Nemorexant
- CAS NO.:1505484-82-1
- Empirical Formula: C23H23ClN6O2
- Molecular Weight: 450.92
- Update Date: 2025-11-07 18:03:09
What is Nemorexant?
Absorption
Daridorexant reaches peak plasma concentrations within one to two hours. Daridorexant has an absolute bioavailability of 62%. While a high-fat and high-calorie meal delayed the Tmax by 1.3 hours and decreased the Cmax by 16% in healthy subjects, the total exposure (AUC) was not affected.
Toxicity
There is limited clinical experience with daridorexant overdose. In clinical pharmacology studies, healthy subjects were administered single doses of up to 200 mg, four times the maximum recommended dose. Somnolence, muscle weakness, cataplexy-like symptoms, sleep paralysis, disturbance in attention, fatigue, headache, and constipation were observed in these patients.
There is no specific antidote to overdosage of daridorexant. In the event of an overdose, general symptomatic and supportive medical care, along with immediate gastric lavage where appropriate, should be provided in addition to careful monitoring. Dialysis is unlikely to be effective as daridorexant is highly protein-bound.
The Uses of Nemorexant
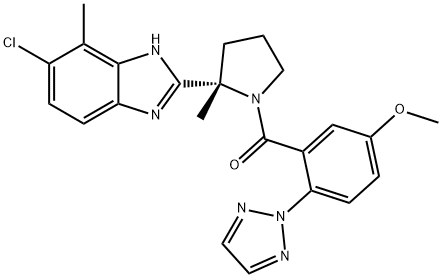
[(2S)-2-(6-Chloro-7-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-2-methyl-1-pyrrolidinyl][5-methoxy-2-(2H-1,2,3-triazol-2-yl)phenyl]methanone,
Indications
In the US and Europe, daridorexant is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with insomnia characterized by difficulties with sleep onset and/or sleep maintenance. The European prescribing information states that insomnia should be characterized by symptoms that are present for at least three months and have a considerable impact on daytime functioning.
Background
Daridorexant, formerly known as nemorexant, is a selective dual orexin receptor antagonist used to treat insomnia. Insomnia is characterized by difficulties with sleep onset and/or sleep maintenance and impairment of daytime functioning. It chronically affects the person's daily functioning and long-term health effects, as insomnia is often associated with comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes, and depression. Conventional treatments for insomnia include drugs targeting gamma-aminobutyric acid type-A (GABA-A), serotonin, histamine, or melatonin receptors; however, undesirable side effects are frequently reported, such as next-morning residual sleepiness, motor incoordination, falls, memory and cognitive impairment. Novel drugs that target orexin receptors gained increasing attention after discovering the role of orexin signalling pathway in wakefulness and almorexant, an orexin receptor antagonist that improved sleep. Daridorexant was designed via an intensive drug discovery program to improve the potency and maximize the duration of action while minimizing next-morning residual activity.
Daridorexant works on orexin receptors OX1R and OX2R to block the binding of orexins, which are wake-promoting neuropeptides and endogenous ligands to these receptors. Daridorexant reduces overactive wakefulness: in the investigational trials, daridorexant reportedly improved sleep and daytime functioning in patients with insomnia. It was approved by the FDA on January 10, 2022, under the name QUVIVIQ. as the second orexin receptor antagonist approved to treat insomnia following suvorexant. Daridorexant was approved by the European Commission on May 3, 2022, as the first dual orexin receptor antagonist approved in the market, and by Health Canada on April 26, 2023.
Pharmacokinetics
Daridorexant binds to and antagonizes the orexin receptors OX1R and OX2R (Ki = 0.47 and 0.93 nM, respectively) equipotentally. In clinical trials, daridorexant improved sleep onset and sleep maintenance, and patient-reported total sleep time. Patient-reported daytime sleepiness was also reportedly reduced. At a dose four times the maximum recommended dose, daridorexant does not prolong the QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent.
Daridorexant is currently being assessed for a controlled substance schedule in the US. In a human abuse potential study, daridorexant showed some abuse potential at doses higher than the recommended dose (100-150 mg), indicated by similar “drug liking” ratings to zolpidem (30 mg) and suvorexant in recreational sedative drug users. However, at clinically relevant concentrations, daridorexant does not bind to abuse-associated CNS targets. In animal studies and clinical trials evaluating physical dependence, chronic administration of daridorexant did not produce withdrawal signs or symptoms upon drug discontinuation, indicating that the drug does not produce physical dependence.
Metabolism
Daridorexant undergoes extensive metabolism primarily mediated by CYP3A4 (89%), mostly via oxidative transformations. Other CYP enzymes individually contribute to less than 3% of metabolic clearance of daridorexant.
Properties of Nemorexant
| Boiling point: | 747.6±70.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.42±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO : ≥ 250 mg/mL (554.42 mM) |
| pka | 10.47±0.30(Predicted) |
Safety information for Nemorexant
Computed Descriptors for Nemorexant
Nemorexant manufacturer
LUPA PHARMACEUTICALS
New Products
DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate N,O-Dimethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE Levothyroxine Impurity-F Montelukast EP Impurity-D/Montelukast USP Related Compound C Atorvastatin FXA Impurity/Atorvastatin Cyclic 6-Hydroxy Impurity Sodium Salt Isosulfan blue Keto N-Oxide Impurity Ivermectin Impurity F N-Nitroso des Methyl Tramadol/N-Nitroso-N-Desmethyl-Tramadol (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 1,4-bis(methylsulfonyl)butane 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene CSA (DL-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid) 2-Hydroxy-4-methylnicotinic acid 3-iodo-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine (2S)-1-((2S,3S)-3-(2-methylbutyl)-4-oxooxetan-2-yl)pentadecan-2-yl formylleucinate 1-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethane-1-sulfonyl chloride S-(1-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) ethanethioateYou may like
-
 Nemorexant 1505484-82-1 98+View Details
Nemorexant 1505484-82-1 98+View Details
1505484-82-1 -
 674783-97-2 98+View Details
674783-97-2 98+View Details
674783-97-2 -
 H-D-TRP(FOR)-OH HCL 98+View Details
H-D-TRP(FOR)-OH HCL 98+View Details
367453-01-8 -
 DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine 117391-50-1 98+View Details
DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine 117391-50-1 98+View Details
117391-50-1 -
 49830-37-7 98+View Details
49830-37-7 98+View Details
49830-37-7 -
 3-Amino-3-(4-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
3-Amino-3-(4-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
325-89-3 -
 1428243-26-8 98+View Details
1428243-26-8 98+View Details
1428243-26-8 -
 1-aminocyclopentane carbonitrile, HCl 98+View Details
1-aminocyclopentane carbonitrile, HCl 98+View Details
16195-83-8
