KETENE
- CAS NO.:63-51-4
- Empirical Formula: C2H2O
- Molecular Weight: 42.04
- MDL number: MFCD01716601
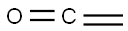
What is KETENE?
Description
Ketene (systematic name ethenone) is a colorless, toxic gas with a “penetrating” odor, according to the?Merck Index. It is soluble in essentially all organic solvents, but it decomposes in water to form acetic acid. Its tautomer, ethynol, is known to exist only by photoisomerizing ketene in an argon matrix. Nobel Prize–winning German chemist Hermann Staudinger discovered the ketene family of organic compounds early in the 20th century.
Ketene is prepared by pyrolyzing acetone, acetic acid, or acetic anhydride or by treating acetyl chloride with a nonprotic nucleophile. It is useful for acetylating nucleophiles to make esters, amides, and other compounds that cannot easily be made with other reagents. Ketenes were used in the synthesis of the early antibiotics penicillin and amoxicillin.
The anions cyanate (NCO–) and 2-phosphaethynolate (PCO–) are isoelectronic with ketene. Now Alexander Hinz and Jose M. Goicoechea at Oxford University (UK) report the?preparation of the arsenic analogue, 2-arsaethynolate (AsCO–) via a three step sequence that starts from elemental arsenic. AsCO–?readily reacts with ketenes and carbodiimides to form 4-membered arsenic heterocycles.
Chemical properties
Colorless gas; disagreeable odor. Readily polymerizes; cannot be shipped or stored in a gaseous state.
The Uses of KETENE
Acetylating agent, generally reacting with compounds having an active hydrogen atom; reacts with ammonia to give acetamide. Starting point for making various commercially important products, especially acetic anhydride and acetate esters.
Definition
A member of a group of organic compounds, general formula R2C:CO, where R is hydrogen or an organic radical. The simplest member is the colorless gas ketene, CH2:CO; the other ketenes are colored because of the presence of the double bonds. Ketenes are unstable and react with other unsaturated compounds to give cyclic compounds.
Hazard
Toxic by inhalation, strong irritant to skin and mucous membranes.
Safety information for KETENE
New Products
Mirtazapine Impurity C/Mirtazapine Lactam Impurity N,O-Dimethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile 4-Fluorothiophenol (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 4-Bromo BenzylcyanideYou may like
-
 Bendamustine deschloroethyl acid ethyl ester 2517968-40-8 NLT 95%View Details
Bendamustine deschloroethyl acid ethyl ester 2517968-40-8 NLT 95%View Details
2517968-40-8 -
 Acebutolol EP Impurity K NLT 95%View Details
Acebutolol EP Impurity K NLT 95%View Details
74143-33-2 -
 Clidinium Bromide Impurity NLT 95%View Details
Clidinium Bromide Impurity NLT 95%View Details
.6581-06-2 -
 192110-67-2 NLT 95%View Details
192110-67-2 NLT 95%View Details
192110-67-2 -
 Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity NLT 95%View Details
Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity NLT 95%View Details
59872-62-1 -
 90717-17-2 Ketamine Impurity-C NLT 95%View Details
90717-17-2 Ketamine Impurity-C NLT 95%View Details
90717-17-2 -
 .2005-04-1 N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A NLT 95%View Details
.2005-04-1 N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A NLT 95%View Details
.2005-04-1 -
 145773-22-1 Lantanoprost rc B NLT 95%View Details
145773-22-1 Lantanoprost rc B NLT 95%View Details
145773-22-1
