Avilamycin
- CAS NO.:11051-71-1
- Empirical Formula: C61H88Cl2O32
- Molecular Weight: 1404.23822
- MDL number: MFCD21607522
- EINECS: 601-595-5
- Update Date: 2024-12-24 18:06:02
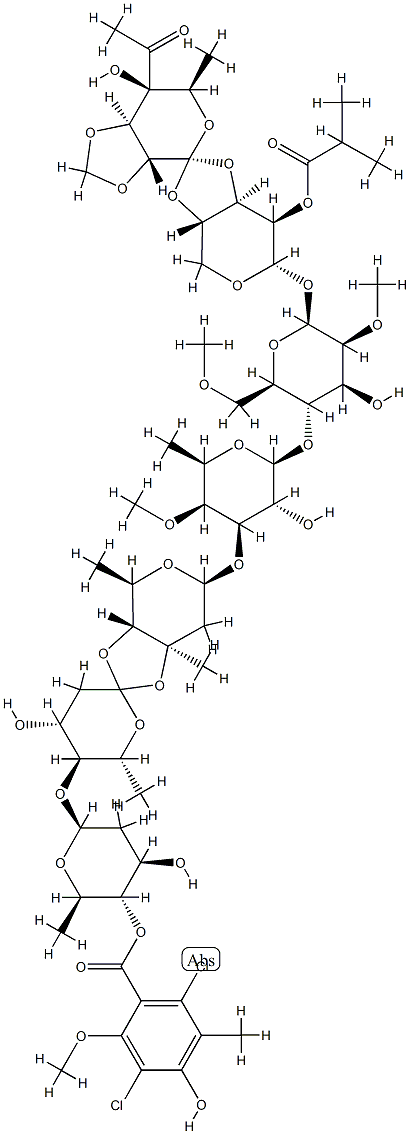
What is Avilamycin?
Originator
Maxus,Eli Lilly
The Uses of Avilamycin
Antibacterial.
Manufacturing Process
Avilamycin is produced from Streptomyces viridochromogenes NRRL 2860:
A nutrient solution is prepared which contains 20.0 g of meat meal, 20.0 g of
salt extract, 10.0 g of calcium carbonate and 1 L of tap water and adjusted to
pH=7. This solution, or a multiple thereof, is charged into conical flasks of 500
ml capacity (100 ml of nutrient solution each) or into fermenters of 500 L
capacity (300 L of nutrient solution each) and sterilized for 20-30 min under a
pressure of 1 atm. The contents of the flasks are then inoculated with up to
10% of a partially sporulating vegetative culture of Streptomyces
viridochromogenes NRRL 2860 and incubated at 27°C with thorough shaking
or stirring, and in the fermenters with aerating with about 1 volume of sterile
air per volume of nutrient solution per minute. The cultures are allowed to
grow for 24-48 h, mixed with about 1.5% of a filtration assistant and then
filtered depending on the volume, through a suction filter or a filter press or a
rotary filter to free the antibiotically active aqueous solution from the
mycelium and other solid constituents.
The medium described above is replaced the nutrient media: 10.0 g of crude
glucose, 5.0 g of peptone, 3.0 g of meat extract (Oxo Lab- Lemco), 5.0 g of
sodium chloride, 10.0 g of calcium carbonate and 1 L of tap water, pH - prior to sterilization: 7.5, analogous sterilization, inoculation with Streptomnyces
viridochromogenes NRRL 2860, incubation at 27°C and filtration likewise yield
aqueous antibiotically active solutions.
90 L of culture filtrate are extracted with 20 L of ethyl acetate, and the extract
is concentrated to 400 ml. When the concentrate is kept for 20 h at 2°C,
avilamycin precipitates in the form of a dense floccular substance which is
filtered off. After having been dried in an exsiccator, the practically colorless
crystal cake consisting of strongly felted small needles weighs 3.07 g. The
mother liquors are concentrated to about 200 ml and mixed with twice the
amount of ether. When the concentrate is kept for 4 days at 0°C, a further
3.28 g of avilamycin crystallize out. 3.0 g of the crystallizate are dissolved in
50 ml of acetone, and a small amount of insoluble sludge is filtered off. The
clear filtrate is mixed with ether and concentrated. On cooling, 2.0 g of
colorless fine needles crystallize out. Concentration of the mother liquors to
about one quarter their volume produces a further 0.48 g of crystals. For
analysis a test portion of these crystals is recrystallized 4 times from
acetone+ether and dried for 20 h in a high vacuum at 70°C. The analytically
pure antibiotic avilamycin have a melting point 188°-189.5°C. Optical rotation
[α]D
20=+0.8° (c=1.165 in absolute ethanol).
brand name
Surmax (Lilly).
Therapeutic Function
Antibiotic
Properties of Avilamycin
| Melting point: | 188-189℃ |
| alpha | D20 +0.8° (c = 1.165 in abs ethanol) and -7.7° (c = 1.083 in chloroform) |
| solubility | Acetone (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Light Beige to Light Brown |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Avilamycin
Computed Descriptors for Avilamycin
New Products
(E)-1-Ethoxyethene-2-boronic Acid Pinacol Ester 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 1,3-Di Iodo Benzene Methyl 2-oxo-2,3-dihydrobenzo[d]oxazole-7-carboxylate 4-(2-Aminoethyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromoen-2-one 3-Hydroxy-4-nitrobromobenzene 2-Ethyl-1,4-diaminobenzene 2-Ethylhexyl 4-aminobenzoate Thio AcetamideYou may like
-
 MFCD22560726 98%View Details
MFCD22560726 98%View Details
MFCD22560726 -
 3-Hydroxy-4-nitrobromobenzene 98%View Details
3-Hydroxy-4-nitrobromobenzene 98%View Details
2768-84-0 -
 4-(2-Aminoethyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromoen-2-one 98%View Details
4-(2-Aminoethyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromoen-2-one 98%View Details
1234064-08-4. -
 2-Ethyl-1,4-diaminobenzene 98%View Details
2-Ethyl-1,4-diaminobenzene 98%View Details
MFCD19203885 -
 85-81-4 6-Methoxy-8-nitroquinoline 98%View Details
85-81-4 6-Methoxy-8-nitroquinoline 98%View Details
85-81-4 -
 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 98%View Details
2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 98%View Details -
 Hot Sales:Thio AcetamideView Details
Hot Sales:Thio AcetamideView Details
62-55-5 -
 CosmoticsView Details
CosmoticsView Details
26218-04-2
