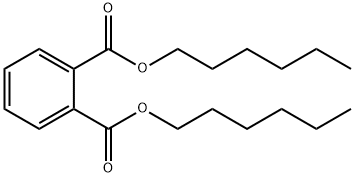
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate
Synonym(s):‘Dioctyl’ phthalate;Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate;DEHP;DOP;Phthalic acid bis(2-ethylhexyl ester)
- CAS NO.:117-81-7
- Empirical Formula: C24H38O4
- Molecular Weight: 390.56
- MDL number: MFCD00009493
- EINECS: 204-211-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2026-01-28 14:58:11
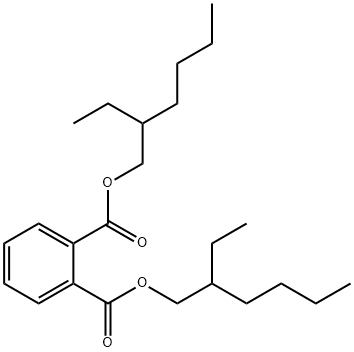
What is Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate?
Description
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, known by a variety of other names and usually abbreviated DEHP, was patented in 1950 and first used as vacuum pump oil. But since then, it has become the most widely used plasticizer for poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) and other plastics. Recently, relatively high levels of DEHP have been found in foods, especially foods high in oils and fats. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration now restricts its use in packaging materials to water-based foods. The European Commission has banned the use of DEHP and other phthalates in PVC toys.
Chemical properties
Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate is a colorless liquid with a slight odor. It is miscible with mineral oil and hexane, and soluble in most organic solvents. Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate is insoluble in water (NTP, 1994a).
The Uses of Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) is a benzenedicarboxilate ester which is the most widely used plasticizer to soften resins. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration now restricts its use in packaging materials to water-based foods. The European Commission has banned the use of DEHP and other phthalates in PVC toys.
Production Methods
DEHP is commercially produced via esterification of phthalic acid anhydride and 2-ethylhexanol. Esterification is completed with an acid or metal catalyst or with no catalyst at high temperature.
Reactivity Profile
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate reacts with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing with alkali metals and hydrides. Incompatible with nitrates .
Health Hazard
The acute oral toxicity is of extremelylow order. The oral LD50 value in miceis in the range 30,000 mg/kg. Ingestion ofabout 10 mL of the liquid may produce gas trointestinal pain, hypermotility, and diar rhea in humans. Chronic administration byoral route did not produce any adverseeffect in animals.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reaction; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Potential Exposure
Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate is primarily used as one of several plasticizers in polyvinyl chloride resins used for fabricating flexible vinyl products. It has also been reported as being used as a replacement for polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in dielectric fluids for electric capacitors and in vacuum pumps (NTP, 1994a; Merck, 1989). The primary stationary sources that have reported emissions of bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate in California are furniture and fixtures manufacturing, and lumber and wood products manufacturing (ARB, 1997b).
Carcinogenicity
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Metabolism
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate is metabolized in fish by enzymatic hydrolysis to mono-2-ethylhexyl phthalate, phthalic acid, and glucuronides of these compounds (Stalling et al., 1973).
Storage
Bis (2-ethylhexyl)phthalate must be stored to avoid contact with oxidizing materials, such as permanganates, nitrates, peroxides,chlorates, and perchlorates, since violent reactions occur.Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilatedarea away from heat.
Shipping
The name of this material is not on the DOT listof materials for label and packaging standards. However,based on regulations, it may be classified as anEnvironmentally hazardous substances, liquid, n.o.s. It fallsin Hazard Class 9 and Packing Group III.[20,21]
Purification Methods
Wash the ester with Na2CO3 solution, then shake it with water. After the resulting emulsion has been broken by adding ether, the ethereal solution is washed twice with water, dried (CaCl2), and evaporated. The residual liquid is distilled several times under reduced pressure, then stored in a vacuum desiccator over P2O5.
Incompatibilities
Nitrates, strong oxidizers, strong acids,strong alkalis.
Properties of Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate
| Melting point: | -50 °C |
| Boiling point: | 386 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.985 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | >16 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1.2 mm Hg ( 93 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 405 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Miscible with mineral oil and hexane (U.S. EPA, 1985) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | APHA: ≤10 |
| Odor | Very slight, characteristic. |
| Water Solubility | Negligible |
| FreezingPoint | <-60℃ |
| Merck | 14,2864 |
| BRN | 1890696 |
| Henry's Law Constant | (x 10-5 atm?m3/mol):
1.1 at 25 °C (calculated, Howard, 1989) |
| Exposure limits | Potential occupational carcinogen. NIOSH REL: TWA 5, STEL 10,
IDLH 5,000; OSHA PEL: TWA 5; ACGIH TLV: TWA 5 (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 5.1(24℃) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 117-81-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate(117-81-7) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. Sup 7, 77, 101) 2013 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (117-81-7) |
Safety information for Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate manufacturer
New Products
Paroxetine Impurity G/Paroxetine Related Compound E 1-Aminocyclopentane carbonitrile (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) Benzyl (3R,4S)-3-(2-bromoacetyl)-4-ethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Benzyl-3-pyrrolidinecarbonitrile Betahistine EP Impurity C Cyclobenzaprine N-oxide/Citalopram Related Compound E Chlorthalidone Impurity I Carbamazepine EP Impurity G Sumatriptan Succinate USP Related Compound C 2,2'-(5-methyl-1,3-phenylene)-di(2-Methylpropionitrile) 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 4-Bromo Benzylcyanide 3-Hydroxypropionitrile valeronitrile 3,4 Dimethoxy Benzylcyanide 3-chlorobenzyl cyanide 2-Chloro BenzylcyanideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Dioctyl phthalate 98%View Details
Dioctyl phthalate 98%View Details -
 Dioctyl Phthalate CASView Details
Dioctyl Phthalate CASView Details -
 Dioctyl Phthalate pure CAS 117-81-7View Details
Dioctyl Phthalate pure CAS 117-81-7View Details
117-81-7 -
 Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, puriss CAS 117-81-7View Details
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, puriss CAS 117-81-7View Details
117-81-7 -
 Dioctyl Phthalate CASView Details
Dioctyl Phthalate CASView Details -
 Dioctyl phthalate 98% CAS 117-81-7View Details
Dioctyl phthalate 98% CAS 117-81-7View Details
117-81-7 -
 Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate 95% CAS 117-81-7View Details
Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate 95% CAS 117-81-7View Details
117-81-7 -
 Dioctyl Phthalate Liquid CAS 117-81-7View Details
Dioctyl Phthalate Liquid CAS 117-81-7View Details
117-81-7
