CITRONELLOL
- CAS NO.:26489-01-0
- Empirical Formula: C10H20O
- Molecular Weight: 156.27
- MDL number: MFCD00002935
- EINECS: 203-375-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:39
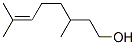
What is CITRONELLOL?
Chemical properties
The enantiomers (3R)-(+)-citronellol and (3S)-(?)-citronellol
occur in many essential oils.
(?)-Citronellol isolated from natural sources is often named rhodinol. At
present, the name rhodinol is also used for the isopropenyl isomer α-citronellol
or a mixture of the two isomers.
In many natural products, citronellol occurs as a mixture of its two enantiomers;
the pure (+) or (?) formis seldom found. (?)-Citronellol is the predominant enantiomer
in geranium and rose oils, both of whichmay contain up to 50% citronellols.
Citronellol is a colorless liquid with a sweet rose-like odor. The odor of (?)-
citronellol is more delicate than that of (+)-citronellol.
Citronellol undergoes the typical reactions of primary alcohols. Compared with
geraniol, which contains one more double bond, citronellol is relatively stable.
Citronellol is converted into citronellal by dehydrogenation or oxidation; hydrogenation
yields 3,7-dimethyloctan-l-ol. Citronellyl esters are easily prepared by
esterification with acid anhydrides.
Preparation
(?)-Citronellol is still obtained mainly from geranium oil by
saponification followed by fractional distillation (“rhodinol”). Although of high
odor quality, this grade does not possess the true (?)-citronellol odor due to
impurities. Much larger quantities of (+)-citronellol and racemic citronellol are
used and are prepared by partial or total synthesis.
1) Synthesis from citronellal: Citronellal can be hydrogenated to citronellol
by the use of special catalysts and/or special hydrogenation techniques,
for example, [122]. The citronellal that is used as the starting material
may originate from synthetic production or from isolation of essential
oils. Citronellal from citronella oil yields (+)-citronellol; the corresponding
material from citronellal from Eucalyptus citriodora oil is racemic. Pure
(+)-citronellol is also obtained from (+)-citronellal, which is produced as an
intermediate of (?)-menthol. By this asymmetric technology,
pure (?)-citronellal and, therefore, pure (?)-citronellol are also available.
2) Synthesis of racemic or slightly dextrorotatory citronellol from geraniol
fractions of essential oils: This citronellol is produced by catalytic hydrogenation of saponified geraniol fractions (also containing (+)-
citronellol) obtained from Java citronella oil, followed by fractional
distillation. Selective hydrogenation of the double bond in the 2-position
of geraniol in geraniol–citronellol mixtures isolated from essential oils
can be achieved by using Raney cobalt as a catalyst; overhydrogenation to
3,7-dimethyloctan-l-ol can be largely avoided by this method.
3) Synthesis of racemic citronellol from synthetic geraniol, nerol, or citral: A considerable
amount of commercial synthetic racemic citronellol is produced by
partial hydrogenation of synthetic geraniol and/or nerol. Another starting
material is citral, which can be hydrogenated, for example, in the presence
of a catalyst system consisting of transition metals and amines.
4) Preparation of (?)-citronellol from optically active pinenes: (+)-cis-Pinane is
readily synthesized by hydrogenation of (+)-α-pinene or (+)-β-pinene and is
then pyrolyzed to give (+)-3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadiene. This compound can
be converted into (?)-citronellol (97% purity) by reaction with triisobutylaluminumor
diisobutylaluminumhydride, followed by air oxidation and hydrolysis
of the resulting aluminum alcoholate.
Definition
ChEBI: Citronellol is a monoterpenoid that is oct-6-ene substituted by a hydroxy group at position 1 and methyl groups at positions 3 and 7. It has a role as a plant metabolite.
Contact allergens
L-Citronellol is a constituent of rose and geranium oils. d-Citronellol occurs in Ceylon and Java citronella oils. As a fragrance allergen, citronellol has to be mentioned by name in cosmetics within the EU.
Properties of CITRONELLOL
| Melting point: | 77-83 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 225 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.857 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 5.4 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | ~0.02 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 209 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 26489-01-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for CITRONELLOL
Computed Descriptors for CITRONELLOL
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran






You may like
-
 2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 -
 1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) -
 2856-63-5 99%View Details
2856-63-5 99%View Details
2856-63-5 -
 3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
3,4 Diethoxy Benzylcyanide 99%View Details
27472-21-5 -
 Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
7252-83-7 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 -
 5-azidovalericacidView Details
5-azidovalericacidView Details
79583-98-5
