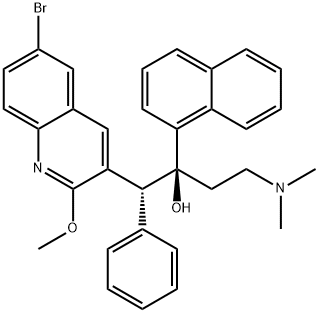
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Color/Form | White solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 118 °C |
| Solubility | Insoluble |
| Optical Rotation | Specific optical rotation: -166.98 deg at 20 °C/D (c = 0.505 in dimethyl formamide) |
| Other Experimental Properties | White to almost white powder; practically insoluble in aqueous media/Bedaquiline fumarate/ |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 555.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 7.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Exact Mass | 554.15689 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 554.15689 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 45.6 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 37 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 715 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Bedaquiline is a quinoline-based antimycobacterial drug used (as its fumarate salt) for the treatment of pulmonary multi-drug resistant tuberculosis by inhibition of ATP synthase, an enzyme essential for the replication of the mycobacteria. It has a role as an antitubercular agent and an ATP synthase inhibitor. It is a member of quinolines, a member of naphthalenes, an organobromine compound, an aromatic ether, a tertiary alcohol and a tertiary amino compound. It is a conjugate base of a bedaquiline(2+).