Isavuconazonium sulfate
Synonym(s):;BAL 8557-002;BAL8557
- CAS NO.:742049-41-8
- Empirical Formula: C35H35F2N8O5S+
- Molecular Weight: 717.77
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-12-18 17:43:23
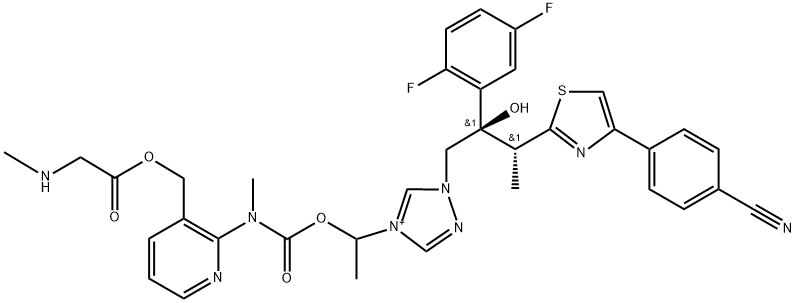
What is Isavuconazonium sulfate?
Absorption
When administered intravenously as isavuconazonium, >99% of the prodrug is quickly converted to active isavuconazole (catalyzed by plasma esterases). Oral administration of isavuconazonium shows 98% oral bioavailability, however administration with food results in a 20% decrease in AUC (area under concentration-time curve) as well as decreasing maximum serum concentration (Cmax) by 50% and increasing time to Cmax by 1.5 hours.
Toxicity
Isavuconazole, the active moiety of isavuconazonium, is classified as Pregnancy Class C and should be avoided in pregnant women. It was also found to be excreted in breast milk in animal studies in rats, therefore it should be avoided in breastfeeding women.
Description
Isavuconazonium sulfate is a broad spectrum antifungal agent that was codeveloped by Basilea Pharmaceutica (a subsidiary of Hoffmann-La Roche acquired in 2000) and Astellas Pharma, which obtained its first approval by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis, available as both oral and intravenous formulations. Isavuconazonium sulfate is a water-soluble prodrug, which is rapidly hydrolyzed by esterases (mainly butylcholinesterase) in plasma into the active moiety isavuconazole (BAL-4815) and an inactive cleavage product (BAL-8728). Isavuconazole inhibits cytochrome P450 (CYP)- dependent enzyme lanosterol 14-ademethylase (CYP51) and thereby inhibits the synthesis of ergosterol, a key component of the fungal cell membrane.4 Isavuconazole displayed potent fungistatic or fungicidal activity in vitro against a broad range of clinically important yeasts and molds, namely Candida spp., Cryptococcus spp., Trichosporon spp., Geotrichum capitatum, Pichia spp., Rhodotorula spp., Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Aspergillus spp., and most species known to cause mucormycosis (Mucorales mucorales). This broad range of antifungal activity renders this drug more clinically appealing compared to other azoles with narrower indications. Furthermore, isavuconazole does not require a cyclodextrin vehicle due to its water solubility, and currently does not require therapeutic drug monitoring. Moreover, isavuconazole has displayed improved safety and tolerability compared to voriconazole.
The Uses of Isavuconazonium sulfate
Isavuconazonium Sulfate can be prepared to be used as an antifungal drug.
Background
Isavuconazonium is a second-generation triazole antifungal approved on March 6, 2015 by the FDA for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis, marketed by Astellas under the brand Cresemba. It is the prodrug form of isavuconazole, the active moiety, and it is available in oral and parenteral formulations. Due to low solubility in water of isavuconazole on its own, the isovuconazonium formulation is favorable as it has high solubility in water and allows for intravenous administration. This formulation also avoids the use of a cyclodextrin vehicle for solubilization required for intravenous administration of other antifungals such as voriconazole and posaconazole, eliminating concerns of nephrotoxicity associated with cyclodextrin. Isovuconazonium has excellent oral bioavailability, predictable pharmacokinetics, and a good safety profile, making it a reasonable alternative to its few other competitors on the market.
Indications
Indicated in the treatment of invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis.
Definition
ChEBI: Isavuconazonium is an organic cation that is the cationic portion of isavuconazonium sulfate (a prodrug for isavuconazole, an antifungal agent used for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis). It has a role as a prodrug, an ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitor, an EC 1.14.13.70 (sterol 14alpha-demethylase) inhibitor and an antifungal agent.
Synthesis
The synthesis of active moiety isavuconazole 8 was started
with commercial 1-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-2-(1H-l,2,4-triazol-lyl)
ethanone (1). Triazole 1 was
treated with n-BuLi followed by exposure to propionitrile (2)
and acidic quench to give racemic alcohol 3 in 65% yield. Next,
resolution of this racemic alcohol was facilitated through the
use of camphor derivative 4 to provide alcohol 5 in 38% yield
and 99% ee. Nitrile 5 was then treated with concentrated
H2SO4 and H2S to furnish thioamide 6, and this was followed
by a cyclization reaction involving 4-(2-chloroacetyl)-
benzonitrile (7) which gave rise to isavuconazole 8 in 81%
yield across the two-step sequence.
The preparation of water-soluble side chain 15
was initiated from commercially available 2-chloronicotinic acid
(9), which was converted to the corresponding tert-butyl ester
11 via acid halide 10 in excellent yield for the two-step
protocol. Subjection of pyridyl chloride 11 to methanolic
methylamine furnished aminopyridine 12 in 92% yield, and this
compound was subsequently reduced with lithium aluminum
hydride to give aminoalcohol 13 in 76% yield. Next, Nacylation
of 13 with 1-chloroethyl chloroformate (14) followed
by treatment with N-Boc-sarcosine under esterification
conditions delivered chloroethyl ester 15 in 73% yield. The
union of the aminopyridyl side chain 15 with thiazoloalcohol 8
was facilitated by reacting the two compounds in the presence
of KI in acetonitrile, and this alkylation was followed by
removal of the Boc group with hydrochloric acid to give rise to
isavuconazonium iodide hydrochloride (16) in 79% yield.
Finally, isavuconazonium sulfate (I) was prepared from 16
using an anion exchange resin in 93% yield to finish the
construction of the API.

Metabolism
Metabolism is primarily hepatic, with CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 involved in phase I metabolism, followed by modification by uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT).
Safety information for Isavuconazonium sulfate
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile valeronitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideYou may like
-
 Isavuconazonium sulfate 98%View Details
Isavuconazonium sulfate 98%View Details -
 2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 -
 1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) -
 2856-63-5 99%View Details
2856-63-5 99%View Details
2856-63-5 -
 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
27472-21-5 -
 Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
7252-83-7 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8
