Copper(II) sulfate
Synonym(s):Cupric sulfate;Copper(II) sulfate;Copper(II) sulfate solution;Cupric sulfate solution acc. to Fehling;Cupric sulfate standard
- CAS NO.:7758-98-7
- Empirical Formula: CuO4S
- Molecular Weight: 159.61
- MDL number: MFCD00010981
- EINECS: 231-847-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-13 11:26:55
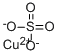
What is Copper(II) sulfate?
Description
Copper sulfate is a greenish-white crystallinesolid; the pentahydrate is blue powder or granules, or ultramarine crystalline solid. Molecular weight =159.60; 249.70(pentahydrate). Boiling point =150℃ (pentahydrate) with25H2O; Melting point = (decomposes) .200℃; decomposes .110℃ (pentahydrate) with 24H2O; copper sulfatedecomposes to CuO at 650℃. Hazard Identification (basedon NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 2, Flammability 0,Reactivity 0. Highly soluble in water; forms a bright bluesolution.
Chemical properties
Cupric sulfate, a bluish crystalline powder, also known as hydrocyanite and copper sulfate, vitriol, chalcanthite, and bluestone, is an azure blue material used in the It is used in the leather industry. It is prepared by the reaction of sulfuric acid and copper. It is also obtained as a by-product from copper refineries.
Chemical properties
Copper sulfate (anhydrous form) is green or gray-white powder, whereas pentahydrate, the most commonly encountered salt, is bright blue. The anhydrous form occurs as a rare mineral known as chalcocyanite. Hydrated copper sulfate occurs in nature as chalcanthite. Copper sulfate is made by the action of sulfuric acid with a variety of copper compounds. Copper sulfate is used in hair dyes, coloring glass, processing of leather, textiles, and in pyrotechnics as a green colorant. Copper sulfate pentahydrate is used as a fungicide and a mixture with lime is called Bordeux mixture and is used to control fungus on grapes, melons, and other berries, as a molluscicide for the destruction of slugs and snails, particularly the snail host of the liver fl uke. Copper sulfate is used in Fehling and Benedict’s solution to test reducing sugars
Chemical properties
Copper sulfate is a greenish-white crystalline solid; the pentahydrate is Blue powder or granules, or ultramarine crystalline solid.
The Uses of Copper(II) sulfate
Copper(II) sulfate may be employed for the following studies:
- As a catalyst for the acetylation of alcohols and phenols under solvent-free conditions.
- To compose the electrolyte for the electrodeposition of Cu-Zn-Sn precursors, required for the preparation of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) thin films.
- As a Lewis acid catalyst for the dehydration of alcohols.5
The Uses of Copper(II) sulfate
Used as an antimicrobial and molluscicide.
The Uses of Copper(II) sulfate
Copper Sulfate is a nutrient supplement and processing aid most often used in the pentahydrate form. This form occurs as large, deep blue or ultramarine, triclinic crystals, as blue granules, or as a light blue powder. The ingredient is prepared by the reaction of sulfuric acid with cupric oxide or with copper metal. May be used in infant formula. It is also termed cupric sulfate.
The Uses of Copper(II) sulfate
Copper sulfate is also known as blue vitriol, this substance was made by the action of sulfuric acid on elemental copper. The bright-blue crystals are soluble in water and alcohol. Mixed with ammonia, copper sulfate was used in liquid filters. The most common application for copper sulfate was combining it with potassium bromide for making copper bromide bleach for intensification and toning. Some photographers used copper sulfate as a restrainer in ferrous sulfate developers that were used in the collodion process.
Indications
Elemental use in copper deficiency
Copper and copper containing compounds are broadly used in medical practice. Metallic copper is used already for many years in dental fillings and in copper intrauterine devices (IUD) for reversible contraception. Ointments containing copper, which release copper ions that are absorbed by the skin in the management of cramps, disturbances of renal function, peripheral, venous hypostatic circulatory disturbances, rheumatic disease and swelling associated with trauma. There are also cosmetic facial creams containing copper as their main active ingredient .
Background
Cupric sulfate is a salt created by treating cupric oxide with sulfuric acid. This forms as large, bright blue crystals containing five molecules of water (CuSO4?5H2O) and is also known as blue vitriol. The anhydrous salt is created by heating the hydrate to 150 °C (300 °F). Cupric sulfate is used primarily for agricultural purposes, as a pesticide, germicide, feed additive, and soil additive. Some of its secondary uses are as a raw material in the preparation of other copper compounds, as a reagent in analytic chemistry, as an electrolyte for batteries and electroplating baths, and in medical practice as a locally applied fungicide, bactericide, and astringent .
Copper is an essential trace element and an important catalyst for heme synthesis and iron absorption. After zinc and iron, copper is the third most abundant trace element found in the human body. Copper is a noble metal and its properties include high thermal and electrical conductivity, low corrosion, alloying ability, and malleability. Copper is a component of intrauterine contraceptive devices (IUD) and the release of copper is necessary for their important contraceptive effects. The average daily intake of copper in the USA is approximately 1 mg Cu with the diet being a primary source .
Interestingly, the dysregulation of copper has been studied with a focus on neurodegenerative diseases, such as Wilson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease. Data from clinical observations of the neurotoxic effects of copper may provide the basis for future treatments affecting copper and its homeostasis .
Definition
ChEBI: A metal sulfate compound having copper(2+) as the metal ion.
Definition
A compound prepared as the hydrate by the action of dilute sulfuric acid on copper( II) oxide or copper(II) carbonate. On crystallization, blue triclinic crystals of the pentahydrate (blue vitriol, CuSO4.5H2O) are formed. Industrially copper(II) sulfate is prepared by passing air through a hot mixture of dilute sulfuric acid and scrap copper. The solution formed is recycled until the concentration of the copper(II) sulfate is sufficient. Copper(II) sulfate is readily soluble in water. The monohydrate (CuSO4.H2O) is formed at 100°C and the anhydrous salt at 250°C. Anhydrous copper( II) sulfate is white; it is extremely hygroscopic and turns blue on absorption of water. It decomposes on heating to give copper(II) oxide and sulfur(VI) oxide.
Copper(II) sulfate is used as a wood preservative, a fungicide (in Bordeaux mixture), and in the dyeing and electroplating industries.
General Description
A white or off-white solid. Melting point 200°C with decomposition. Non-combustible.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Anhydrous Cupric sulfate serves as a weak oxidizing agent. Causes hydroxylamine to ignite. Gains water readily. The hydrated salt is vigorously reduced by hydroxylamine [Mellor 8:292(1946-1947)]. Both forms are incompatible with finely powdered metals. Both are incompatible with magnesium, corrode steel and iron, may react with alkalis, phosphates, acetylene gas, hydrazine, or nitromethane, and may react with beta-naphthol, propylene glycol, sulphathiazole and triethanolamine if the pH exceeds 7 . Both act as acidic salts, corrode metals and irritate tissues.
Hazard
Toxic; highly irritant.
Health Hazard
INGESTION: copper sulfate may induce severe gastroenteric distress (vomiting, gastroenteric pain, and local corrosion and hemorrhages), prostration, anuria, hematuria, anemia, increase in white blood cells, icterus, coma, respiratory difficulties, and circulatory failure.
Health Hazard
Workers who accidentally ingest copper sulfate experience abdominal pain and cramps, burning sensation, corrosive effects, nausea, vomiting, loose bowel movement, and a metallic taste. Exposures to copper sulfate by ingestion or skin absorption cause severe irritating effects to the eyes and skin The aerosol is irritating to the respiratory tract, and effects on the blood, kidneys and liver result in hemolytic anemia, kidney impairment, liver impairment, and shock or collapse. At large doses, accidental intake of copper sulfate causes renal failure, comatose, and even death. Long-term exposure to copper sulfate may lead to liver damage, lung diseases, and decreased female fertility.
Agricultural Uses
Fungicide, Algaecide, Bactericide, Herbicide, Molluscicide: Copper sulfate is a fungicide used to control bacterial and fungal diseases of fruit, vegetable, nut, and field crops. These diseases include mildew, leaf spots, blights, and apple scab. It is used as a protective fungicide (Bordeaux mixture) for leaf application and seed treatment. It is also used as an algaecide and herbicide, and to kill slugs and snails in irrigation and municipal water treatment systems. It has been used to control Dutch elm disease. It is available as a dust, wettable powder, or liquid concentrate. Used as a fungicide and algaecide, in veterinary medicine and others. Copper sulfate is also used todetect and to remove trace amounts of water from alcohols and organic compounds.
Industrial uses
Copper sulfate (CuSO4·5H2O) is widely used as an activator for sphalerite, pyrite,
pyrrhotite and other sulfides during processing of base metal ores. During flotation of
some silicate minerals, copper sulfate is used as depressant, e.g. zirconium.
In manufacturing copper sulfate, sulfuric acid and scrap copper metal are used. The
process is based on the oxidation of metal and dissolution with H2SO4 according to the
following reaction:
4Cu + O2 = 2Cu2O
Cu2O + H2SO4 = CuSO4 + H2O
2Cu2SO4 + 2H2SO4 + O2 = 4CuSO4 + 2H2O
Usually, in mineral processing applications, copper sulfate is delivered in crystal
form.
Trade name
AGRITOX®; BASICOP®; BCS COPPER FUNGICIDE®; BSC FLOWABLE®[C]; COPSIN®; CP BASIC SULFATE®; CUPROFIX®; FUNGI-SPERSE II[C]; SULTRACOB®; TNCS® 53; TRIANGLE®
Pharmacokinetics
Copper is an essential mineral that plays a key role in many physiological processes, including angiogenesis, skin generation and expression and stabilization of skin proteins. Copper is found naturally in many food sources including meats, vegetables, and grains. Copper has potent biocidal properties and is used to eliminate bacteria, viruses and parasites , .
Copper is one of the nine essential minerals for humans, as it plays an imperative role in various physiological pathways in basically all human tissue, as well as in the health of the dermis and epidermis .
In addition to the above, copper is essential in wound healing, as it promotes angiogenesis and skin extracellular matrix formation and stabilization .
Safety Profile
A human poison by ingestion. An experimental poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, parenteral, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: gastritis, Qarrhea, nausea or vomiting, damage to kidney tubules, and hemolysis. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. Reacts violently with hydroxylamine, magnesium. See also COPPER COMPOUNDS and SULFATES. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SOx
Potential Exposure
Copper sulfate is used as intermediate and wood preservative; also used in production of copper compounds; to detect and to remove trace amounts of water from alcohols and organic compounds; as a fungicide and algicide; in veterinary medicine and others.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Note to physician: Empty stomach by lavage with 0.1%solution of potassium ferrocyanide or milk. Liver or kidneyfunction tests may be indicated. May result inmethemoglobinemia
Absorption
Primarily absorbed in the small intestine .
Based on studies with radioactive isotopes of copper, most copper is absorbed from the stomach
and duodenum of the gastrointestinal tract.
Maximum blood copper levels are observed within 1 to 3 hours following oral administration, and about 50 percent of ingested copper was absorbed. Copper absorption is proposed to occur by two mechanisms, one energy- dependent and the other enzymatic. Factors that can interfere with copper absorption include competition for binding sites with zinc, interactions with molybdenum and sulfates, chelation with phytates, and inhibition by ascorbic acid (vitamin C) .
Copper absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract is transported rapidly to blood serum and deposited in the liver bound to metallothionein .
From 20 to 60% of the dietary copper is absorbed .
Metabolism
Maximum blood copper levels were observed within 1 to 3 hours following oral administration, and about 50 percent of ingested copper was absorbed. Copper absorption is believed to occur by two mechanisms, one energy- dependent and the other enzymatic. Factors that can interfere with copper absorption include competition for binding sites with zinc, interactions with molybdenum and sulfates, chelation with phytates, and inhibition by ascorbic acid . Copper absorbed from the intestine is transported quickly into blood serum and deposited in the liver bound to metallothionein. It is released and incorporated into ceruloplasmin, a copper-specific transport protein. The remaining copper in the serum binds to albumin or amino acids or is contained in the erythrocytes. About 80 percent of the absorbed copper is bound to liver metallothionein; the remainder is included into cytochrome c oxidase or sequestered by lysosomes .
Toxicity
Acute oral toxicity (LD50): 300 mg/kg in rats .
Copper sulfate ingestion (accidental or deliberate) is a rare form of poisoning usually limited to the Indian subcontinent. Though the rates are on the decline, it is essential that physicians are aware of its lethal complications and management strategies. The main complications of copper sulfate ingestion include intravascular hemolysis, methemoglobinaemia, acute kidney injury, and rhabdomyolysis .
Severe gastrointestinal effects may occur with acute overdosage. In extreme or long-term overdosage, symptoms may be similar to those of Wilson's disease, a disease in which the liver does not filter copper adequately and copper accumulates in the liver, brain, eyes, and other organs. Gradually, high copper levels may cause life-threatening organ damage .
Ingestion of more than 15 mg of copper has been reported to be toxic to humans. In a survey of human clinical case studies, 5.3 mg/day was the lowest oral dose at which local gastrointestinal irritation was seen. Ingestion of gram quantities of copper sulfate resulted in death by suicide, whereas less severe effects were reported from estimated copper doses of 40 to 50 mg from ingestion of carbonated beverages in contact with copper containers. Limited data are available on the chronic toxicity of copper. The hazard from dietary intakes of up to 5 mg/day appears to be low .
Treatment of cupric sulfate toxicity is symptomatic and may involve the use of a chelating agent (e.g. penicillamine, trientine and zinc) to remove any excessive metal that has been absorbed. In addition, dialysis may be useful .
Storage
Workers should keep copper sulfate stored in a cool, dry area with suffi cient ventilation. It should be kept away from alkalis, magnesium, ammonia, acetylene, and sodium hypobromite.
Shipping
UN3288 Toxic solids, inorganic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
After adding 0.02g of KOH to a litre of nearly saturated aqueous solution of the sulfate, it is left for two weeks, then the precipitate is filtered on to a fibreglass filter with pore diameter of 5-15 microns. The filtrate is heated to 90o and allowed to evaporate until some CuSO4.5H2O crystallises out. The solution is then filtered hot and cooled rapidly to give crystals which are freed from mother liquor by filtering under suction [Geballe & Giauque J Am Chem Soc 74 3513 1952]. Alternatively crystallise the sulfate from water (0.6mL/g) between 100o and 0o. The pentahydrate is slowly efflorescent, losing 2H2O at 30o, two more H2O are lost at 110o and a white anhydrous powder (dessicant) is obtained on heating above 250o.
Incompatibilities
Aqueous solution is an acid. May form explosive materials on contact with acetylene and nitromethane. Incompatible with strong bases; hydroxylamine, magnesium; zirconium, sodium hypobromite, hydrazine.
Waste Disposal
Copper-containing soluble wastes can be concentrated through the use of ion exchange, reverse osmosis, or evaporators to the point where copper can be electrolytically removed and sent to a reclaiming firm. If recovery is not feasible, the copper can be precipitated through the use of caustics and the sludge deposited in a chemical waste landfill Add soda ash to waste CuSO4 solution; let stand 24 hours. Decant and neutralize solution before flushing to sewer. Landfill sludge.
Precautions
During handling and use of copper sulfate, students and occupational workers should wear safety glasses and should not breathe the material in powder form. Copper sulfate is an environmental pollutant and must be carefully incorporated when used in its varied applications. Workers should wear protective clothing, goggles, impermeable gloves, and rubber boots to avoid skin contact
Properties of Copper(II) sulfate
| Melting point: | 200 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Density | 3.603 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 7.3 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | powder |
| color | Slightly greenish to gray |
| Specific Gravity | 3.603 |
| PH Range | 3.7 - 4.5 |
| PH | 3.5-4.5 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | 203 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,2653 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 10.3(0.0℃) |
| Stability: | hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7758-98-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Cupric sulfate(7758-98-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cupric sulfate (7758-98-7) |
Safety information for Copper(II) sulfate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Copper(II) sulfate
| InChIKey | ARUVKPQLZAKDPS-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
Copper(II) sulfate manufacturer
New Products
Cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxylic acid Cyclopentane-1,2-dione 2-Bromo-5-iodopyridine 4-isothiocyanato-2-(trifluoroMethyl)benzonitrile Amino-4-methoxyben-zeneacetic acid 3-Aminophenylacetic acid 1-AMino-cyclobutaneMethanol HCl (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid Cefuroxime EP Impurity-A N-Nitroso hydroxy Cetrizine EP Impurity-A Noradrenaline EP Impurity D/Noradrenaline Methyl Ether Cetirizine EP Impurity A/Cetirizine CBHP Impurity Lantanoprost rc B Clidinium Bromide Impurity 3-Hydroxypropionitrile valeronitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro Benzylcyanide 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 5-azidovalericacid 4-bromo-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid Isopropyl amine Hydrochloride tert-butyl 4-(6-(8-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-7-oxo-6-vinyl-7,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-2-ylamino)pyridin-3-yl)piperazine-1-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Copper Sulphate 98%View Details
Copper Sulphate 98%View Details -
 Copper Sulphate 99%View Details
Copper Sulphate 99%View Details -
 Copper(II) sulfate 99%View Details
Copper(II) sulfate 99%View Details -
 copper sulphate CASView Details
copper sulphate CASView Details -
 Fehling's solution A CASView Details
Fehling's solution A CASView Details -
 Fehling`s solution A CASView Details
Fehling`s solution A CASView Details -
 FEHLING SOLUTION 'A' CASView Details
FEHLING SOLUTION 'A' CASView Details -
 FEHLING SOLUTION 'B' CASView Details
FEHLING SOLUTION 'B' CASView Details
