Methylparaben
Synonym(s):Methyl paraben;Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate;NIPAGIN;p-Hydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester;Methylis parahydroxybenzoas
- CAS NO.:99-76-3
- Empirical Formula: C8H8O3
- Molecular Weight: 152.15
- MDL number: MFCD00002352
- EINECS: 202-785-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-02-02 18:10:39
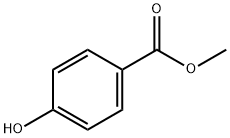
What is Methylparaben?
Description
Methylparaben, designated as food additive E218 in Europe, is a preservative that inhibits the growth of bacteria and fungi in many products, but it is frequently used in cosmetics. It and other parabens are produced by esterfying?para-hydrobenzoic acid (hence the name "paraben").
Chemical properties
Methylparaben occurs as colorless crystals or a white crystalline powder. It is odorless or almost odorless and has a slight burning taste. Soluble in alcohol,ether; slightly soluble in water, benzene, and carbontetrachloride.
Occurrence
Reported present in cloudberry, yellow passion fruit juice, white wine, botrytised wine and Bourbon vanilla.
The Uses of Methylparaben
Methyl paraben is a stable, non-volatile compound and finds application as an anti-microbial preservative in foods, drugs and cosmetics. Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate is used as an anti-fungal agent. It is also used as a preservative in foods, beverages and cosmetics. It acts as an inhibitor of growth of molds and to lesser extent bacteria and as a vehicle for ophthalmic solution.
Definition
ChEBI: Methylparaben is a 4-hydroxybenzoate ester resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid with methanol. It is the most frequently used antimicrobial preservative in cosmetics. It occurs naturally in several fruits, particularly in blueberries. It has a role as a plant metabolite, an antimicrobial food preservative, a neuroprotective agent and an antifungal agent.
Preparation
Methylparaben is produced through the methanol esterification of p-hydroxybenzoic acid in the presence of sulfuric acid. The materials are heated in a glass-lined reactor and distilled under reflux. The resulting acid is neutralized with caustic soda, then crystallized through cooling. The crystallized product is centrifuged, washed, dried under vacuum, milled and blended, all in corrosion-resistant equipment to avoid metallic contamination.
Hazard
Toxic. Use in foods restricted to 0.1%.
Contact allergens
This substance is one of the parabens family. Parabens are esters formed by p-hydroxybenzoic acid and an alcohol. They are largely used as biocides in cosmetics and toiletries, medicaments, or food. They have synergistic power with other biocides. Parabens can induce allergic contact dermatitis, mainly in chronic dermatitis and wounded skin.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, also called methyl paraben or nipagin, comprises the ester of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. It is present naturally in cloudberry, white wine and bourbon vanilla. Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate has antimicrobial and antifungal functionality and is commercially used as a preservative in the food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industry. Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate has cytotoxic effects on keratinocytes in the presence of sunlight. Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate upon solar irradiation mediates DNA damage and modulates esterase metabolism resulting in skin damage and favors cancer progression. Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate has estrogenic functionality and upregulates estrogen-related genes.
Toxicity
Methylparaben and other parabens are widely used as antimicrobial
preservatives in cosmetics and oral and topical pharmaceutical
formulations. Although parabens have also been used as preservatives
in injections and ophthalmic preparations, they are now
generally regarded as being unsuitable for these types of formulations
owing to the irritant potential of the parabens. These
experiences may depend on immune responses to enzymatically
formed metabolites of the parabens in the skin.
Parabens are nonmutagenic, nonteratogenic, and noncarcinogenic.
Sensitization to the parabens is rare, and these compounds do
not exhibit significant levels of photocontact sensitization or
phototoxicity.
Hypersensitivity reactions to parabens, generally of the delayed
type and appearing as contact dermatitis, have been reported.
However, given the widespread use of parabens as preservatives,
such reactions are relatively uncommon; the classification of overstated.
Immediate hypersensitivity reactions following injection of
preparations containing parabens have also been reported.
Delayed-contact dermatitis occurs more frequently when parabens
are used topically, but has also been reported to occur after oral
administration.
Unexpectedly, preparations containing parabens may be used by
patients who have reacted previously with contact dermatitis
provided they are applied to another, unaffected, site. This has
been termed the paraben paradox.
Concern has been expressed over the use of methylparaben in
infant parenteral products because bilirubin binding may be
affected, which is potentially hazardous in hyperbilirubinemic
neonates.
The WHO has set an estimated total acceptable daily intake for
methyl-, ethyl-, and propylparabens at up to 10 mg/kg bodyweight.
LD50 (dog, oral): 3.0 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IP): 0.96 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, SC): 1.20 g/kg
Carcinogenicity
The carcinogenic potential of methyl paraben has been studied in rodents. Several studies are available, but none that expose animals via oral or dermal routes. No evidence of a carcinogenic effect was observed following intravenous or subcutaneous injection .
Storage
Aqueous solutions of methylparaben at pH 3–6 may be sterilized by
autoclaving at 120°C for 20 minutes, without decomposition.
Aqueous solutions at pH 3–6 are stable (less than 10%
decomposition) for up to about 4 years at room temperature, while
aqueous solutions at pH 8 or above are subject to rapid hydrolysis
(10% or more after about 60 days storage at room temperature);
Methylparaben should be stored in a well-closed container in a
cool, dry place.
Incompatibilities
The antimicrobial activity of methylparaben and other parabens is
considerably reduced in the presence of nonionic surfactants, such
as polysorbate 80, as a result of micellization.However,
propylene glycol (10%) has been shown to potentiate the
antimicrobial activity of the parabens in the presence of nonionic
surfactants and prevents the interaction between methylparaben
and polysorbate 80.
Incompatibilities with other substances, such as bentonite,
magnesium trisilicate,talc,tragacanth,sodium alginate,
essential oils,sorbitol,and atropine,have been reported. It
also reacts with various sugars and related sugar alcohols.
Absorption of methylparaben by plastics has also been reported;
the amount absorbed is dependent upon the type of plastic and the
vehicle. It has been claimed that low-density and high-density
polyethylene bottles do not absorb methylparaben.
Methylparaben is discolored in the presence of iron and is
subject to hydrolysis by weak alkalis and strong acids.
Regulatory Status
Methylparaben and propylparaben are affirmed GRAS Direct Food
Substances in the USA at levels up to 0.1%. All esters except the
benzyl ester are allowed for injection in Japan. In cosmetics, the EU
and Brazil allow use of each paraben at 0.4%, but the total of all
parabens may not exceed 0.8%. The upper limit in Japan is 1.0%.
Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the
FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IM, IV, and SC injections;
inhalation preparations; ophthalmic preparations; oral capsules,
tablets, solutions and suspensions; otic, rectal, topical, and vaginal
preparations). Included in medicines licensed in the UK. Included in
the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
References
The Protective Effect of Rosmarinic Acid against Unfavorable Influence of Methylparaben and Propylparaben on Collagen in Human Skin Fibroblasts DOI:10.3390/nu12051282
https://www.byrdie.com/methylparaben-for-skin-4779820
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Methylparaben
Handa O, et al. (2006). Methylparaben potentiates UV-induced damage of skin keratinocytes. DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.07.018
Parabens in Cosmetics https://www.fda.gov/cosmetics/productsingredients/ingredients/ucm128042.htm
Okamoto T, et al. (2008). Combined activation of methyl paraben by light irradiation and metabolism toward oxidative DNA damage. DOI:10.1021/tx800066u
Properties of Methylparaben
| Melting point: | 125-128 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 298.6 °C |
| Density | 1,46g/cm |
| vapor pressure | 0.000005 hPa (20 °C) |
| FEMA | 2710 | METHYL P-HYDROXYBENZOATE |
| refractive index | 1.4447 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 280°C |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | ethanol: soluble0.1M, clear, colorless |
| pka | pKa 8.15(H2O,t =20.0) (Uncertain) |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| color | White to almost white |
| PH | 5.8 (H2O, 20°C) (saturated solution) |
| Odor | odorless or faint char. odor, sl. burning taste |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble in water. |
| FreezingPoint | 131℃ |
| Merck | 14,6107 |
| BRN | 509801 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 99-76-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzoic acid, 4-hydroxy-, methyl ester(99-76-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Methylparaben (99-76-3) |
Safety information for Methylparaben
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Methylparaben
| InChIKey | LXCFILQKKLGQFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Methylparaben manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Clickchem Research LLP
New Products
Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Rifaximin EP Impurity-G N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile 4-Fluorothiophenol (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 4-Bromo BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 METHYL PARABEN 99%View Details
METHYL PARABEN 99%View Details -
 Nipagin 99%View Details
Nipagin 99%View Details -
 Methyl Paraben(SQ) CAS 99-76-3View Details
Methyl Paraben(SQ) CAS 99-76-3View Details
99-76-3 -
 Methyl-4-Hydroxybenzoate (Methyl Paraben) ExiPlus CAS 99-76-3View Details
Methyl-4-Hydroxybenzoate (Methyl Paraben) ExiPlus CAS 99-76-3View Details
99-76-3 -
 Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate 99% CAS 99-76-3View Details
Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate 99% CAS 99-76-3View Details
99-76-3 -
 Powder Methyl-4-Hydroxybenzoate, 99-76-3, Packaging Type: DrumView Details
Powder Methyl-4-Hydroxybenzoate, 99-76-3, Packaging Type: DrumView Details
99-76-3 -
 Granules Methyl Paraben- 310View Details
Granules Methyl Paraben- 310View Details
99-76-3 -
 Trimethylhydroquinone (700-13-0)View Details
Trimethylhydroquinone (700-13-0)View Details
700-13-0
