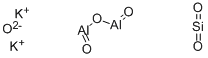
kyanite
- CAS NO.:1302-76-7
- Empirical Formula: Al2H6O5Si
- Molecular Weight: 168.093216
- EINECS: 215-106-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
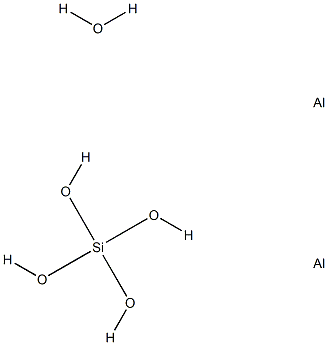
What is kyanite ?
Description
Kyanite is easily distinguished from sillimanite or andalusite by its tabular, long-bladed, or acicular habit and by its bluish color and slightly lower hardness than sillimanite and andalusite. The decomposition of kyanite is unpredictable; it first starts to decompose slowly at 1310°C, and the reaction disrupts at about 1350 to 1380°C with an important volume expansion of 17 vol.%. For that reason, kyanite must always be calcined prior to being incorporated into a refractory in order to avoid blistering and spalling.
Chemical properties
white powder(s) [STR93]
Physical properties
Habit: blady, columnar, tabular, fibrous.
Color: blue, white, yellowish, gray, green,
or black.
Luster: vitreous (i.e., glassy), pearly.
Diaphaneity: translucent to transparent.
Streak: white.
Fracture: uneven, brittle.
Luminescence: pink to red.
Cleavage: (100) perfect, (010) imperfect.
Twinning: {100}. Chemical: insoluble in strong mineral acids.
Occurrence
The mineral kyanite is an aluminum silicate, corresponding to the formula Al2SiO5. It is triclinic, and has a good cleavage parallel to the macropinacoid. Its hardness varies considerably, depending on the crystallographic direction from 5 to 7.5; specific gravity, 3.56–3.67; luster, vitreous to pearly; color, commonly blue to white, but sometimes gray to green or nearly black; transparent to translucent; usually found in long-bladed crystals or columnar to fibrous structures. Kyanite is found in some metamorphic rocks as gneisses or mica schists. Of the many European localities for fine specimens might be mentioned the Ural Mountains of the former U.S.S.R.; the Czech Republic and Slovakia; Austria; Trentino, Italy; the St. Gotthard region of Switzerland; and France. In the United States, Chesterfield, Massachusetts; Litchfield, Connecticut; and Gaston County, North Carolina, have furnished fine specimens. Kyanite derives its name from the Greek word meaning blue, in reference to the delicate blue of the inner portions of the bladed crystals.
The Uses of kyanite
Kyanite in the form of mullite is widely used in the manufacture of glass, burner tips, spark plugs, heating elements, and high-voltage electrical insulations and in the ceramic industry. India is the largest producer of kyanite in the world.
Properties of kyanite
| Density | 2.600 |
| color | blue or gray triclinic
crystals, crystalline |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Kyanite (Al2O(SiO4)) (1302-76-7) |
Safety information for kyanite
Computed Descriptors for kyanite
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile valeronitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 -
 1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) -
 1529-41-5 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 99%View Details
1529-41-5 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 99%View Details
1529-41-5 -
 2856-63-5 99%View Details
2856-63-5 99%View Details
2856-63-5 -
 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
27472-21-5 -
 Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
7252-83-7 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8