9,9-Bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)fluorene Dianhydride
- CAS NO.:135876-30-1
- Empirical Formula: C29H14O6
- Molecular Weight: 458.42
- MDL number: MFCD30342552
- EINECS: 218-362-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-10-28 16:00:23
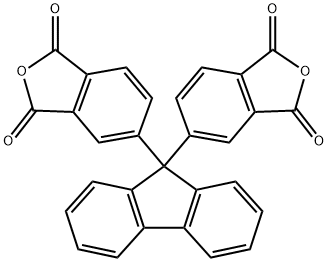
What is 9,9-Bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)fluorene Dianhydride?
Description
9,9-Bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)fluorene Dianhydride is a dianhydride that is used in the production of polymers. It has a melting point of about 240°C and can be used as a catalyst for the thermal oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons. 9,9-Bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)fluorene Dianhydride is also a crystallization agent for organic compounds and can be used as an oxidizing agent in the process of dehydrating crystals. The reaction product of 9,9-Bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)fluorene Dianhydride is epoxy resin.
Chemical properties
white to almost white powder to crystal
The Uses of 9,9-Bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)fluorene Dianhydride
Used in Polyimide Monomer
What are the applications of Application
9,9-Bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)fluorene Dianhydride (BPAF) can be used in the preparation of new imine oligomers and thermosets. The BPAF-derived imide oligomers exhibited improved organic solvents solubility and higher melt viscosity compared to those based on 2,3,3′,4′-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride (3,4′-BPDA), due to their bulky, twisted, and sterically hindered cardo architectures. The imide oligomers under pressure were converted into thermosets by the thermal crosslinking of phenylethynyl at 370 °C for 2 h. The BPAF-derived thermosets exhibited much higher glass transition temperature (Tg) (> 404 °C), 5% weight-loss temperature (T5%) (> 549 °C) in an air environment, and more excellent high-frequency dielectric properties from 30 to 45 GHz (dielectric constant as low as 2.85 and dielectric loss factor as low as 0.0037) while possessing comparable or even better mechanical properties relative to the 3,4′-BPDA-derived polymers. Therefore, these polymers based on BPAF may have potential applications as matrix resins for heat-resistant, structural and functional composites[1].
References
[1] XIANGSHENG MENG. High performance imide oligomers and thermosets derived from 9,9-bis (3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)fluorene dianhydride[J]. Polymer, 2023. DOI:10.1016/j.polymer.2023.126086.
Properties of 9,9-Bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)fluorene Dianhydride
| Melting point: | 269 °C |
| Boiling point: | 687.9±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.521±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| form | powder to crystal |
| color | White to Almost white |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C29H14O6/c30-25-19-11-9-15(13-21(19)27(32)34-25)29(16-10-12-20-22(14-16)28(33)35-26(20)31)23-7-3-1-5-17(23)18-6-2-4-8-24(18)29/h1-14H |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 135876-30-1 |
Safety information for 9,9-Bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)fluorene Dianhydride
Computed Descriptors for 9,9-Bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)fluorene Dianhydride
| InChIKey | FMACFWAQBPYRFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(C2C=CC3C(=O)OC(=O)C=3C=2)(C2C=CC3C(=O)OC(=O)C=3C=2)C2=C(C=CC=C2)C2=C1C=CC=C2 |
New Products
DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine Tetrabutylammonium perchlorate N,O-Dimethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride (RS)-beta-Amino-beta-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid 2-Amino-5-bromo-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine(RM for Indian lab) N,N CARBONYL DIIMIDAZOLE Levothyroxine Impurity-F Montelukast EP Impurity-D/Montelukast USP Related Compound C Atorvastatin FXA Impurity/Atorvastatin Cyclic 6-Hydroxy Impurity Sodium Salt Isosulfan blue Keto N-Oxide Impurity Ivermectin Impurity F N-Nitroso des Methyl Tramadol/N-Nitroso-N-Desmethyl-Tramadol (R)-BoroLeu-(+)-Pinanediol-CF3COOH 1,4-bis(methylsulfonyl)butane 4-(5-amino-1-methyl-1h-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-butyric acid isopropyl ester. 5-Methyl-1,3-benzenediacetonitrile 4-Fluorothiophenol 1-methyl amino-2,4-dinitro benzene CSA (DL-10-Camphorsulfonic Acid) 2-Hydroxy-4-methylnicotinic acid 3-iodo-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine (2S)-1-((2S,3S)-3-(2-methylbutyl)-4-oxooxetan-2-yl)pentadecan-2-yl formylleucinate 1-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethane-1-sulfonyl chloride S-(1-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) ethanethioateYou may like
-
 9,9-Bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)fluorene Dianhydride CAS 135876-30-1View Details
9,9-Bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenyl)fluorene Dianhydride CAS 135876-30-1View Details
135876-30-1 -
 674783-97-2 98+View Details
674783-97-2 98+View Details
674783-97-2 -
 H-D-TRP(FOR)-OH HCL 98+View Details
H-D-TRP(FOR)-OH HCL 98+View Details
367453-01-8 -
 DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine 117391-50-1 98+View Details
DL-beta-(3-Bromophenyl)alanine 117391-50-1 98+View Details
117391-50-1 -
 49830-37-7 98+View Details
49830-37-7 98+View Details
49830-37-7 -
 3-Amino-3-(4-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
3-Amino-3-(4-fluorophenyl)propanoic acid 98+View Details
325-89-3 -
 1428243-26-8 98+View Details
1428243-26-8 98+View Details
1428243-26-8 -
 1-aminocyclopentane carbonitrile, HCl 98+View Details
1-aminocyclopentane carbonitrile, HCl 98+View Details
16195-83-8
