Oliceridine
- CAS NO.:142128-57-2
- Empirical Formula: C26H28Cl2N4O4
- Molecular Weight: 531.43
- Update Date: 2026-01-27 08:46:37
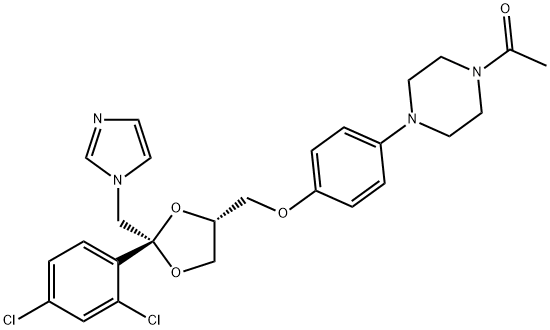
What is Oliceridine?
Absorption
Levoketoconazole has a Tmax of ~1.5-2 hours regardless of dose, while the Cmax increases proportionally with the dose. The AUC increases greater than dose proportionally over the recommended range of 150-600 mg. Co-administration of a single 600 mg oral dose with a high-fat meal increased the AUC by 30% with no change in Cmax and a delay in the median Tmax from two to four hours. The pharmacokinetics of racemic ketoconazole are not significantly different in patients with renal impairment; given the extensive hepatic metabolism of ketoconazole, it is expected that hepatic impairment will affect the pharmacokinetics of levoketoconazole.
Toxicity
Toxicity information regarding levoketoconazole is not readily available. Patients experiencing an overdose are at an increased risk of severe adverse effects such as nausea, vomiting, hypokalemia, hemorrhage, systemic hypertension, headache, hepatic injury, abnormal uterine bleeding, erythema, fatigue, abdominal pain/dyspepsia, arthritis, upper respiratory infection, myalgia, arrhythmia, back pain, insomnia/sleep disturbances, and peripheral edema. Symptomatic and supportive measures are recommended; within the first hour following ingestion, activated charcoal may be beneficial.
The Uses of Oliceridine
(-)-Ketoconazole along with other Ketoconazle stereoisomers can be used in pharmacological activity and biological study for inducing CYP4501A1 in human and mouse hepatoma. (-)-Ketoconazole has adverse effect as impurities contained in antifungal drug ketoconazole are potent activators of human aryl hydrocarbon receptor.
Background
Cushing's syndrome (CS) is underpinned by chronic hypercortisolism leading to multisystem morbidity, including effects on the cardiovascular and endocrine systems, metabolic syndrome with accompanying changes in body composition, neuropsychiatric effects, changes in blood pressure and chemistry, and opportunistic infections. Ketoconazole has been used both on- and off-label to treat CS due to its ability to inhibit cortisol production. Still, toxicity has limited its use, notably hepatic toxicity and a tendency to prolong the QT interval. Levoketoconazole is one of two enantiomers present in racemic ketoconazole. It possesses most of the inhibitory effect towards steroidogenic enzymes, making it an attractive candidate for CS treatment with a potentially lower toxicity profile than its racemate.
Levoketoconazole was approved by the FDA on December 30, 2021, and is currently marketed under the registered trademark RECORLEV by Xeris Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Indications
Levoketoconazole is indicated for the treatment of endogenous hypercortisolemia in adult patients with Cushing’s syndrome for whom surgery is not an option or has not been curative. Levoketoconazole is not indicated for the treatment of fungal infections.
Definition
ChEBI: (2S,4R)-ketoconazole is a cis-1-acetyl-4-(4-{[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-imidazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy}phenyl)piperazine which dioxolane moiety has (2S,4R)-configuration. It is an enantiomer of a (2R,4S)-ketoconazole.
Pharmacokinetics
Levoketoconazole is a steroidogenic inhibitor that reduces morbidity and mortality due to hypercortisolism associated with Cushing's syndrome. Due to its mechanism of action, levoketoconazole may cause hypocortisolism and decreased serum testosterone levels in both sexes. Levoketoconazole is known to cause dose-dependent increases in the QTc interval; at dose levels between 150 and 600 mg twice daily, the largest mean increase in the QTc was 24 msec. Hypersensitivity to levoketoconazole has been observed, and anaphylaxis has been reported with the racemic ketoconazole.
Metabolism
No in vitro or in vivo studies of levoketoconazole metabolism have been performed. Ketoconazole is known to be hepatically metabolized to several inactive metabolites, mainly through oxidation of the imidazole and piperazine rings, together with oxidative O-dealkylation and aromatic hydroxylation. Levoketoconazole is known to both induce and strongly inhibit CYP3A4.
Properties of Oliceridine
| solubility | DMSO:33.33(Max Conc. mg/mL);62.72(Max Conc. mM) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for Oliceridine
Computed Descriptors for Oliceridine
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideYou may like
-
 2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 -
 1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) -
 2856-63-5 99%View Details
2856-63-5 99%View Details
2856-63-5 -
 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
27472-21-5 -
 Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
7252-83-7 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 -
 5-azidovalericacidView Details
5-azidovalericacidView Details
79583-98-5
