Melamine
Synonym(s):2,4,6-Triamino-1,3,5-triazine;Melamine;sym-Triaminotriazine
- CAS NO.:108-78-1
- Empirical Formula: C3H6N6
- Molecular Weight: 126.12
- MDL number: MFCD00131581
- EINECS: 203-615-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-04 14:24:59
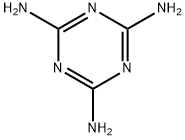
What is Melamine?
Description
Melamine, or 1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine, is formally a trimer of cyanamide, but its most common manufacturing method is heating dicyandiamide under pressure. It has many industrial uses; the chief one is its reaction with formaldehyde to produce thermosetting plastics and cleaning products. This toxic compound has been in the "news" in recent years because of its use in China as an adulterant in infant formula and pet food to increase the apparent protein content of these products.
Chemical properties
Melamine is a white solid organic compound whose molecules consist of a sixmembered heterocyclic ring of alternate carbon and nitrogen atoms with three amino groups attached to the carbons. Condensation polymerization with methanal or other aldehydes produces melamine resins, which are important thermosetting plastics.
The Uses of Melamine
Melamine can be used to make high-pressure laminating resins (e.g., decorative countertops), molded compounds (e.g., dinnerware), and surface coating resins (e.g., appliance finishes and automotive topcoats). Additional major products are textile and paper treatment resins. Miscellaneous uses include adhesive resins for gluing lumber, plywood, and flooring, and resins for leather tanning agents.
Production Methods
Melamine is prepared almost exclusively by the urea process—the action of ammonia on urea. It is produced worldwide.
Preparation
The standard route to melamine is from urea. Urea is
heated in the presence of ammonia at 250-350??C and 4--20 MPa. The
reaction probably involves the simultaneous dehydration and hydration of
urea to form cyanamide and ammonium carbamate; trimerization of the
cyanamide then leads to melamine:

Thus only 50% of the urea used gives melamine in one step and ammonium carbamate has to be separated and converted to urea for recycling. Despite this limitation, the urea route is the most economical of currently available routes.
Reactivity Profile
Melamine is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and strong acids. Neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Contact allergens
Melamine-formaldehyde resin (MFR) results from condensation of melamine and formaldehyde. It is anactive ingredient of strong (reinforced) plasters, such as industrial or some dental plasters used for molding.It is also used as a textile finish resin. MFR acts as an allergen generally because of formaldehyde releasing.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove any contact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least 15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medical facility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Storage
Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from strong oxidizers and strong acids.
Purification Methods
Crystallise Melamine from water or dilute aqueous NaOH. It sublimes at ~240℃ on prolonged heating.
Properties of Melamine
| Melting point: | >300 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 224.22°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.573 |
| vapor pressure | 66.65 hPa (315 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.872 |
| Flash point: | >110°C |
| storage temp. | no restrictions. |
| solubility | water: soluble25mg/mL, clear to slightly hazy, colorless |
| form | Fine Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 5(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| PH | 7-8 (32g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 3 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,5811 |
| BRN | 124341 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizing agents. Nonflammable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 108-78-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-triamine(108-78-1) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. Sup 7, 73, 119) 2019 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Melamine (108-78-1) |
Safety information for Melamine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Melamine
| InChIKey | JDSHMPZPIAZGSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Melamine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
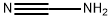

You may like
-
 Melamine 98%View Details
Melamine 98%View Details -
 Melamine 99%View Details
Melamine 99%View Details -
 Melamine 99%View Details
Melamine 99%View Details -
 Melamine CASView Details
Melamine CASView Details -
 Melamine CASView Details
Melamine CASView Details -
 Melamine Technical GradeView Details
Melamine Technical GradeView Details
108-78-1 -
 Melamine Chemical PowderView Details
Melamine Chemical PowderView Details
108-78-1 -
 Melamine Sweet Dish Plate 5" AN-MP-PC-252View Details
Melamine Sweet Dish Plate 5" AN-MP-PC-252View Details
108-78-1
