Chinomethionate
- CAS NO.:2439-01-2
- Empirical Formula: C10H6N2OS2
- Molecular Weight: 234.3
- MDL number: MFCD00055387
- EINECS: 219-455-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-14 11:32:48
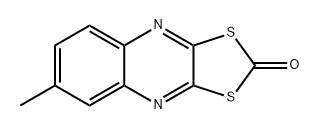
What is Chinomethionate?
Description
Chinomethionate is a quinoxaline fungicide and acaricide introduced in 1968 to control powdery mildew and spider mites on fruits, ornamentals, cucurbits, cotton, coffee, tea, tobacco, walnuts, vegetables and glasshouse crops. It is nonsystemic, with contact activity only.
Chemical properties
Chinomethionate is a tan to yellow crystals. Soluble in benzene, toluene, and dioxane; insoluble in water. It has been shown to have low toxicity to mammals, birds and bees, but is highly toxic to fish and some aquatic invertebrates.
The Uses of Chinomethionate
Chinomethionat exhibits both acaricidal and fungicidal activities. It is a selective, non-systemic contact fungicide with both protective and eradicant control of powdery mildews on fruits, cucurbits, vegetables, ornamentals, tobacco and glasshouse crops.
Definition
ChEBI: A dithioloquinoxaline that results from the formal condensation of 6-methylquinoxaline-2,3-dithiol with phosgene. It has been used as a fungicide and acaricide for the control of mites and powdery mildew on citrus, vegetables, and walnuts, but is not appro ed for use in the EU.
General Description
Yellow crystals. Non-corrosive. Used as a selective fungicide.
Air & Water Reactions
Hydrolyzed in alkaline solution.
Reactivity Profile
A member of the quinoxaline, dithiolane family.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal, ingestion, and skin contact routes. A pesticide. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx.
Environmental Fate
Chemical/Physical. Reacts with ammonia forming 6-methyl-2,3-quinoxalinedithiol.
Metabolic pathway
Limited information is available to describe the degradation and metabolic fate of chinomethionat. Hydrolytic cleavage of the dithiocarbonate ring is the primary degradation reaction in water, plants and animals.
Degradation
Chinomethionat was degraded at pH 4,7 and 9 at 22 °C with DT50 values of 10 days, 3.3 days and 3.6 hours, respectively. It is degraded under alkaline conditions to yield 6-methyl-2,3-quinoxalinedithiol (2) (PM) as shown in Scheme 1. Clark and Loeffler (1980) reported the extensive photodegradation of chinomethionat in benzene in a nitrogen atmosphere under UV light to yield dimeric condensation products and benzene insertion products.
Mode of action
Chinomethionate reacts with sulfur-containing amino acids in proteins, thereby disrupting the function of many enzymes and other proteins. Because there is no single target site, target site resistance is unlikely.
Properties of Chinomethionate
| Melting point: | 172° |
| Boiling point: | 476.6±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.4147 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 2.6 x 10-5 Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6800 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | -5.28±0.20(Predicted) |
| Water Solubility | 1 mg l-1 (20 °C) |
| color | Yellow crystals |
| Merck | 13,7048 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Quinomethionate(2439-01-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chinomethionate (2439-01-2) |
Safety information for Chinomethionate
Computed Descriptors for Chinomethionate
Chinomethionate manufacturer
Aion Pharma LLP
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide valeronitrile 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Chinomethionate CAS 2439-01-2View Details
Chinomethionate CAS 2439-01-2View Details
2439-01-2 -
![(6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE 98%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE 98%View Details
(6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE 98%View Details
0/2/39 -
 2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C NLT 95%View Details
2847776-12-7 -
 1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E NLT 95%View Details
1012886-75-7(HCl Salt)/69675-10-1(Freebase) -
 Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
Bromoacetaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal (stabilized with K2CO3)View Details
7252-83-7 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 -
 157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile 98+View Details
157528-56-8 -
 5-azidovalericacidView Details
5-azidovalericacidView Details
79583-98-5
