbed through the skin. It is highly toxic by inhalation. It is corrosive and causes burns and severe irritation effects. During use and handling of phenol, occupational workers should be very careful. Workers should use protective clothing, rubber boots, and goggles to protect the eyes from vapors and spillage.
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (injections). Included in medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Phenol
| Melting point: | 40-42 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 182 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.071 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.24 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.09 psi ( 55 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 3223 | PHENOL |
| Flash point: | 175 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | liquid |
| pka | 9.89(at 20℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.071 |
| color | faintly yellow |
| Odor | Sweet, medicinal odor detectable at 0.06 ppm |
| PH | 6.47(1 mM solution);5.99(10 mM solution);5.49(100 mM solution); |
| explosive limit | 1.3-9.5%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 0.0056ppm |
| Water Solubility | 8 g/100 mL |
| FreezingPoint | 41℃ |
| Sensitive | Air & Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,7241 |
| JECFA Number | 690 |
| BRN | 969616 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.09 at 5 °C (average derived from six field experiments, Lüttke and Levsen, 1997) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA skin 5 ppm (~19 mg/m3 )
(ACGIH, MSHA, and OSHA); 10-hour TWA 5.2 ppm (~20 mg/m3 ) (NIOSH); ceiling
60 mg (15 minutes) (NIOSH); IDLH 250
ppm (NIOSH). |
| Dielectric constant | 4.3(10℃) |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 108-95-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 47, 71) 1999 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phenol(108-95-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phenol (108-95-2) |
Safety information for Phenol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Phenol
| InChIKey | ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Phenol manufacturer
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile valeronitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Phenol 99%View Details
Phenol 99%View Details -
 Phenol 99%View Details
Phenol 99%View Details -
 Phenol 99%View Details
Phenol 99%View Details -
 Phenol, Stabilized CAS 108-95-2View Details
Phenol, Stabilized CAS 108-95-2View Details
108-95-2 -
 Phenol Crystal CASView Details
Phenol Crystal CASView Details -
 Phenol Crystal CASView Details
Phenol Crystal CASView Details -
 Phenol Detached CrystalsView Details
Phenol Detached CrystalsView Details
108-95-2 -
 PHENOL CRYSTALS 99% AR (1KG)View Details
PHENOL CRYSTALS 99% AR (1KG)View Details
108-95-2
